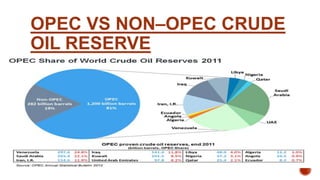
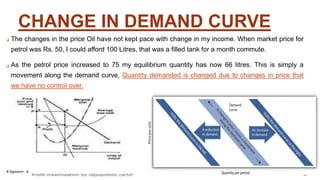
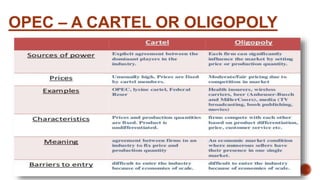
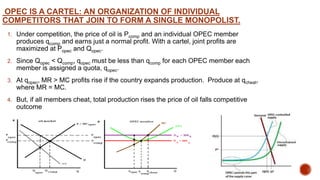
OPEC acts as a cartel by setting production quotas for its members and manipulating the global supply of oil. As the majority of the world's oil reserves and production are controlled by OPEC, it aims to maximize profits by reducing supply to increase prices in the short run. However, in the long run demand and supply become more elastic, limiting OPEC's ability to influence prices. While OPEC still impacts oil prices, its power has declined as non-OPEC producers have increased their market share.