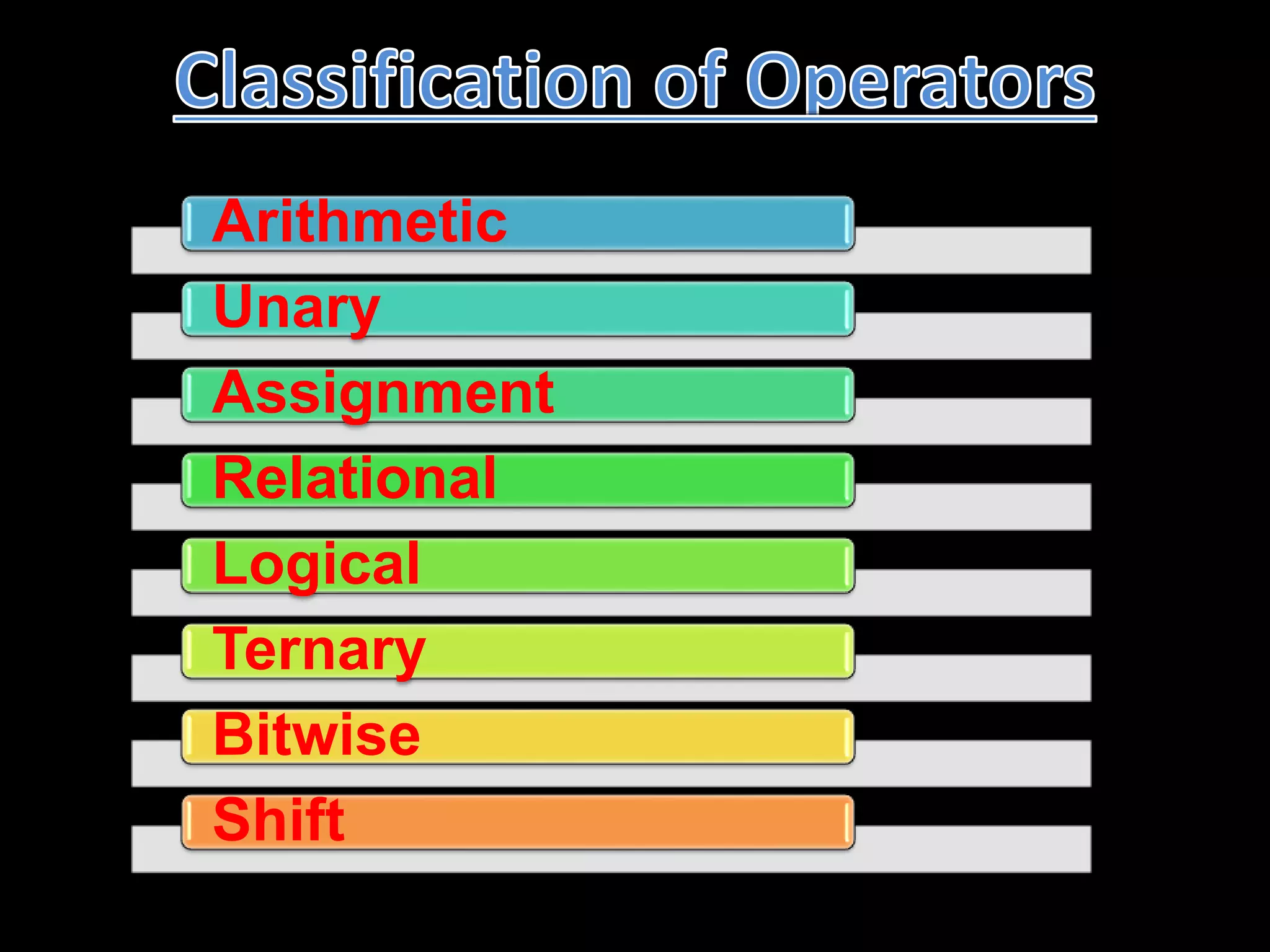
Operators are symbols that tell the compiler to perform mathematical, logical, or other operations on variables and constants. There are several types of operators including arithmetic, unary, assignment, relational, logical, ternary, bitwise, and shift operators. Arithmetic operators represent basic math operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Unary operators operate on a single operand, like increment and decrement operators. Assignment operators assign values, relational operators compare values, and logical operators combine conditional tests.



![Example:
class Weather
{
public static void main(String[] arguments)
{
float fah = 86;
System.out.println(fah + " degrees Fahrenheit is ...");
fah = fah - 32;
fah = fah / 9;
fah = fah * 5;
System.out.println(fah + " degrees Celsiusn");
float cel = 33;
System.out.println(cel + " degrees Celsius is ...");
cel = cel * 9;
cel = cel / 5;
Add 32 to the answer
cel = cel + 32;
System.out.println(cel + " degrees Fahrenheit");
}
}
Output:
86.0 degrees Fahrenheit is ...
30.0 degrees Celsius
33.0 degrees Celsius is ...
91.4 degrees Fahrenheit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-200209121407/75/Operators-5-2048.jpg)

![Example:
class operators
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 20, b = 10, c = 0;
// a=b+++c is compiled as
// b++ +c
// a=b+c then b=b+1
a = b++ + c;
System.out.println("Value of a(b+c), "
+ " b(b+1), c = "
+ a + ", " + b
+ ", " + c);
}
}
Output:
Value of a(b+c), b(b+1), c = 10, 11, 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-200209121407/75/Operators-7-2048.jpg)






