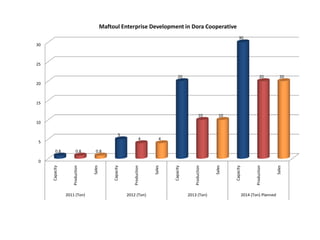
This document summarizes a case study of the Dora Cooperative for Agricultural Processing in Palestine. It outlines several problems faced by rural women in accessing markets and services, and how the cooperative addressed these issues by building relationships with key actors, strengthening members' capacities, stimulating the private sector, and involving more women in decision-making. This led to increased income, jobs, profits, production, and sales for the cooperative from 2011-2014. Areas for improvement included childcare, quality control, marketing, and attracting more members. In the future, revolving loans could be channeled through microfinance institutions.