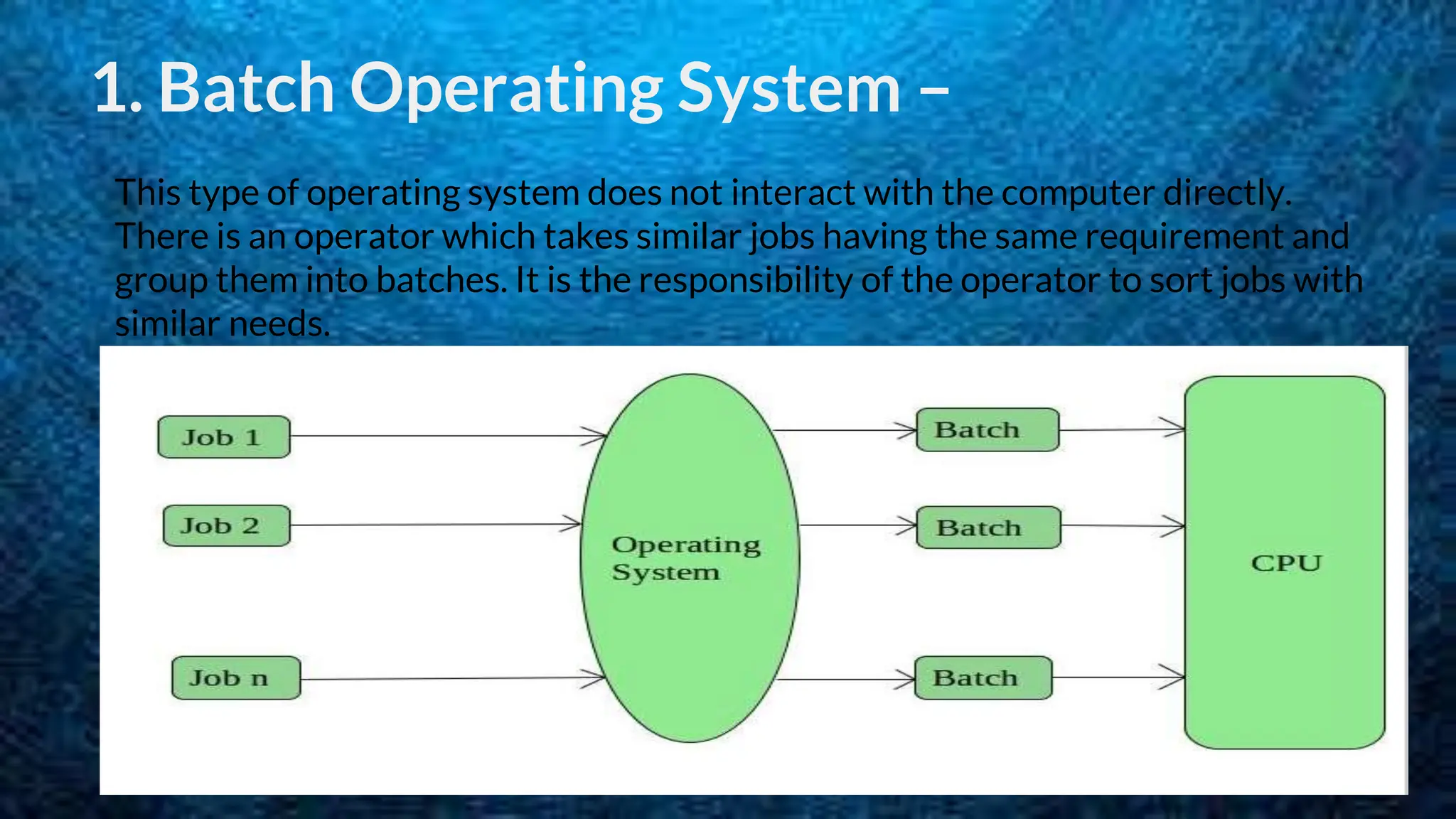
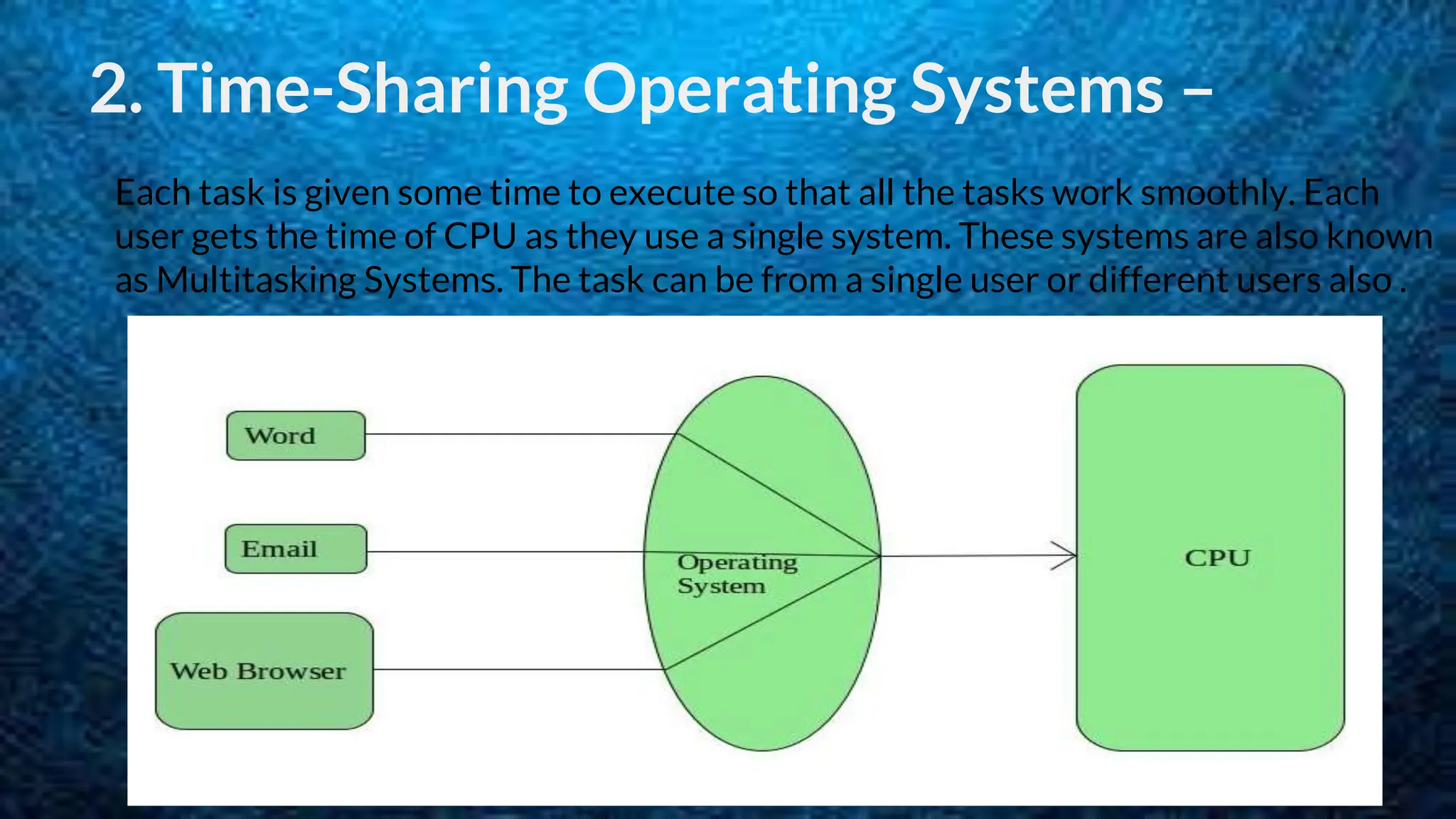
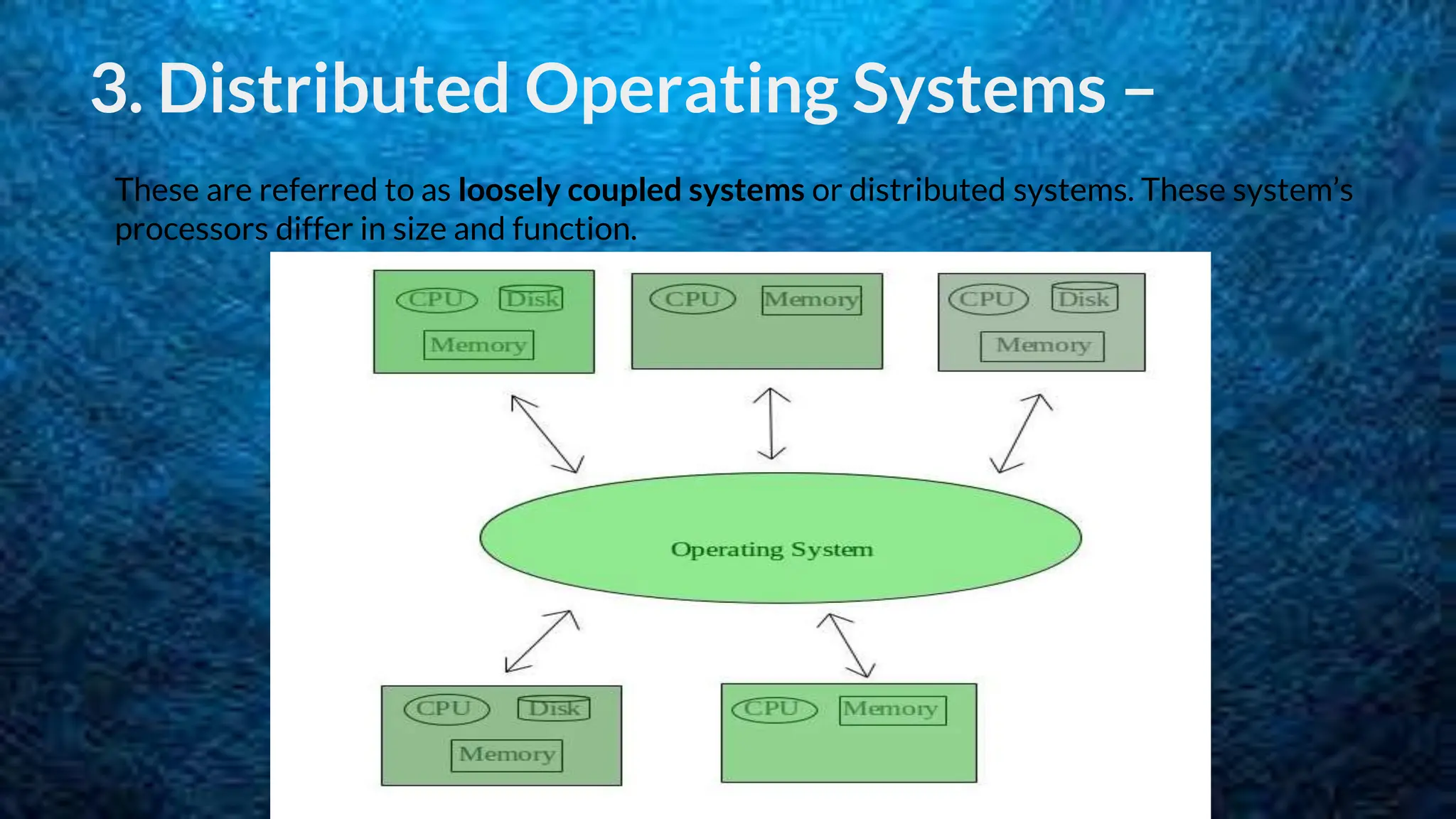
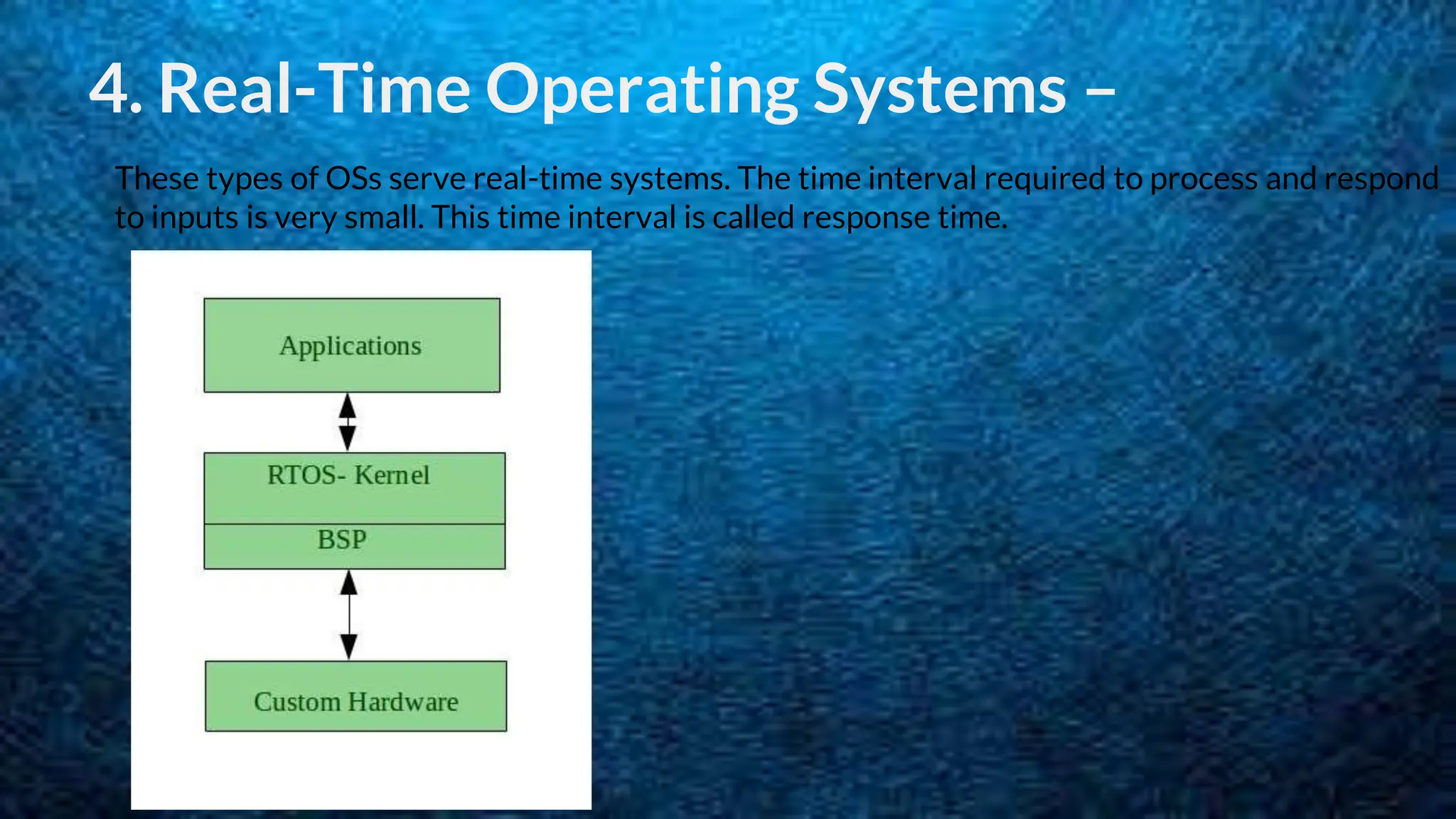
The document discusses 5 types of operating systems: batch, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time. Batch operating systems run jobs in batches without direct user interaction, time-sharing systems allow for multitasking by allocating CPU time to tasks, distributed systems use loosely coupled processors across a network, network operating systems manage servers that provide functionality to connected systems, and real-time systems have very short response times to process inputs for applications like medical devices.