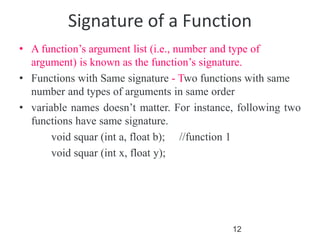
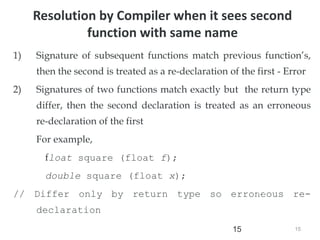
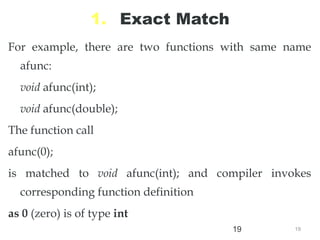
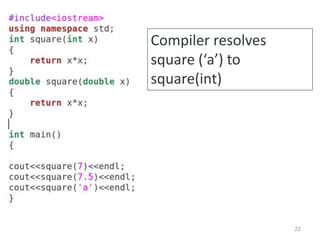
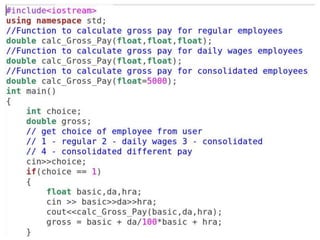
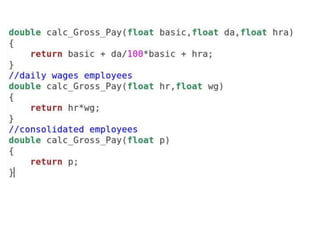
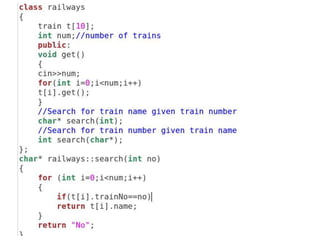
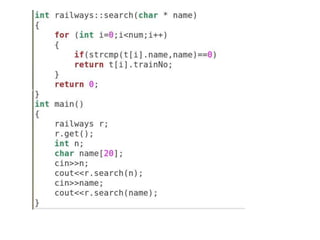
The document discusses function overloading in C++. It explains that function overloading allows functions to have the same name but different signatures. The compiler determines which function to call based on the number, type and order of arguments in the function call. It provides examples of overloading functions to calculate the area of different shapes like circle, rectangle and triangle. The program will use a class with member functions for area() overloaded for the different shapes. Based on user input, it will call the correct area() function to calculate the area and return the result.