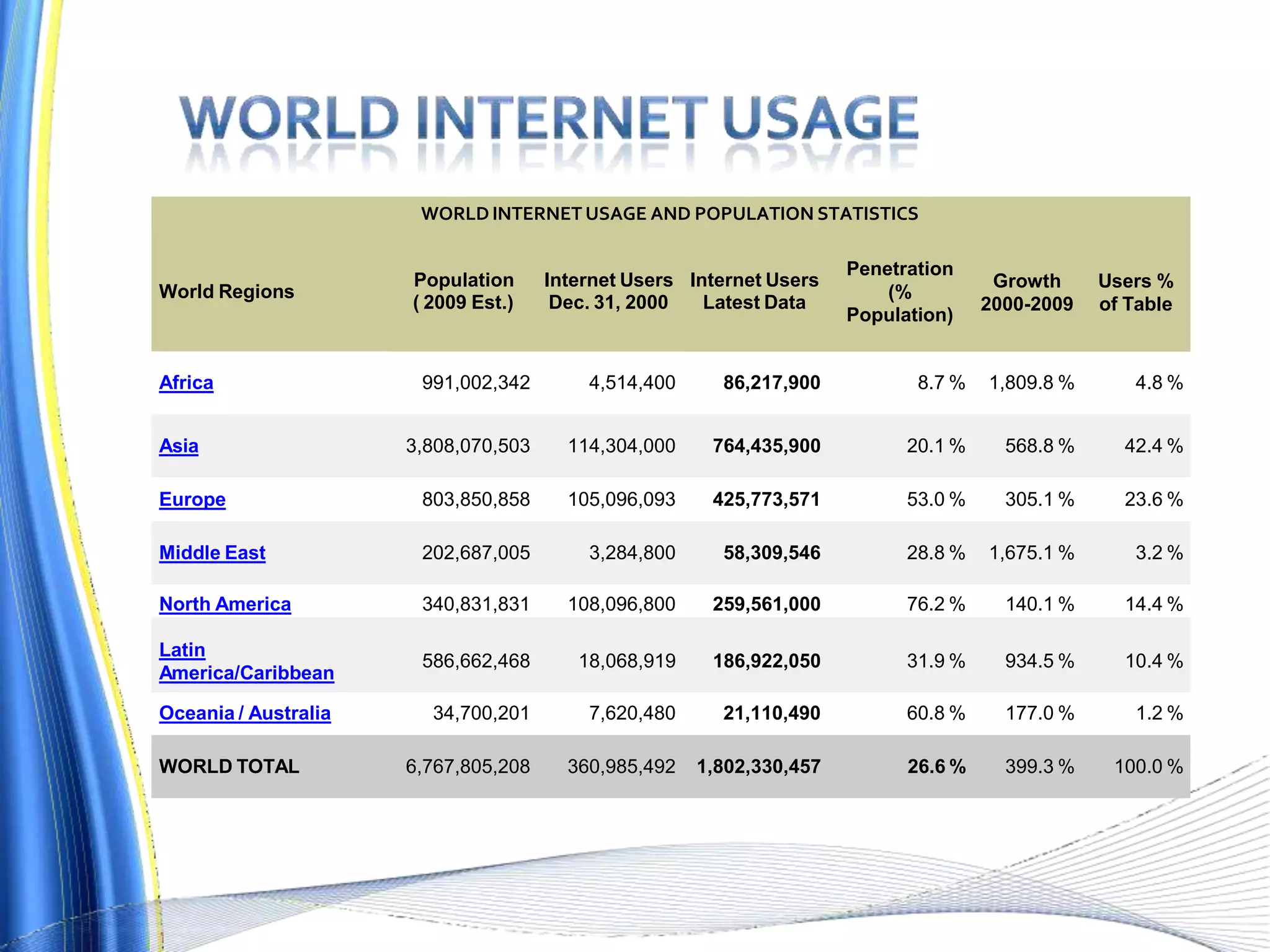
This document discusses various topics related to computer system security including internet security, remote sharing, operating system security, access controls, surveillance, threats, passwords, auditing, cryptography, viruses, worms, spyware, firewalls, and phishing. It provides statistics on world internet usage and penetration rates. It also lists and summarizes features of several internet security software programs and recommends resources for further information on computer security topics.












![ CoolWebSearch, a group of programs, takes advantage of Internet Explorer vulnerabilities.
The package directs traffic to advertisements on Web sites including coolwebsearch.com. It
displays pop-up ads, rewrites search engine results, and alters the infected computer's hosts
file to direct DNS lookups to these sites.
HuntBar, aka WinTools or Adware.Websearch, was installed by an ActiveX drive-by download
at affiliate Web sites, or by advertisements displayed by other spyware programs—an example
of how spyware can install more spyware. These programs add toolbars to IE, track aggregate
browsing behavior, redirect affiliate references, and display advertisements.
MyWebSearch (of Fun Web Products) has a plugin that displays a search toolbar near the top of
a browser window, and it spies to report user search-habits. MyWebSearch is notable for
installing over 210 computer settings, such as over 210 MS Windows registry
keys/values.[39][40] Beyond the browser plugin, it has settings to affect Outlook, email, HTML,
XML, etc. Although tools exist to remove MyWebSearch, it can be hand-deleted in 1 hour, by
users familiar with using Regedit to find and delete keys/values (named with "MyWebSearch").
After reboot, the browser returns to the prior display appearance.
WeatherStudio has a plugin that displays a window-panel near the bottom of a browser
window. The official website notes that it is easy to remove (uninstall) WeatherStudio from a
computer, using its own uninstall-program, such as under C:Program FilesWeatherStudio.
Once WeatherStudio is removed, a browser returns to the prior display appearance, without
the need to modify the browser settings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatingsystemsecurity-130717170639-phpapp01-230112061438-c7f1591f/75/operatingsystemsecurity-130717170639-phpapp01-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![ Internet Optimizer, also known as DyFuCa, redirects Internet Explorer error pages to
advertising. When users follow a broken link or enter an erroneous URL, they see a page of
advertisements. However, because password-protected Web sites (HTTP Basic authentication)
use the same mechanism as HTTP errors, Internet Optimizer makes it impossible for the user to
access password-protected sites.
Zango (formerly 180 Solutions) transmits detailed information to advertisers about the Web
sites which users visit. It also alters HTTP requests for affiliate advertisements linked from a
Web site, so that the advertisements make unearned profit for the 180 Solutions company. It
opens pop-up ads that cover over the Web sites of competing companies (as seen in their
[ZangoEndUser LicenseAgreement]).
Zlob trojan, or just Zlob, downloads itself to a computer via an ActiveX codec and reports
information back to Control Server[citation needed]. Some information can be the search-
history, the Websites visited, and even keystrokes.[citation needed] More recently, Zlob has
been known to hijack routers set to defaults.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatingsystemsecurity-130717170639-phpapp01-230112061438-c7f1591f/75/operatingsystemsecurity-130717170639-phpapp01-pptx-16-2048.jpg)




