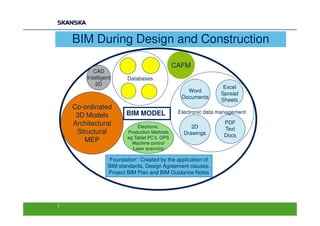
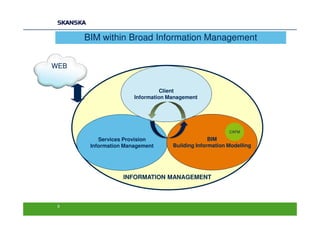
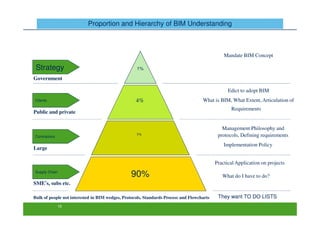
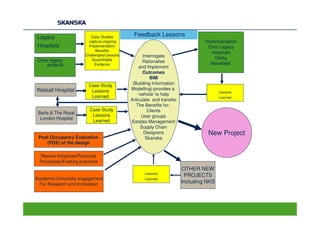
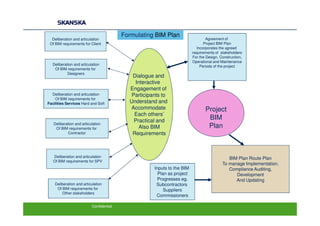
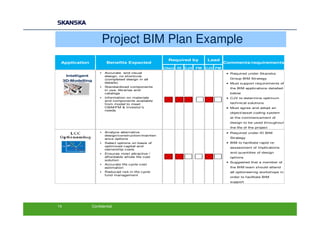
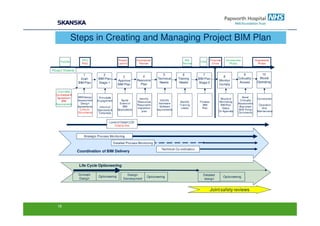
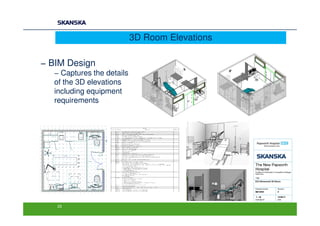
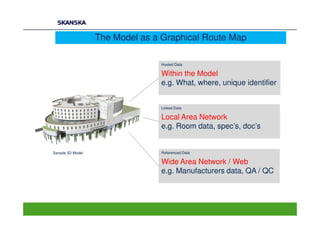
The document discusses an open BIM learning exchange presentation by Dr. Howard Jeffrey, a BIM specialist at Skanska. It summarizes Skanska's definition of BIM and its implementation of BIM across projects since 2009. Some key challenges and opportunities of BIM are outlined. The presentation covers Skanska's approach to BIM delivery, focusing on people, process, and technology. Case studies and lessons learned are discussed to capture benefits and inform future BIM adoptions.