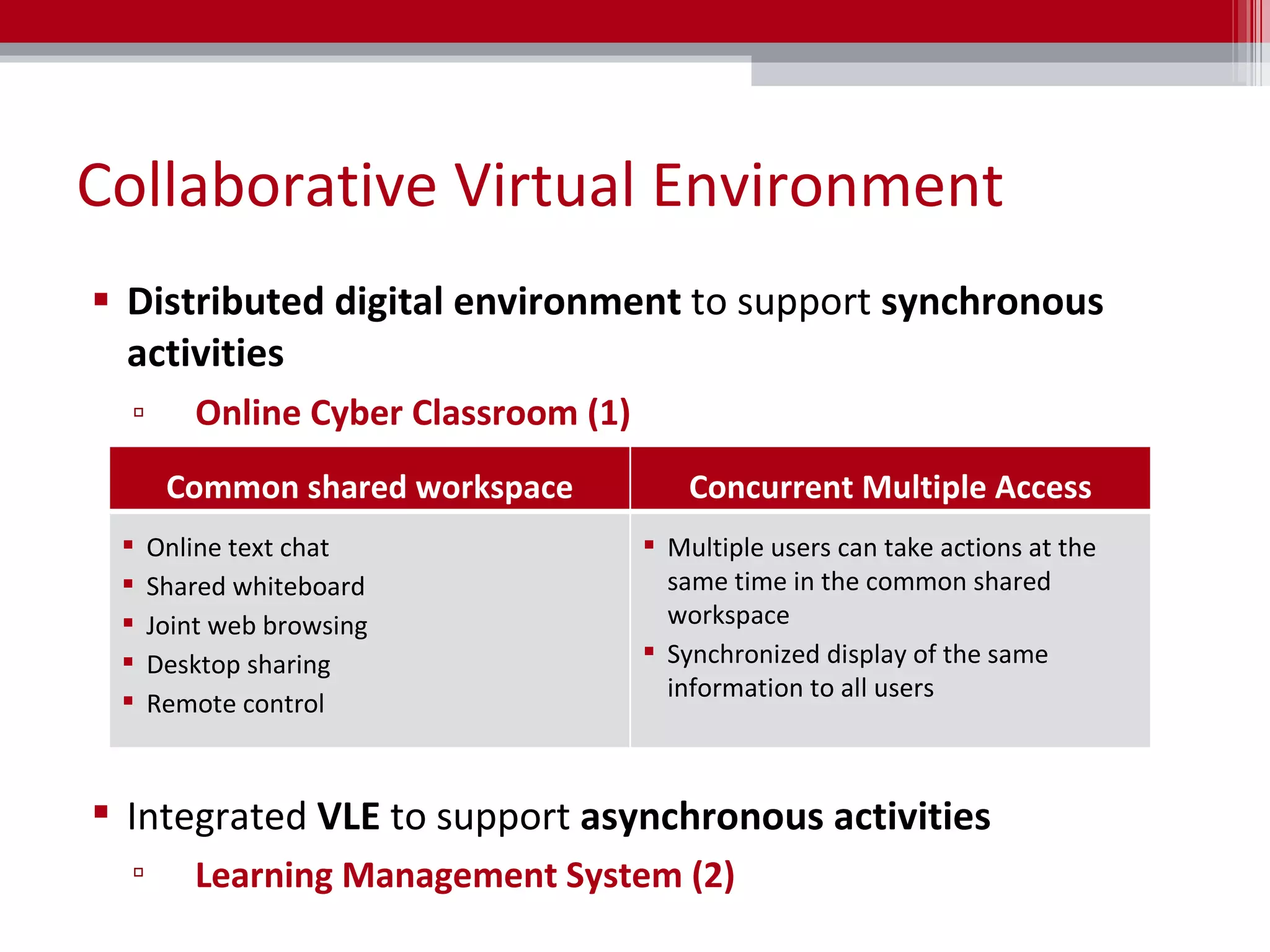
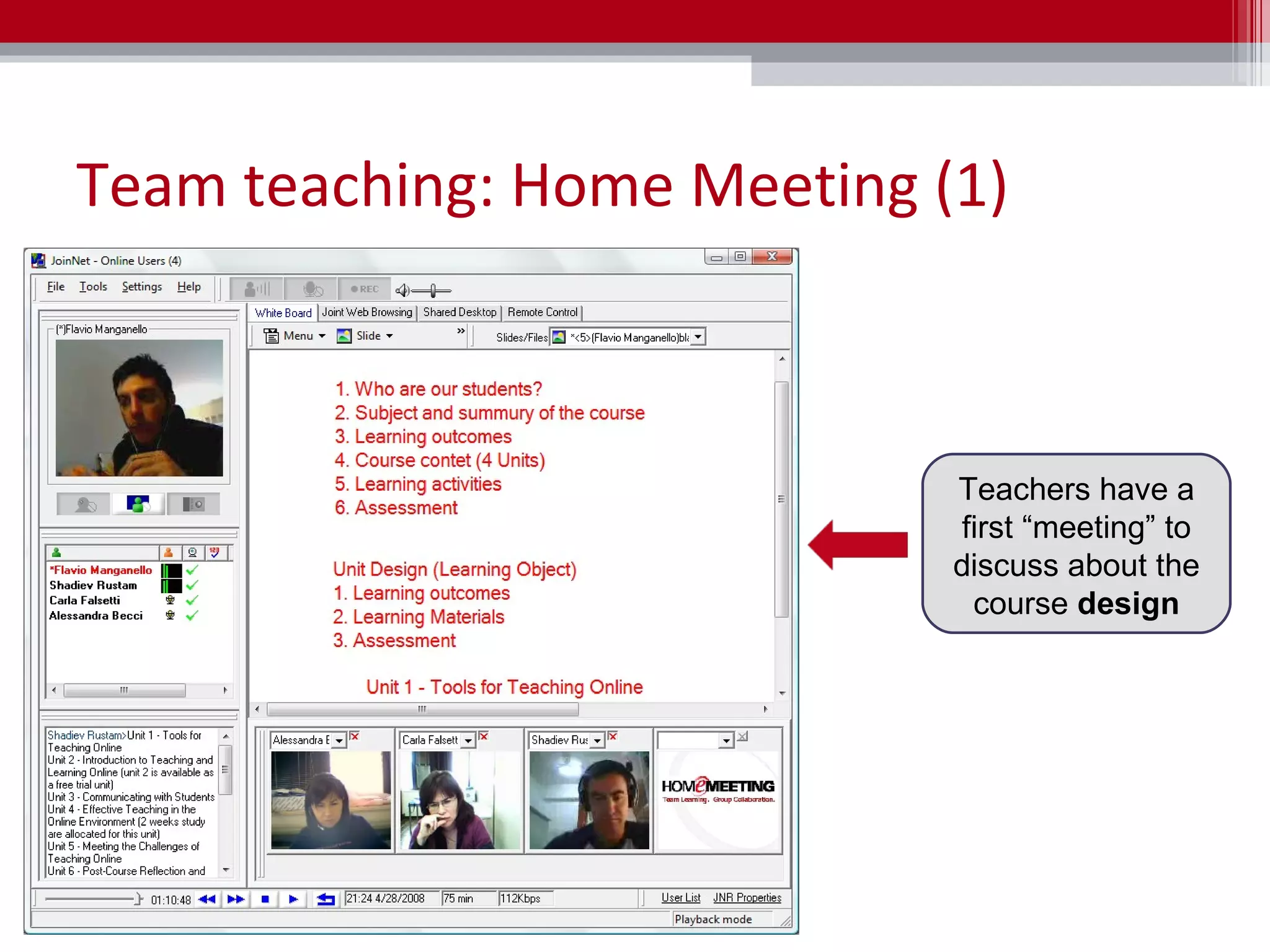
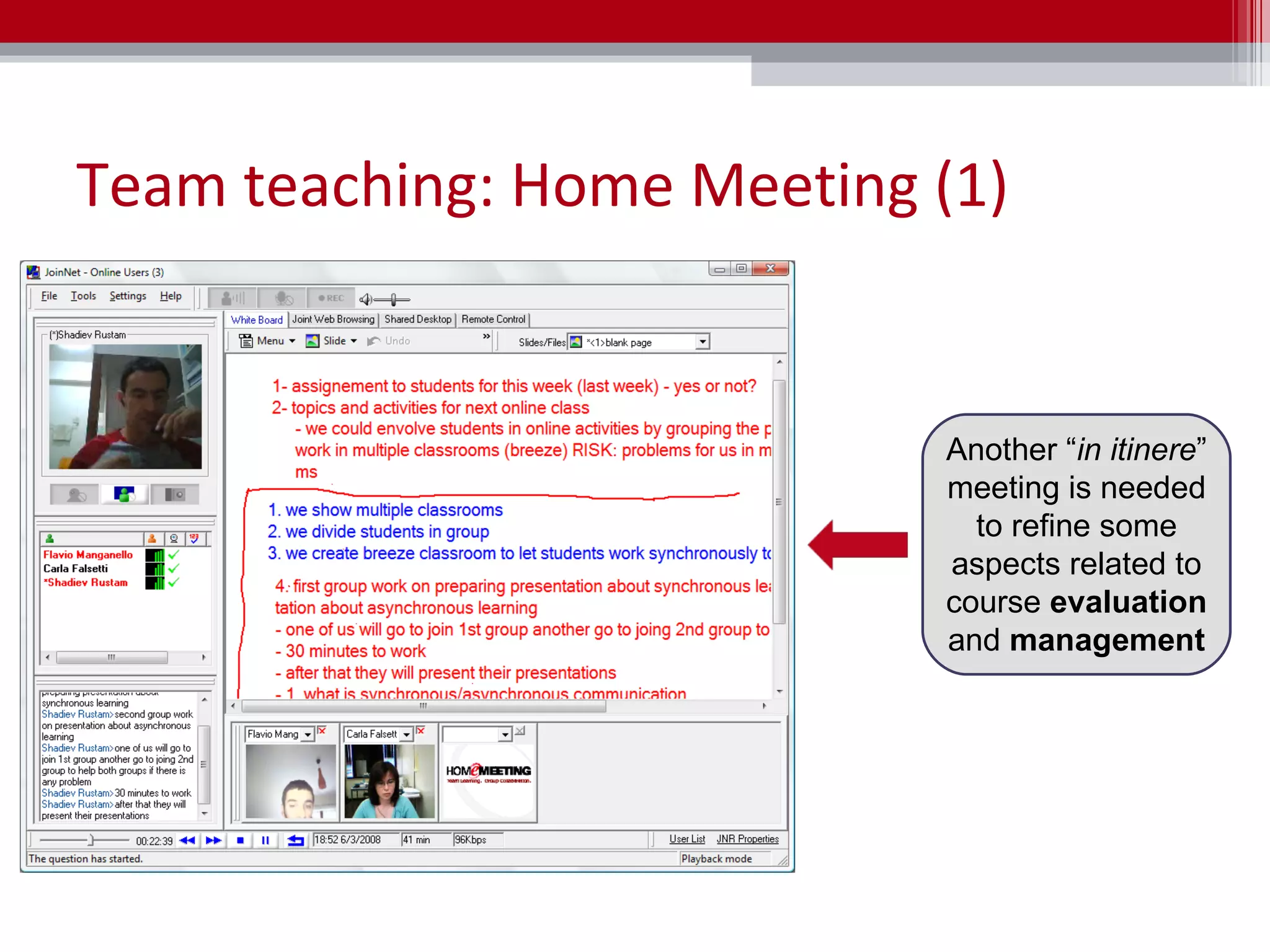
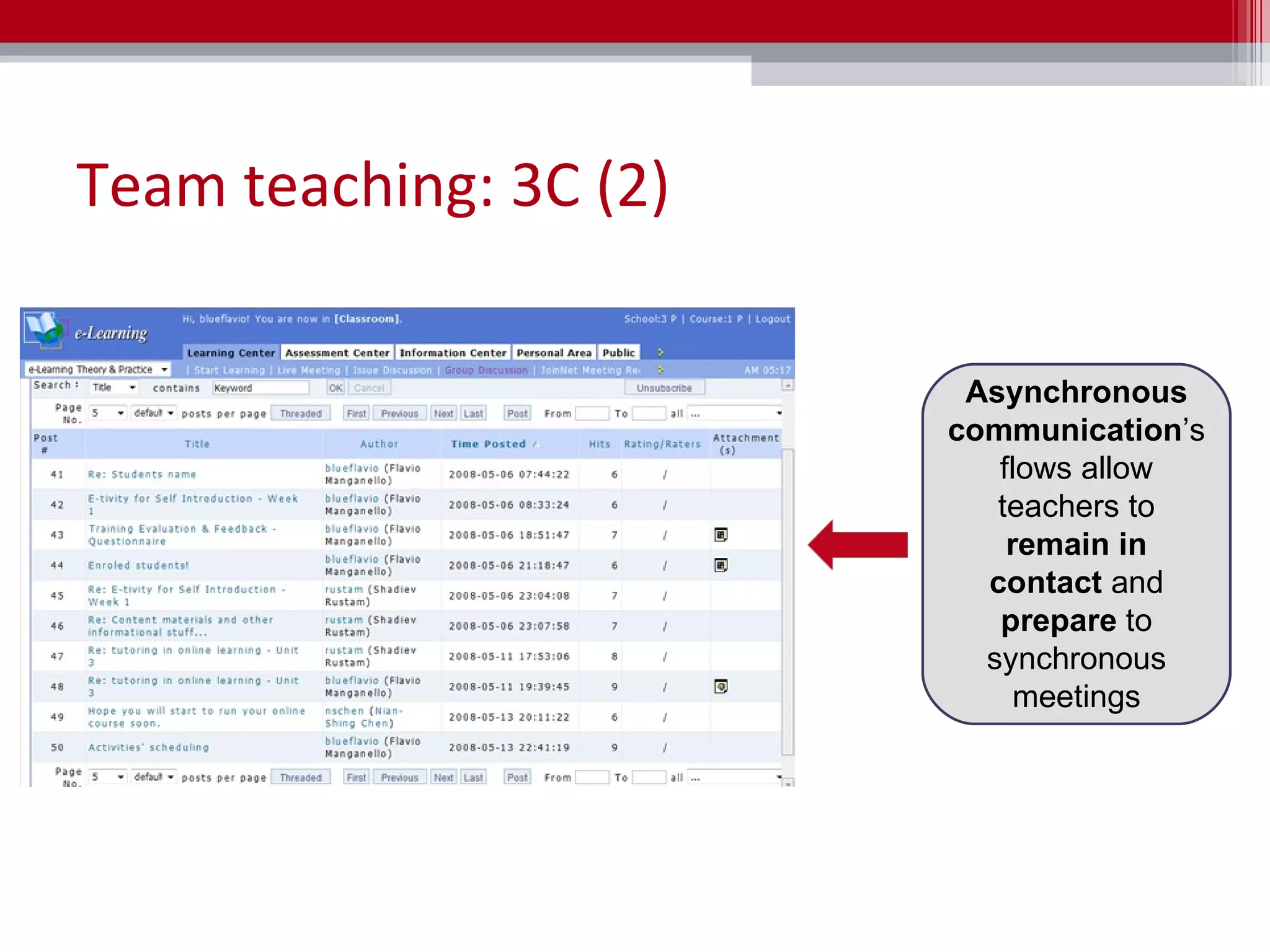
The document discusses the implementation of team teaching in online environments, including synchronous and asynchronous methods supported by digital tools. It emphasizes the importance of effective communication, collaboration, and the roles of teachers in facilitating learning through various pedagogical models. Additionally, it highlights the need for thorough planning, coordination, and the establishment of a collaborative culture among educators.

![Online team teaching Design Evaluation Management Knowledge sharing Reciprocal help [Trentin, 1998] Co ordination Co decision Co llaboration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/online-team-teaching-20090903-090914202538-phpapp01/75/Team-teaching-in-the-age-of-e-collaboration-2-2048.jpg)

![Collaborative team teaching model Problem Based Learning Meaningful Learning [Ausubel, 1962] Scaffolding [Bruner, 1976] TEACHER Facilitator, coach From the movie “Friday Night Lights” (2004)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/online-team-teaching-20090903-090914202538-phpapp01/75/Team-teaching-in-the-age-of-e-collaboration-10-2048.jpg)
![Team teaching models [Chen, 2004] Directive models Collaborative models Synchronous activities (online cyber classroom) Two-teachers model One concentrates on lecturing, the other one concentrates on responding to questions in the text chatroom Three-teachers model One concentrates on lecturing, the second one concentrates on responding to questions in the text chatroom, the third one concentrates on preparing material to the whiteboard Asynchronous/distributed activities Two-teachers (or tutors) Management of a community of practice or of a learning community Synchronous activities (online cyber classroom) Two-teachers (or facilitators) Management of a web seminar or of a student-led discussion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/online-team-teaching-20090903-090914202538-phpapp01/75/Team-teaching-in-the-age-of-e-collaboration-11-2048.jpg)

![Reflections Teachers' step forward Personal and professional identity Performance [Maragliano, 2009] Vocation to collaboration Collaboration is a process that happens if particular instrumental abilities subsist, not only related to the technology Behavioral aspects of digital collaboration and communication Virtual Ethnography [Hine, 2000] Media Richness or Media Naturalness [Kock, 2005] Mutual confidence and trust](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/online-team-teaching-20090903-090914202538-phpapp01/75/Team-teaching-in-the-age-of-e-collaboration-13-2048.jpg)