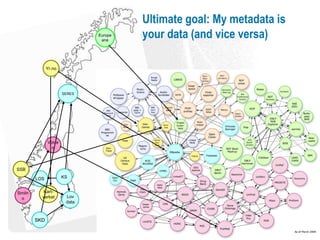
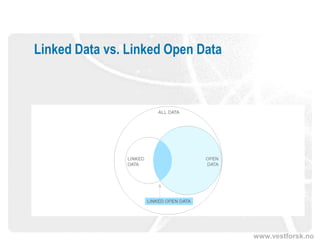
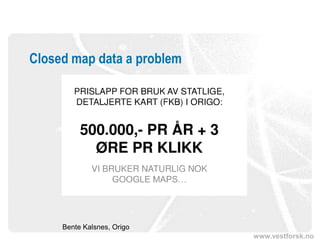
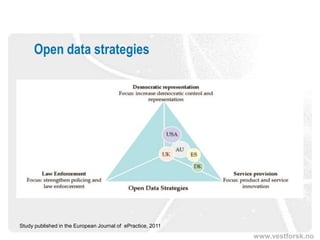
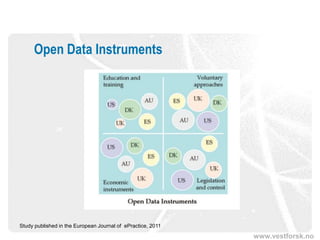
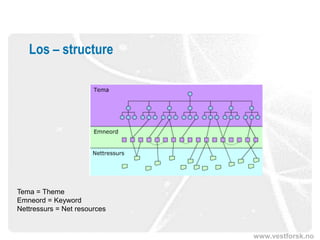
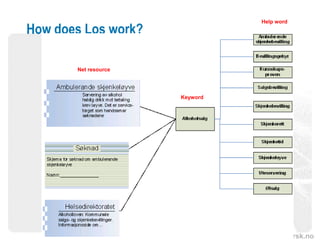
The document discusses the significance and potential of open data, particularly in the context of public sector information and semantic technologies. It explores various projects and initiatives related to linked open data (LOD) and outlines barriers and drivers influencing open data adoption. The document emphasizes the importance of data accessibility for enhancing democratic participation, innovation, and governance.




![Naming things!
[the famous cartoon by Gary Larson showing a man
painting ’the cat’, ’the dog’, ’the house’ on his cat,
dog, and house and explaining ”Now, this should
clear up a few things around here!”]
www.vestforsk.no](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opnedata-uib13-04-2011-utanteikning-110414020247-phpapp01/85/Open-data-and-reuse-of-public-information-5-320.jpg)
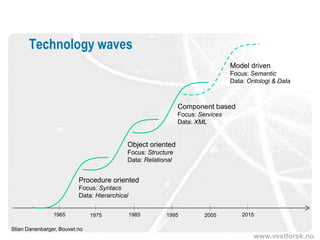
![The ontology spectrum
The ontology spectrum: From weak to strong semantics
1. Vocabulary
• plain text documents/HTML pages – almost no semantic structure
2. Controlled vocabularies (weak semantic structure)
• adding metadata to the information
3. Taxonomies
• metadata and hierarchy
4. Thesauri
• metadata, hierarchy and a limited set of relations (BT, NT, related to ...)
5. Stronger semantic structures/ontologies
• metadata, [hierarchy], any relations
(Daconta et al.: “The Semantic Web”)
www.vestforsk.no](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opnedata-uib13-04-2011-utanteikning-110414020247-phpapp01/85/Open-data-and-reuse-of-public-information-7-320.jpg)