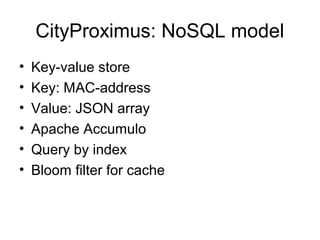
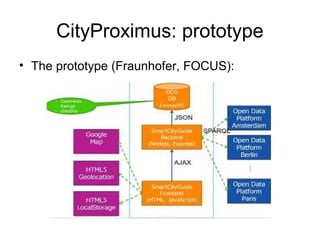
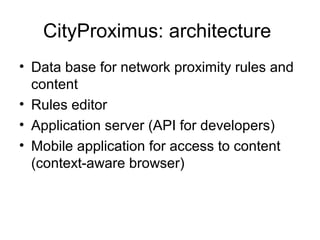
The document discusses a data model for context-aware services that utilizes various wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, to enhance situational awareness and data discovery. It presents a prototype called CityProximus, which leverages network fingerprints to deliver relevant content through a mobile application based on context. Additionally, it outlines the architecture for data processing and storage using a NoSQL model to optimize data access and retrieval.





![CityProximus: data model
Rules: productions
If (fingerprint condition) then { present some
content }
RETE algorithm
REST API with JSON output:
[
{ “type”:”some_type”,”data”:”some_data”},
{“type”: ...},...
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contextaware-151016081144-lva1-app6892/85/On-data-model-for-context-aware-services-12-320.jpg)