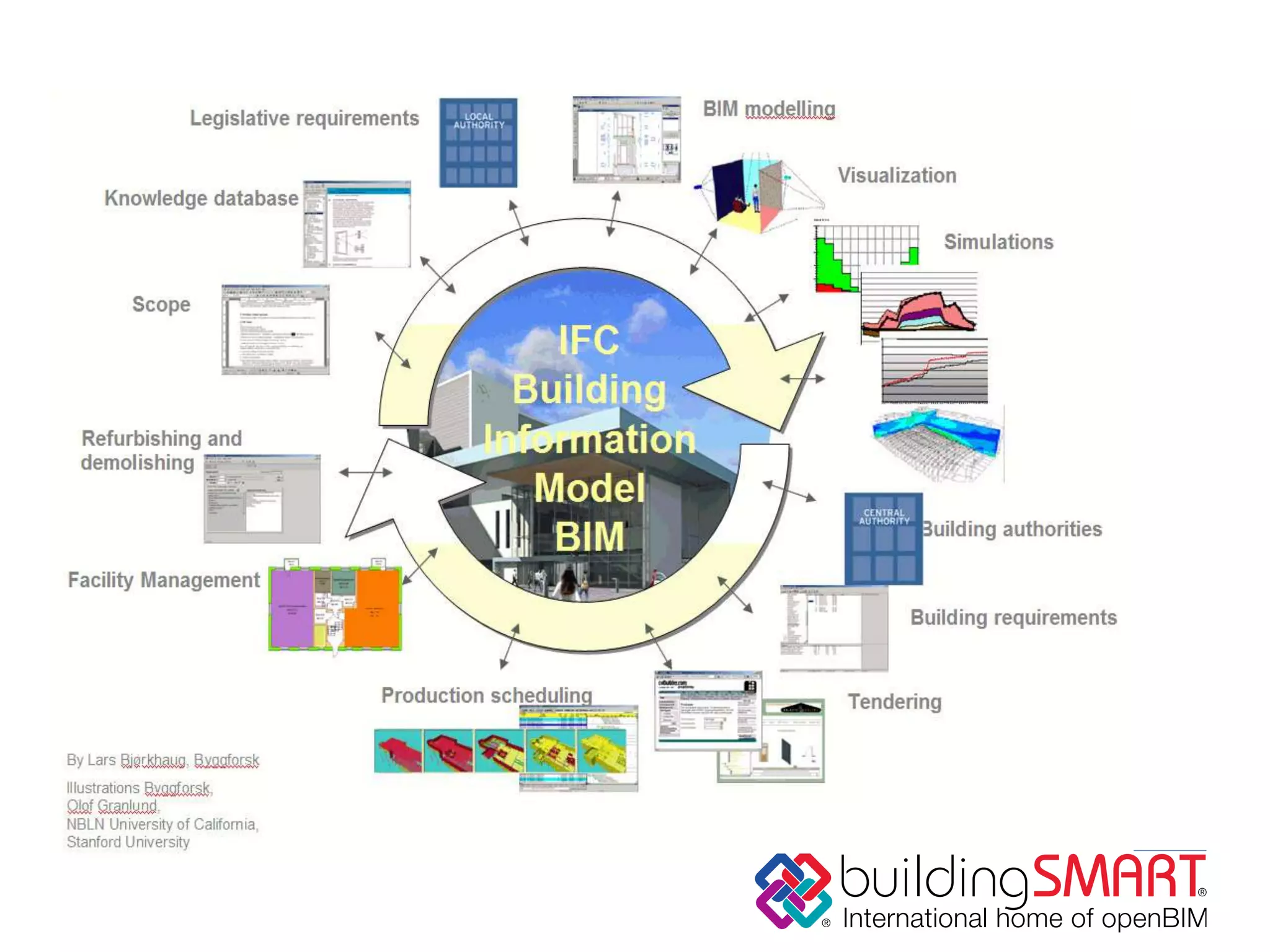
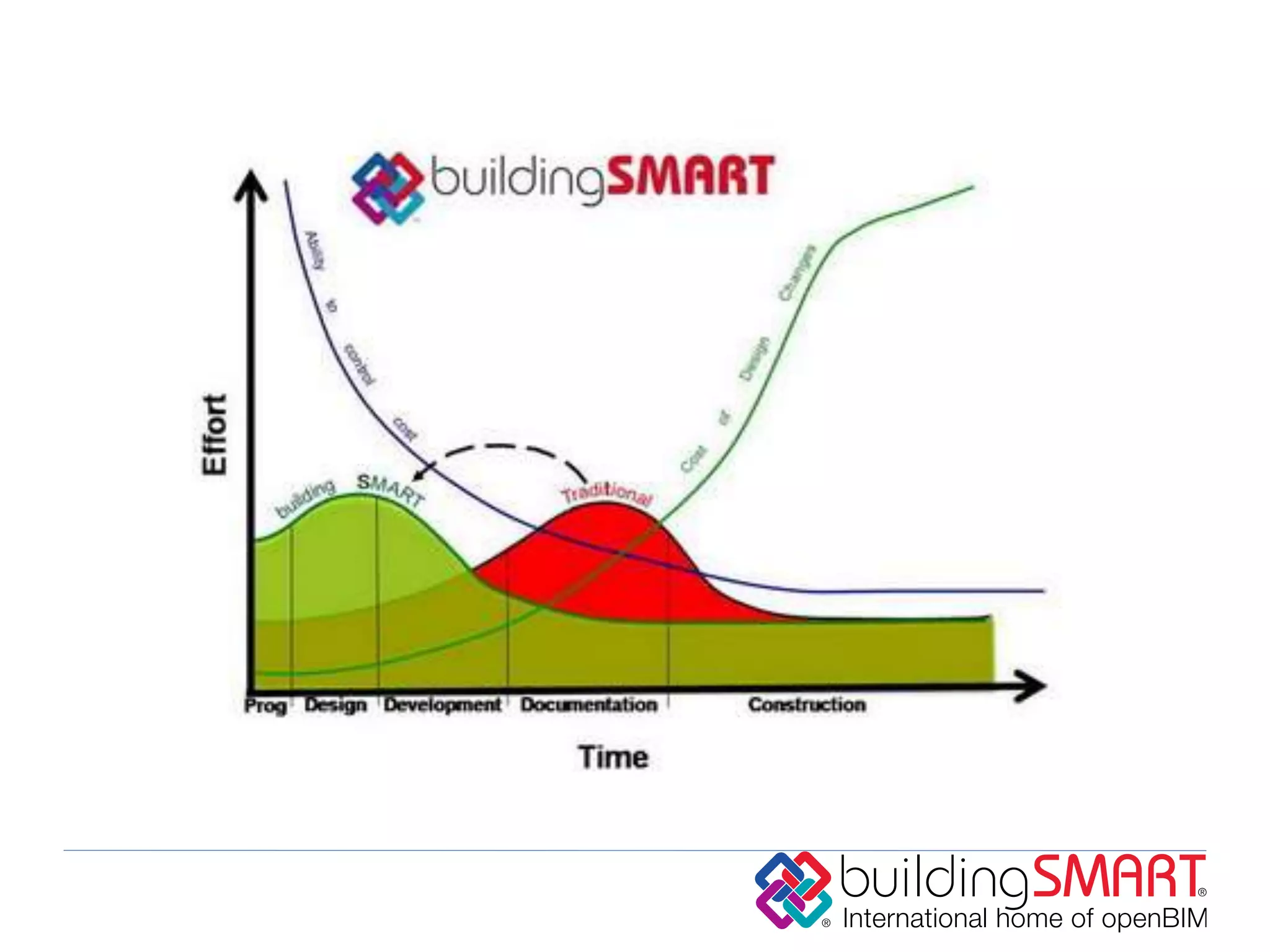
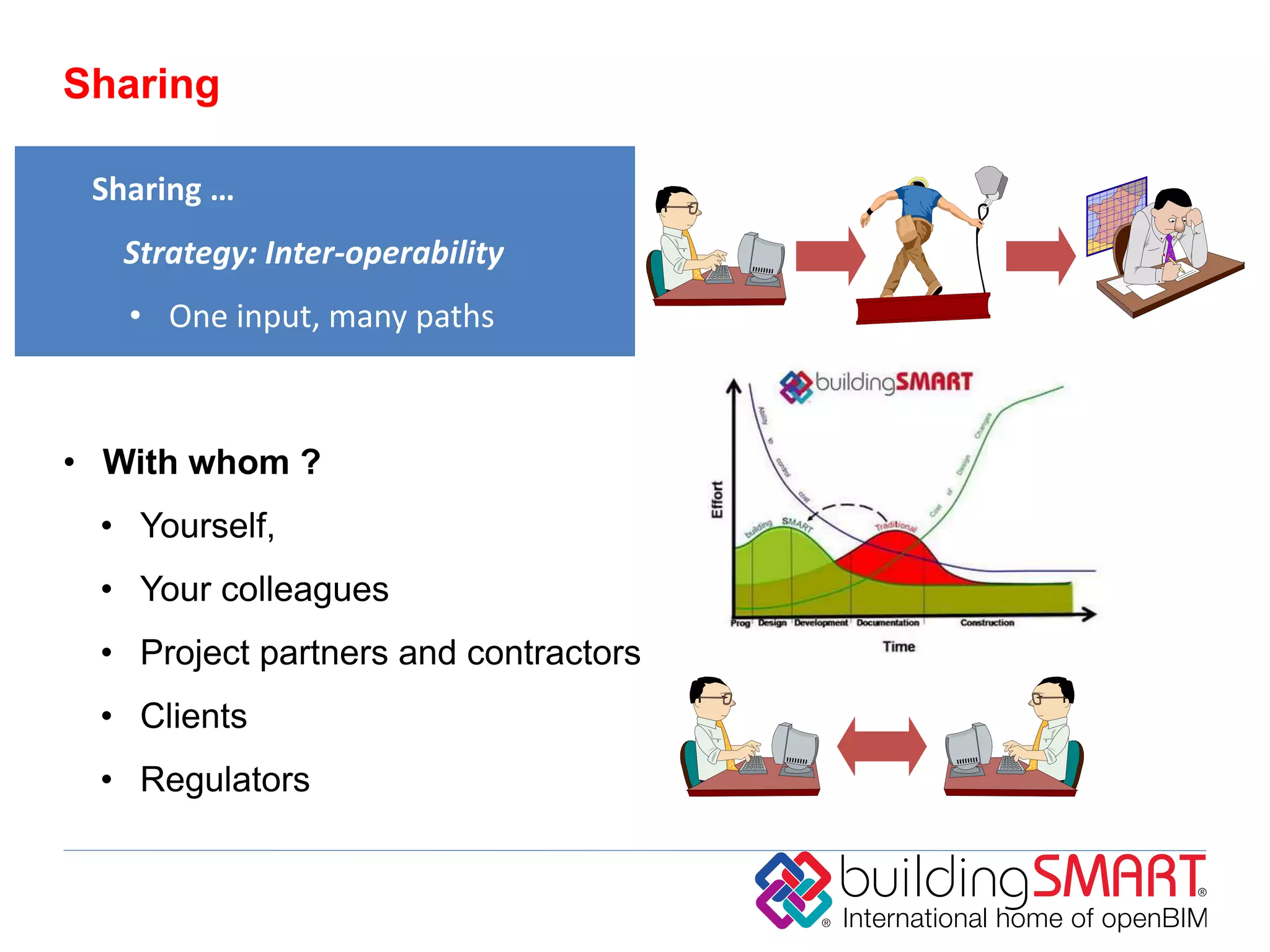
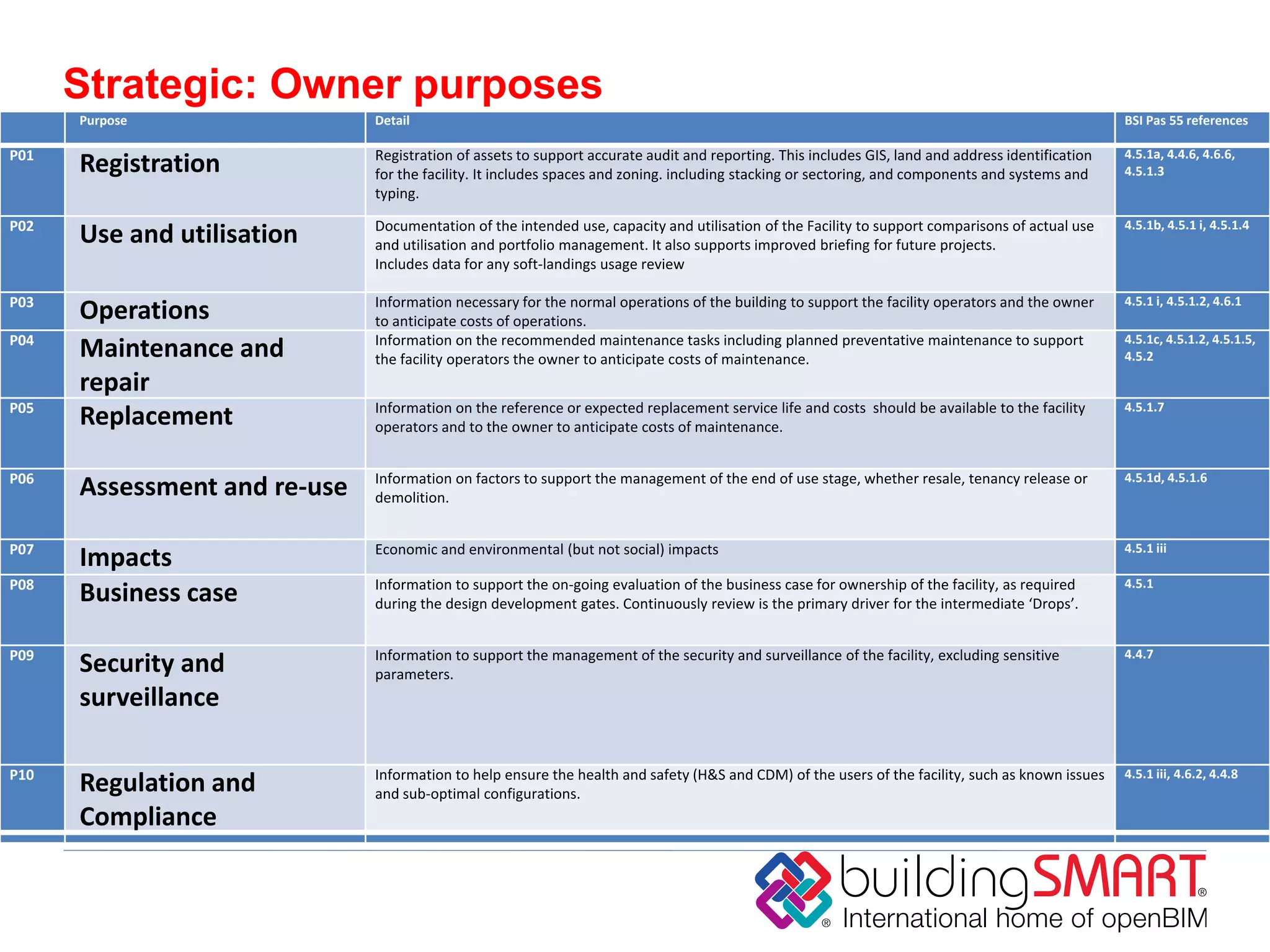
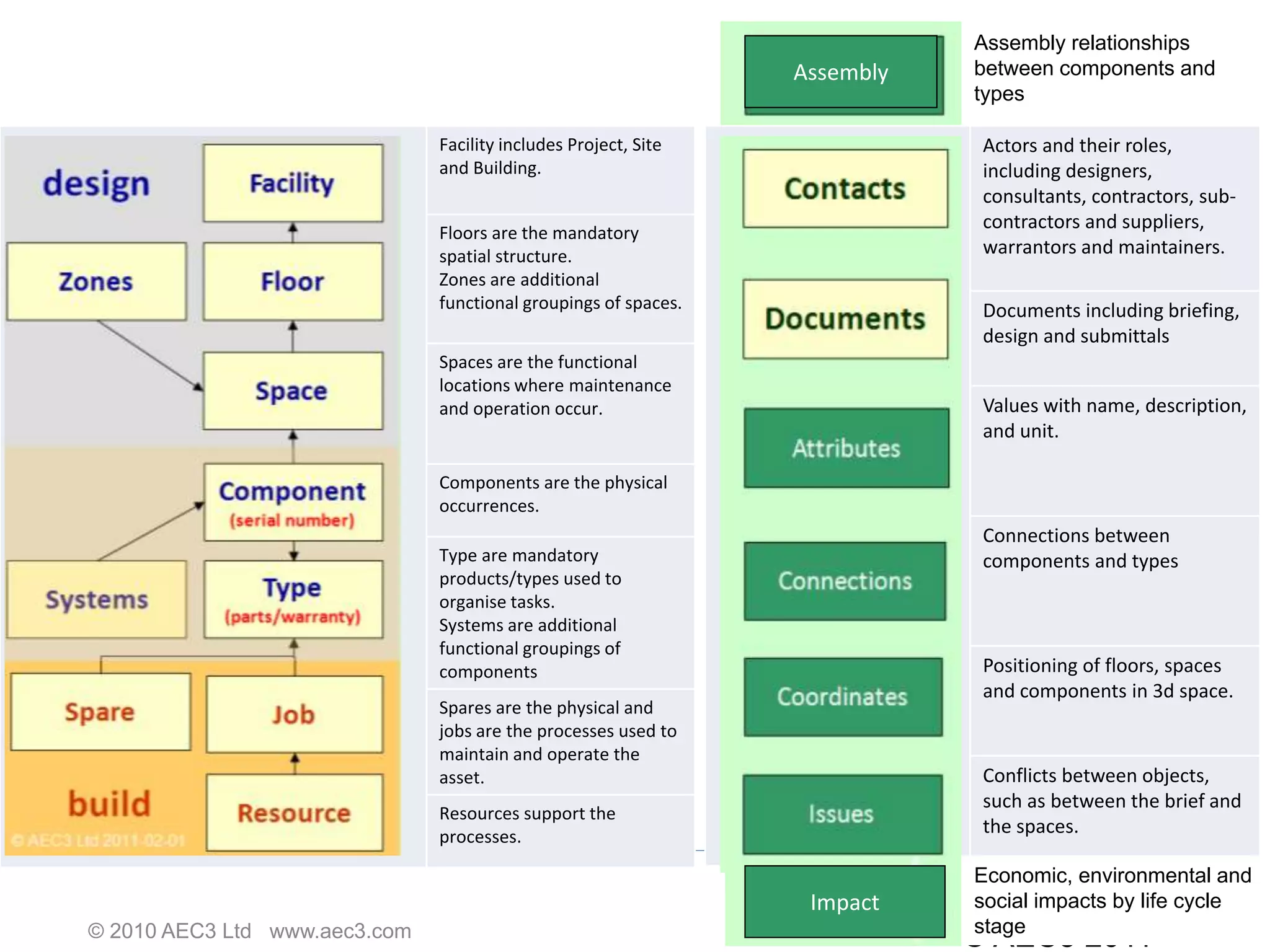
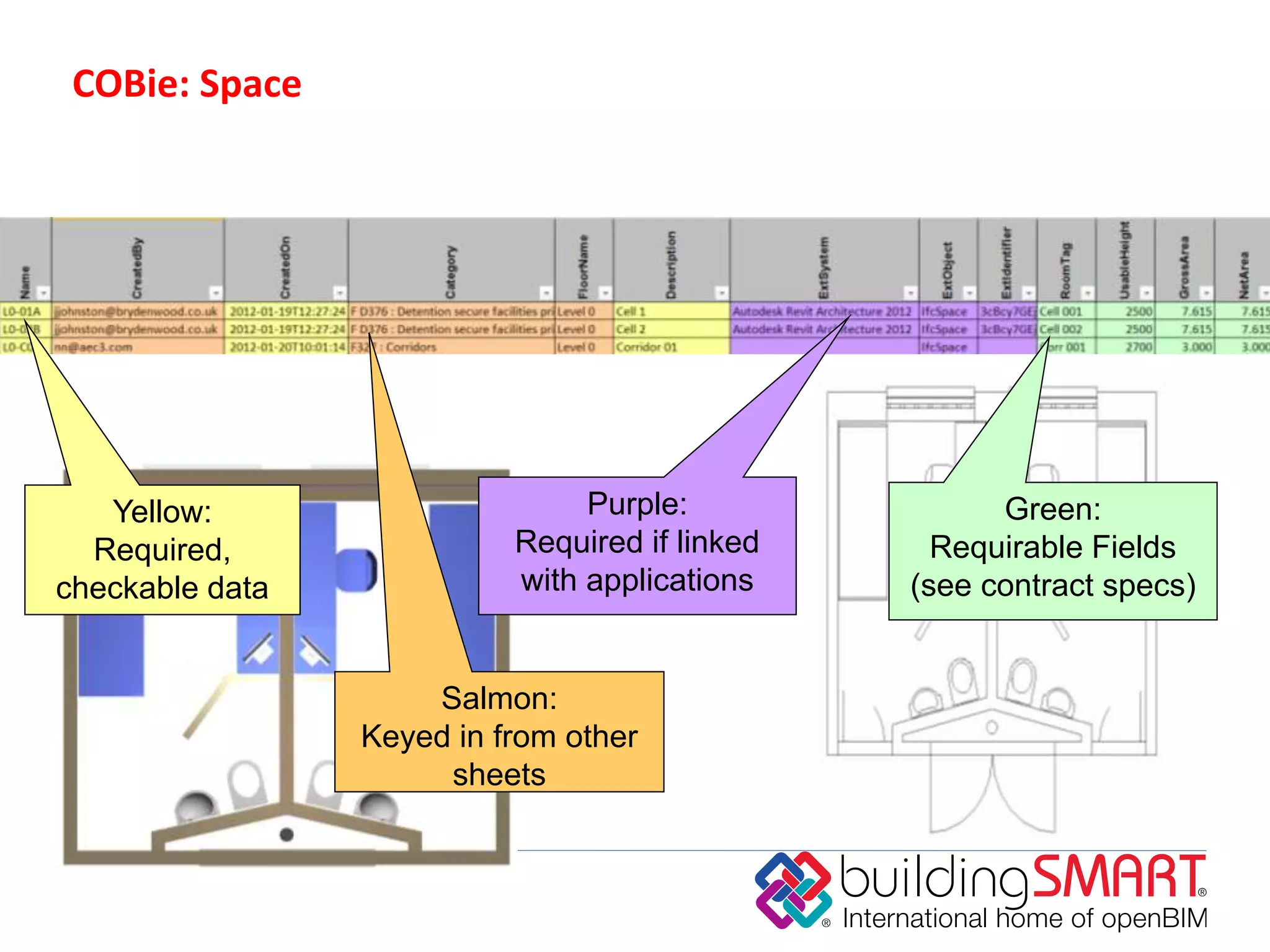
buildingSMART International is a nonprofit organization that develops open standards to support building information modeling (BIM) and sustainable construction. It has 13 chapters across 24 countries. The organization's vision is sustainability through sharing structured building data using open international standards. Its key standards include IFC for defining reusable building information, IDM for documenting information exchanges, and IFD for cataloging building terminology. The organization believes that governments can achieve cost savings, improved value, and lower carbon emissions by using open and shareable building asset information throughout the lifecycle of their facilities.