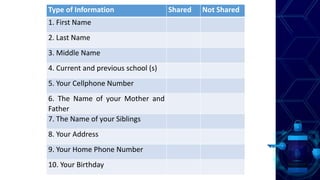
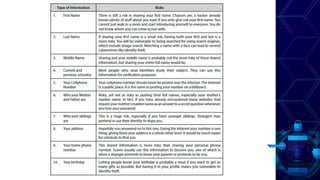
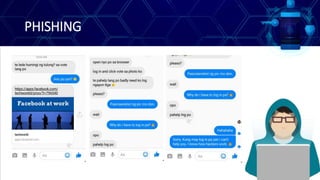
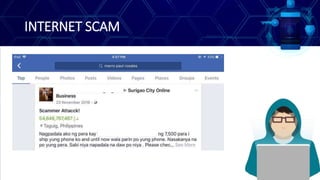
This document discusses online safety, security, ethics and etiquette. It outlines learning competencies around applying appropriate online safety standards, discerning deceptive information, and understanding implications of sharing information publicly. Topics covered include online safety measures, types of online threats like phishing and malware, maintaining privacy, and principles of netiquette and computer ethics. Students will learn to identify different types of online threats, protect their personal information, and behave appropriately online.