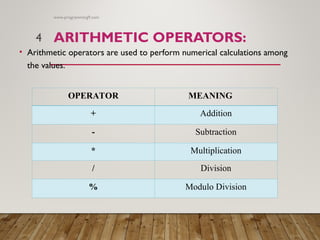
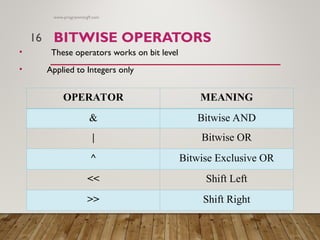
The document explains various types of operators in programming, including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, conditional, bitwise, and special operators. Each operator type is defined with examples, particularly in the C programming language, demonstrating their usage in manipulating data and making decisions. It serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding and using these operators in programming.