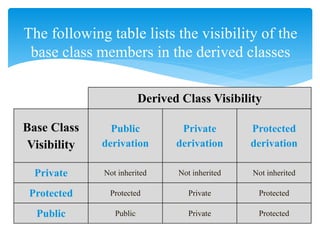
This document provides an overview of the basic concepts of object-oriented programming including objects, classes, data abstraction, encapsulation, hiding, inheritance, polymorphism, binding, and message passing. Objects are instances of classes that interact at runtime and have state and behavior. Classes are collections of similar objects that bind data and functions. Access specifiers include private, public, and protected. Inheritance allows new classes to inherit properties from existing classes. Polymorphism allows different behaviors for the same operation. Binding links procedure calls to execution code. Message passing establishes communication between objects.