Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times



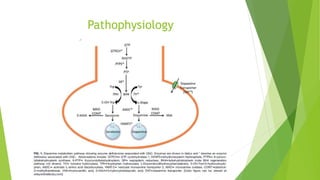


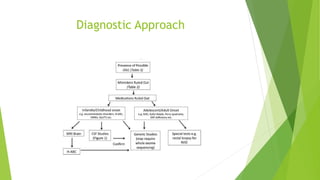



Oculogyric crises are characterized by sustained contractions of the eye muscles causing tonic, conjugate deviations of the eyes, typically upward. They can last from minutes to hours and may be associated with other dystonic symptoms. Oculogyric crises are most often caused by dopamine-receptor blocking agents as a potential complication, and are treated with anticholinergic drugs which work quickly to ameliorate symptoms by addressing the underlying relative cholinergic overactivity caused by the hypodopaminergic state.










