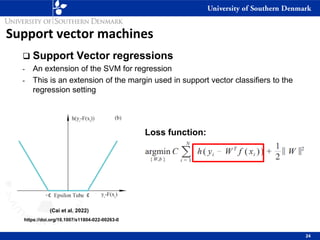
This document provides an overview of support vector machines (SVM) including:
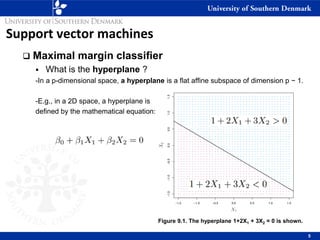
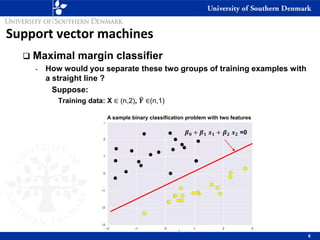
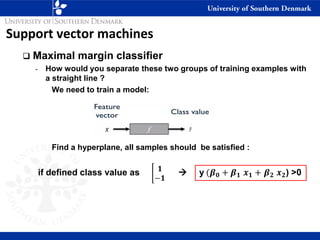
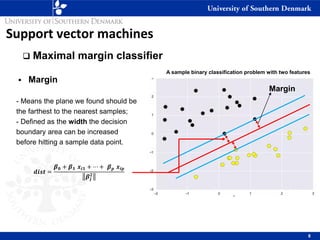
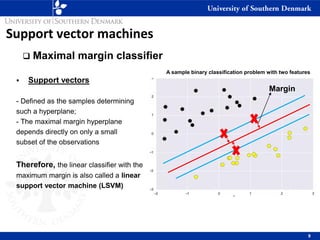
1) Maximal margin classifiers which find the optimal separating hyperplane with the maximum margin between classes. Support vectors are the data points that determine the hyperplane.
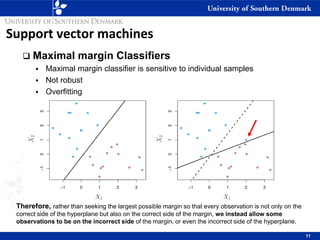
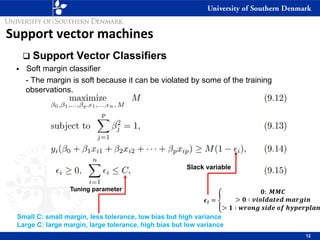
2) Support vector classifiers which allow some misclassified data points by introducing slack variables. This makes the classifier more robust.
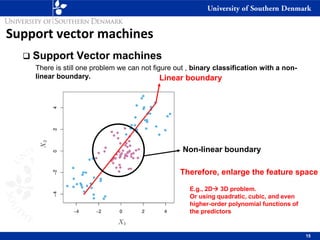
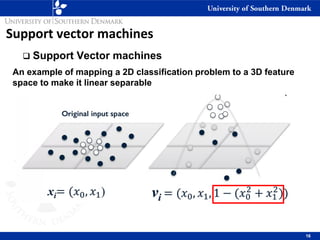
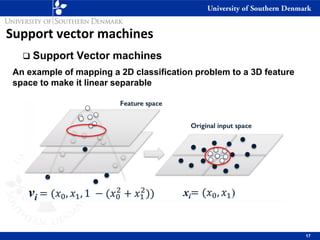
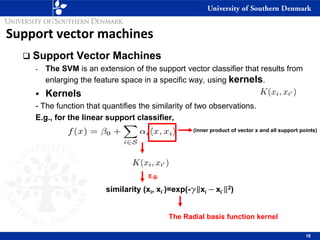
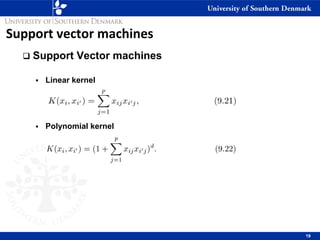
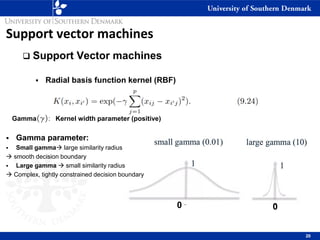
3) SVM can handle non-linear decision boundaries using kernel methods to map data into higher dimensional feature spaces where a linear separator can be found. Common kernels include linear, polynomial and radial basis function kernels.
4) Multi-class classification with SVM can be done with one-vs-one or one-vs-all approaches.
5) SVM




![Support vector machines
❑ Fruit types classification (one-versus-all)
23
Target_names_fruits = ['apple', 'mandarin', 'orange', 'lemon']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/om-ds-fall2022-session10-supportvectormachine-221228094134-cc728bc5/85/OM-DS-Fall2022-Session10-Support-vector-machine-pdf-23-320.jpg)