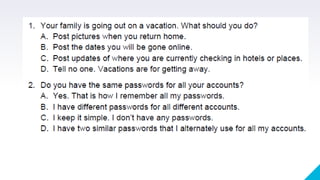
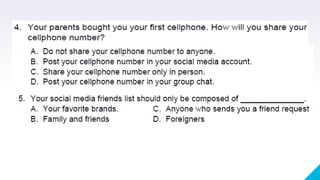
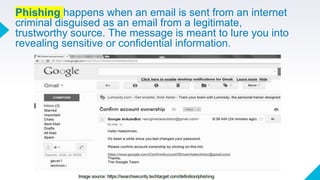
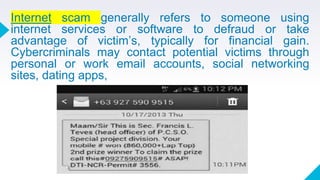
The document discusses online safety, security, and proper etiquette (netiquette) when interacting with others online. It defines netiquette and lists 10 core rules, including remembering the human on the other side, respecting others' privacy and time, and controlling flame wars. It also defines types of online threats like phishing, pharming, internet scams, cyberbullying, and spoofing that users should be aware of. The document provides references to support its discussion.