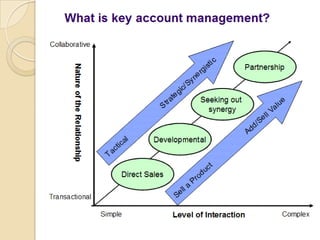
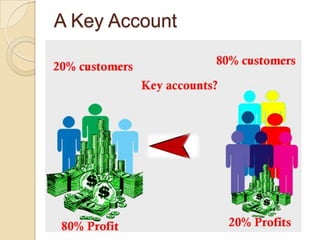
This document provides an overview of key account management. It defines key terms like key account and key account management. It identifies the basic elements of key account management as identifying, analyzing, and selecting relationship strategies for key accounts. It describes the nature of the job as becoming close to decision makers, ensuring quality service, and motivating clients. It also outlines the skills, competencies, and level of qualification needed for the role of a key account manager.