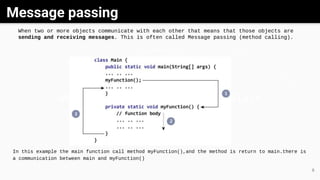
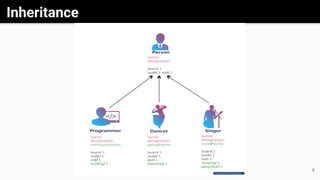
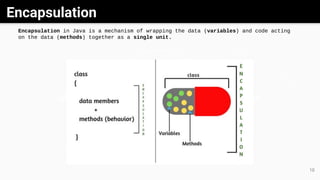
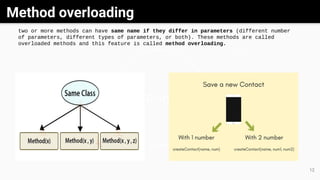
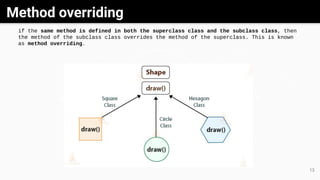
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a methodology that utilizes classes and objects to facilitate software development and maintenance, incorporating key concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. Classes serve as blueprints for creating objects, each possessing specific attributes and methods, while inheritance allows new classes to acquire properties and behaviors from existing ones. Additionally, methods facilitate communication between objects, and both abstract classes and interfaces are tools used to achieve abstraction and define methods in Java.