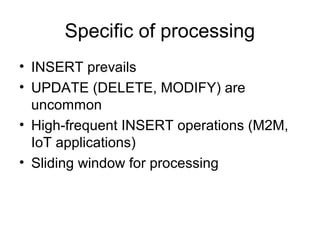
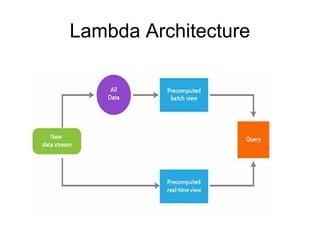
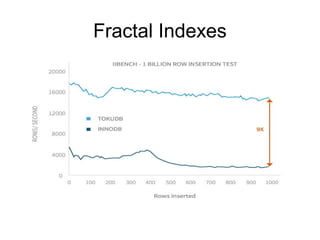
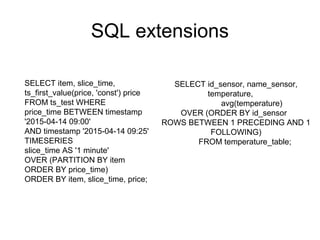
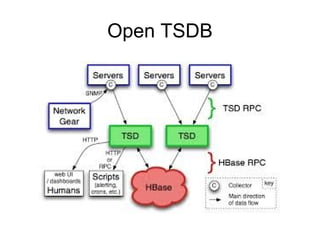
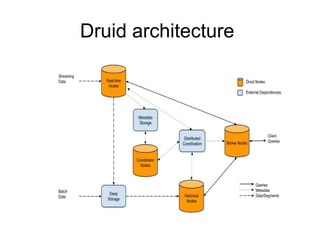
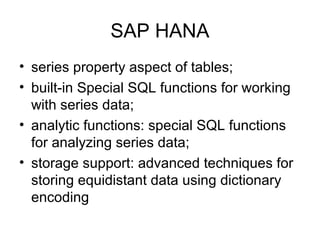
The document discusses time series databases, focusing on their characteristics and typical use cases involving measurements over time, especially in IoT and machine-to-machine communication. It covers both SQL and NoSQL solutions, detailing how to efficiently store and process time series data, including the use of fractal indexes and specific database technologies. Furthermore, it highlights various architectures and systems like InfluxDB and SAP HANA that facilitate time series data management.