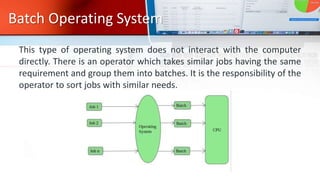
An operating system (OS) manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services to programs. The document discusses five main types of operating systems: batch, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time. Batch systems process jobs in batches without direct user interaction, time-sharing systems allocate CPU time to multiple tasks, distributed systems connect independent systems over a network, network OSs manage shared resources over a private network, and real-time OSs have very strict time constraints to process inputs.