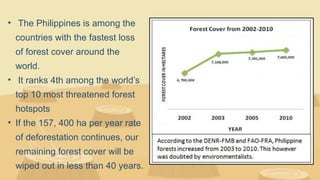
The document discusses various environmental problems in the Philippines, including deforestation, soil erosion, illegal mining, oil spills, and pollution. It highlights the devastating effects of these issues on health, ecosystems, and biodiversity, as well as relevant laws aimed at environmental protection. Additionally, it includes an educational activity to observe water quality through a filtration experiment.