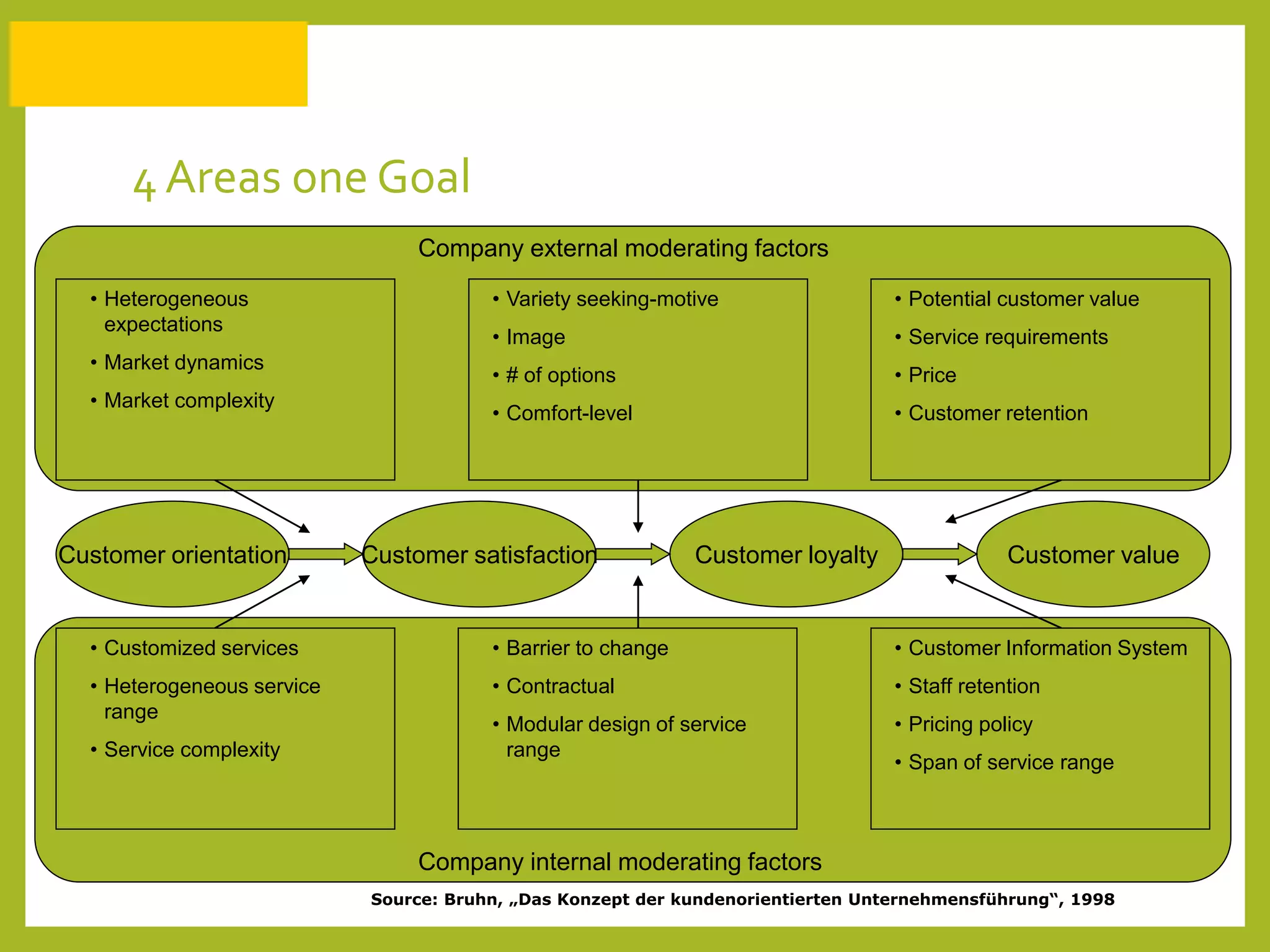
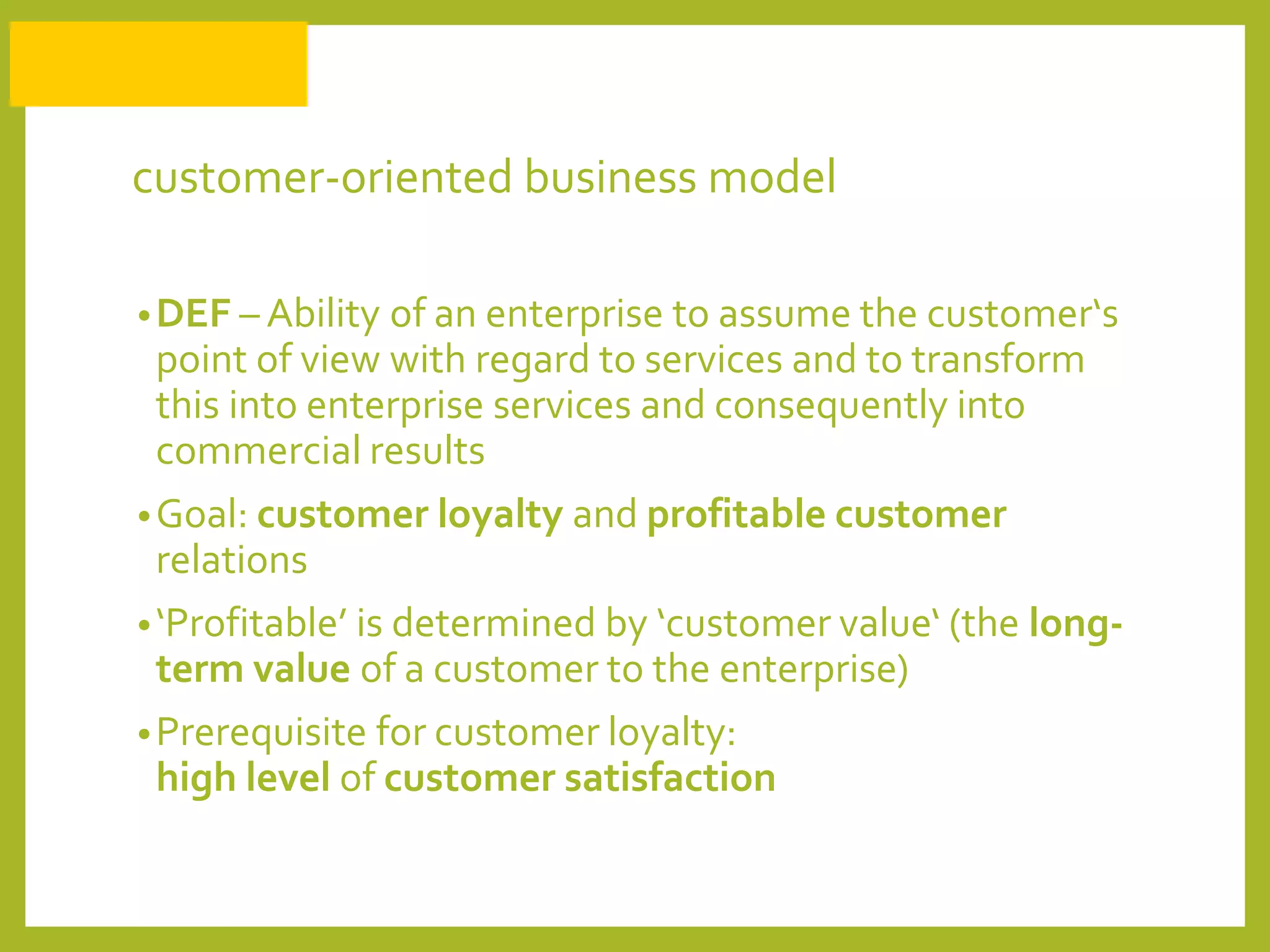
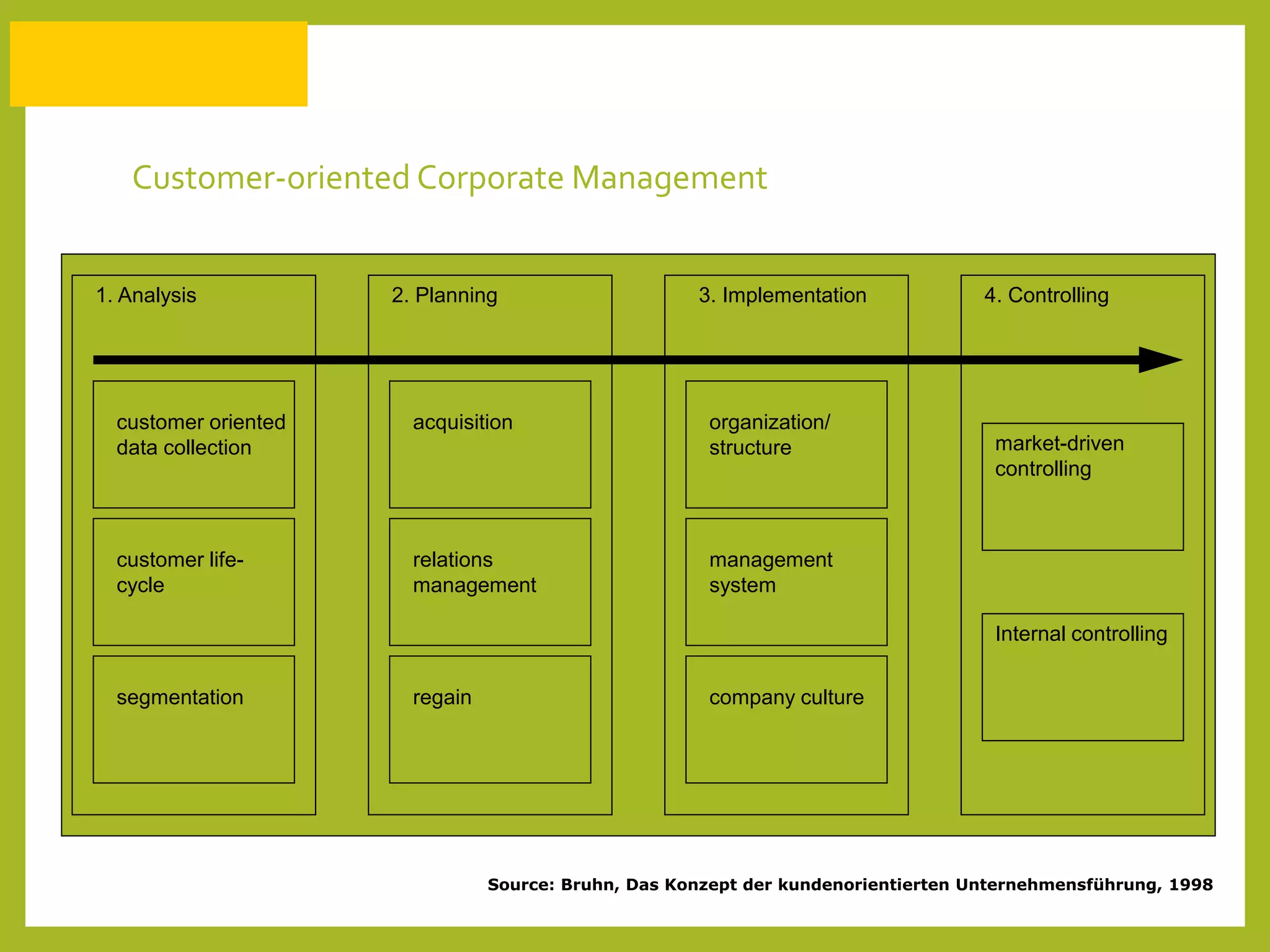
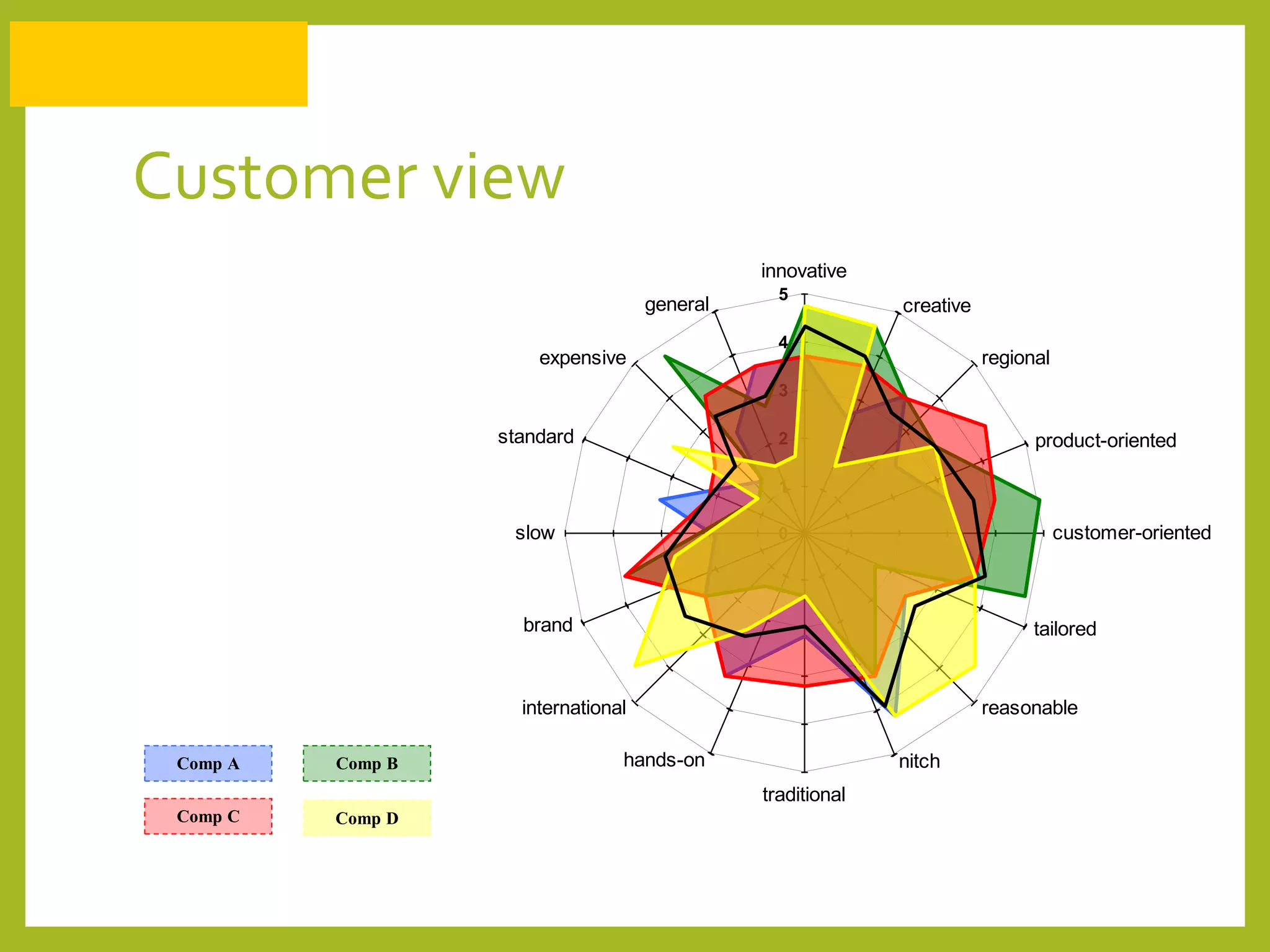
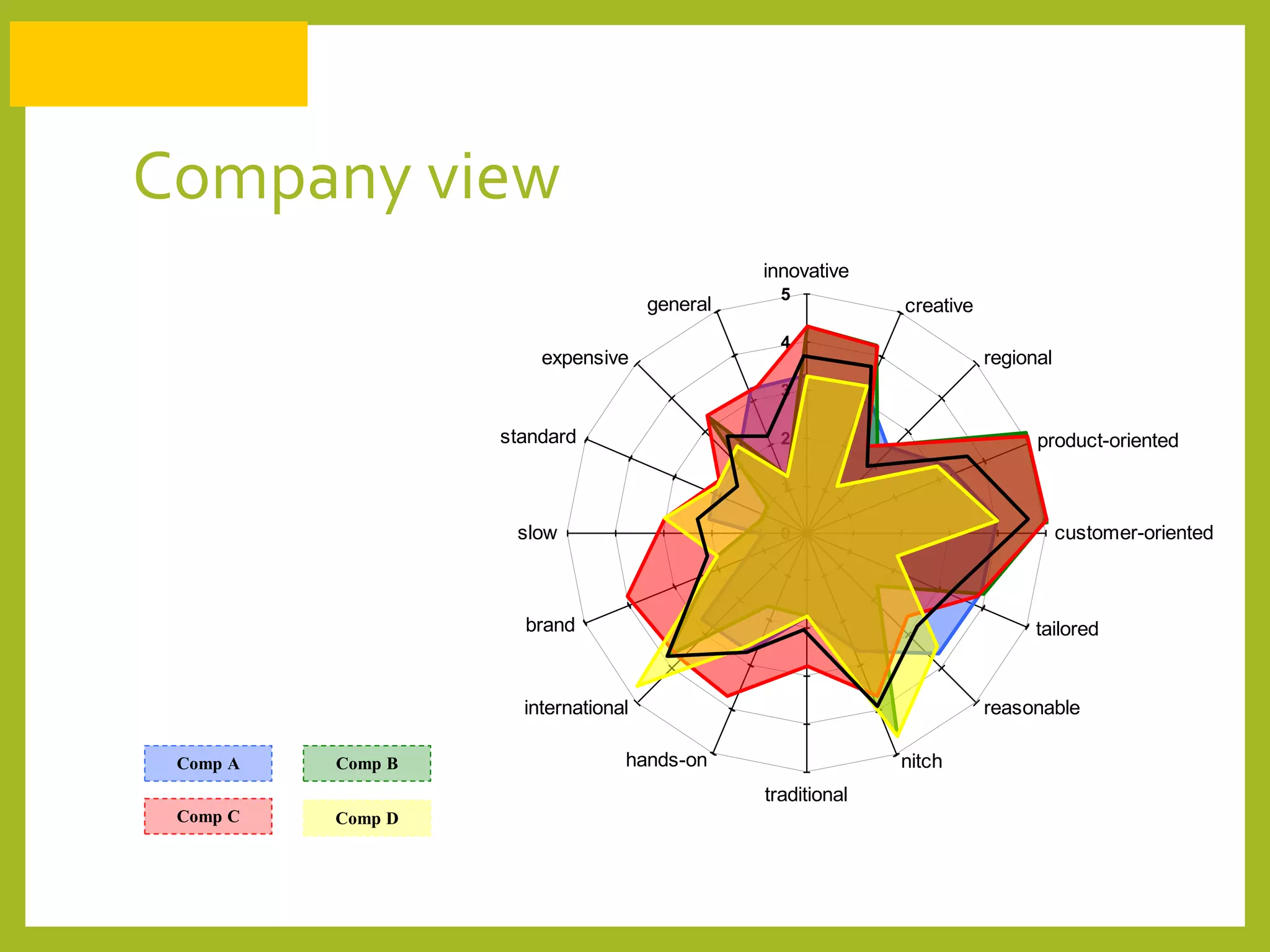
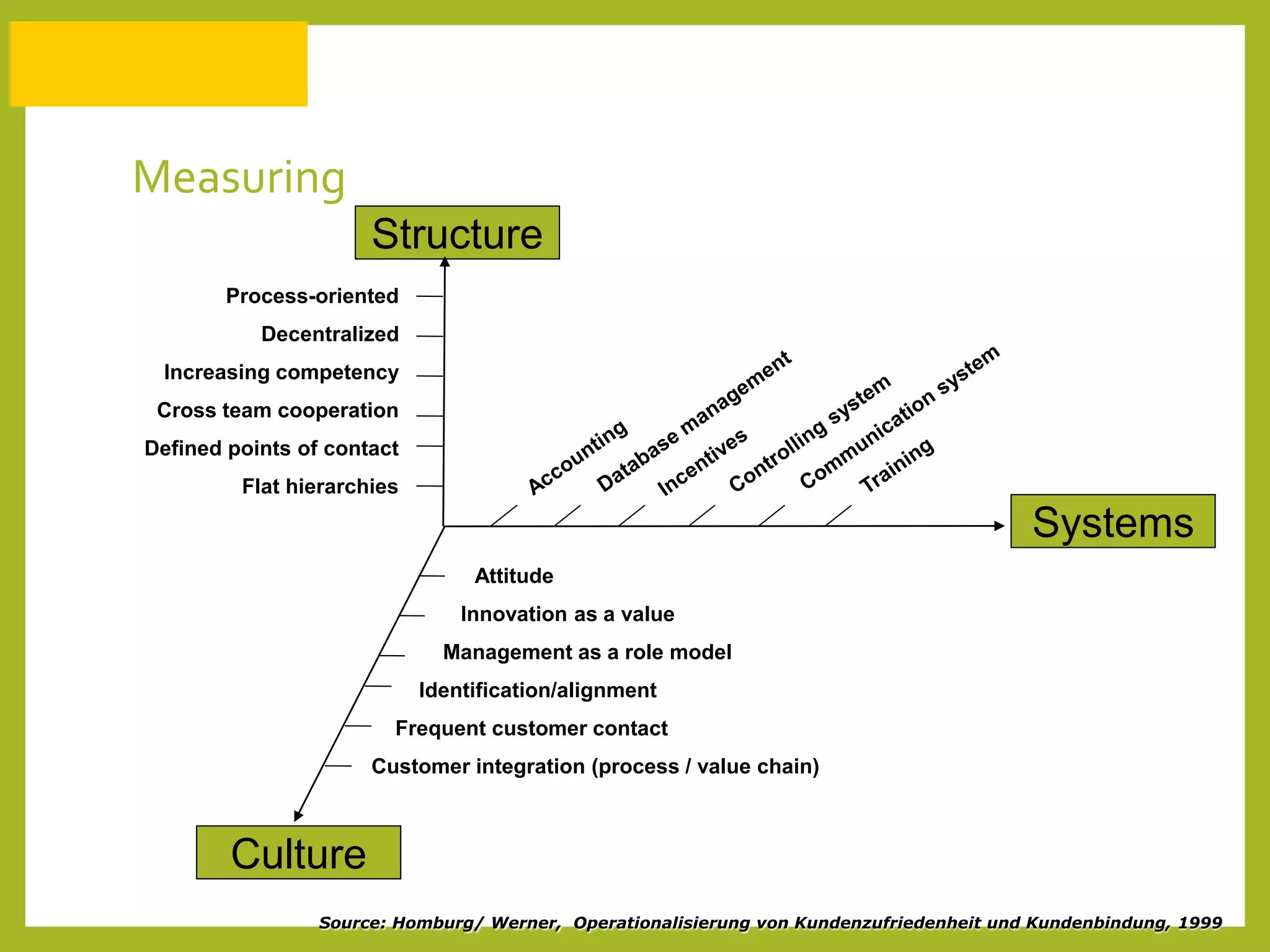
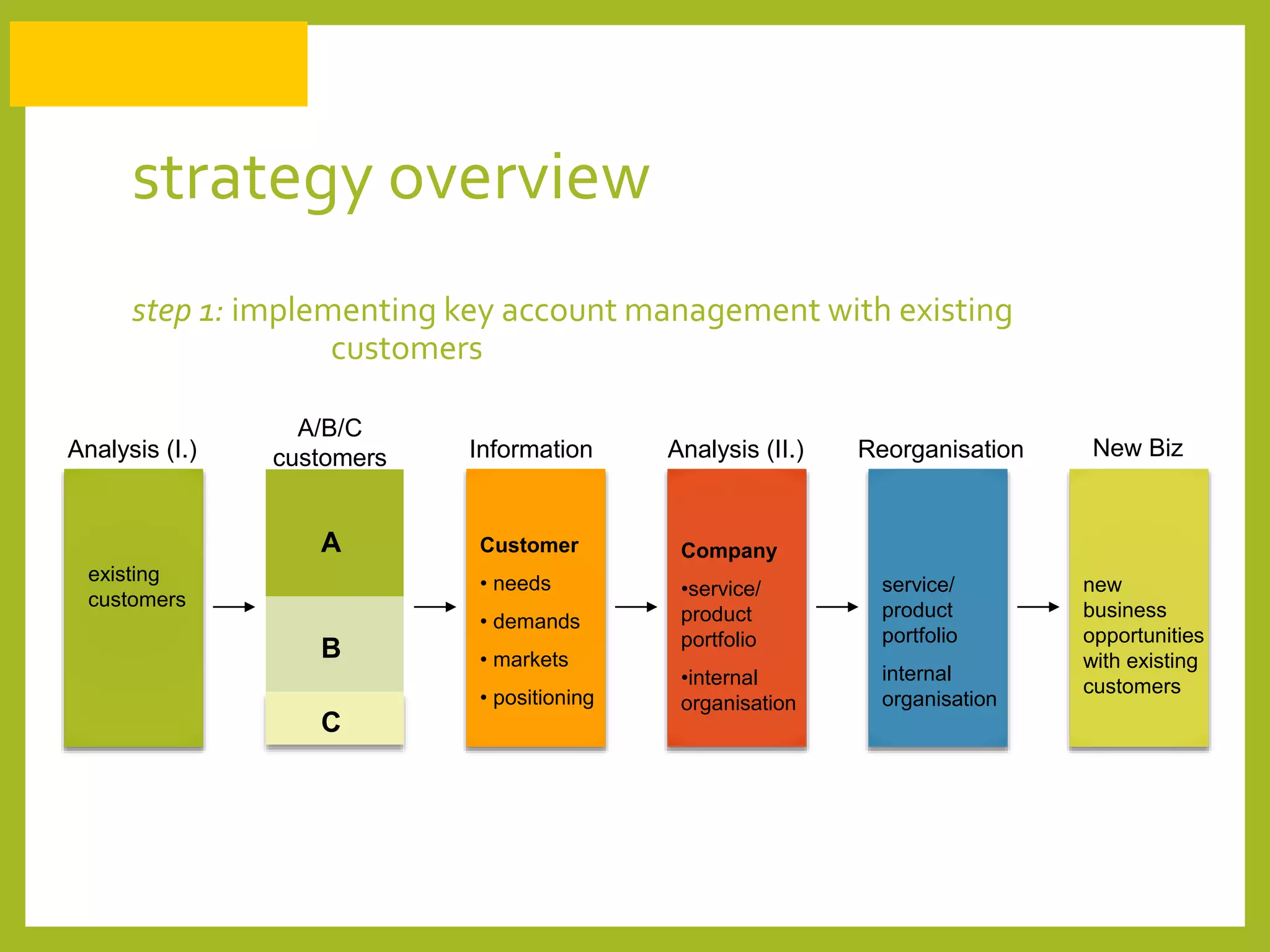
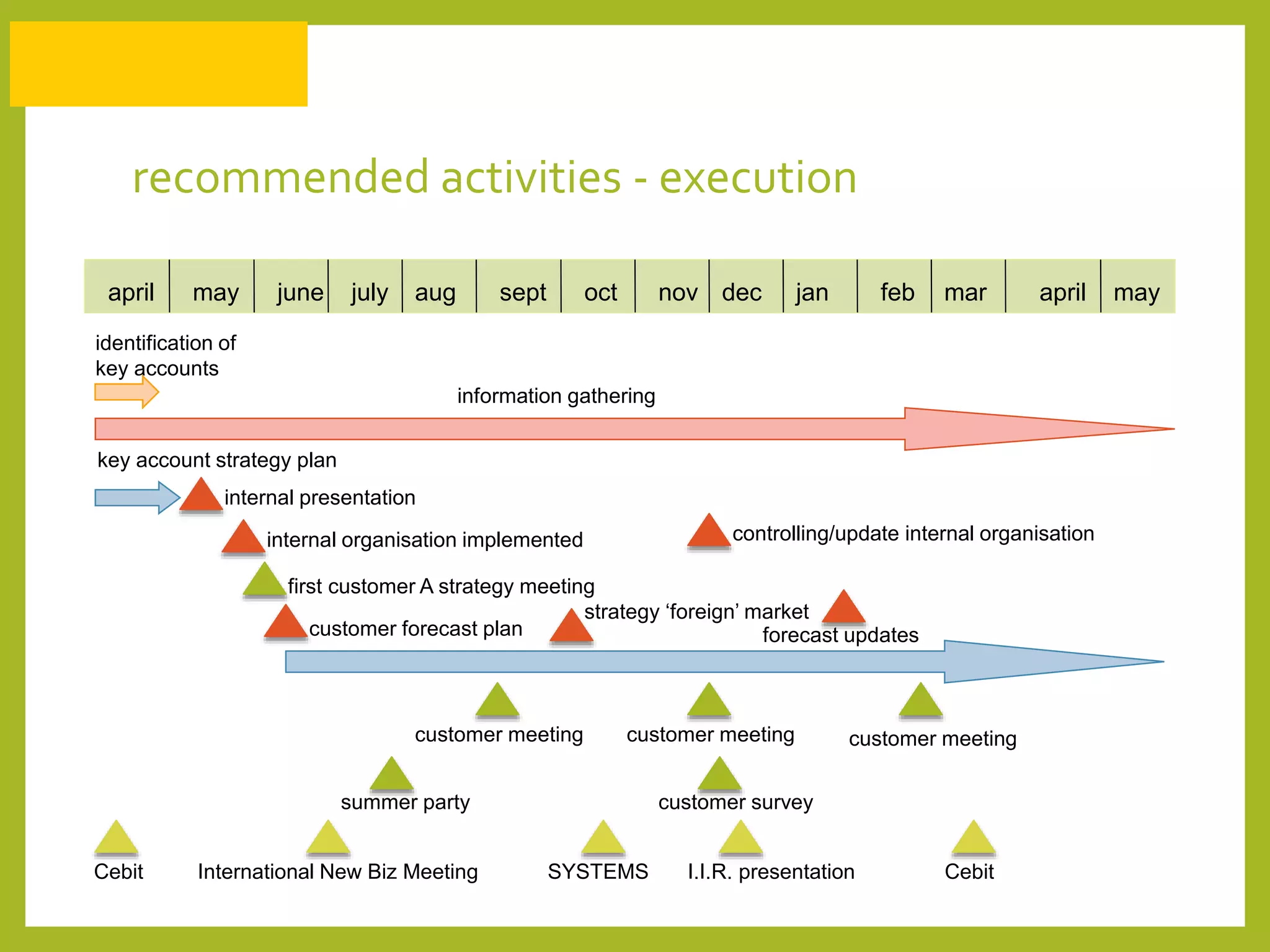
The document discusses how to generate repeat business with key accounts through customer-oriented business practices. It recommends identifying key accounts and gathering customer information to develop customized strategies. Companies should analyze their service portfolio and internal organization, then implement account teams and regular communication like strategy meetings and surveys to ensure high customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term value. The goal is an innovative, flexible approach with a focus on understanding each customer's individual needs to build strong, predictable relationships over time.