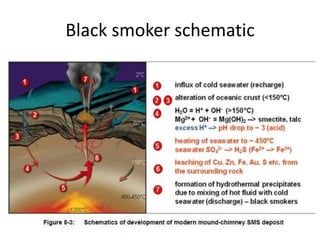
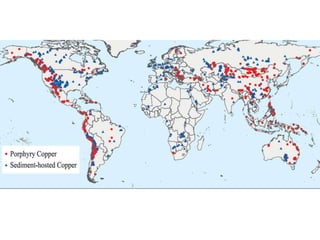
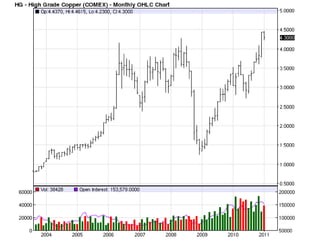
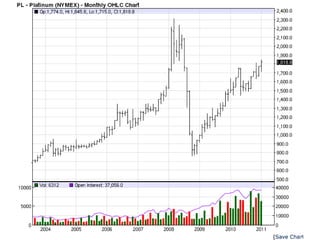
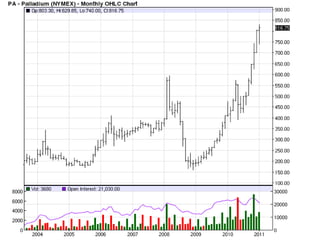
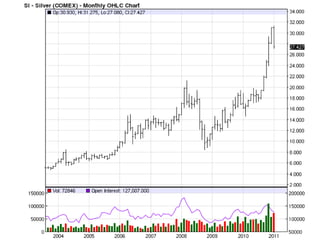
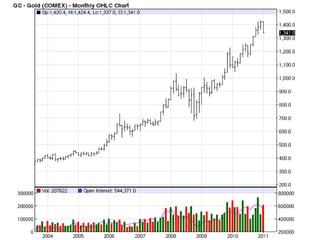
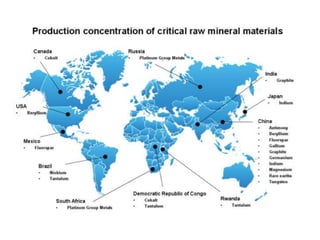
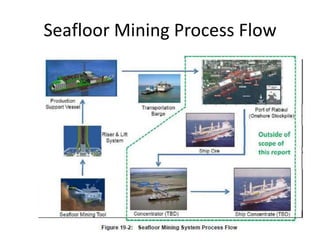
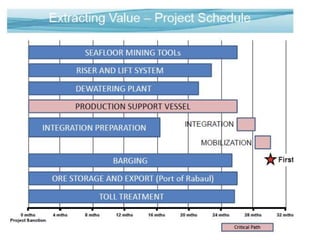
Deep ocean mining targets volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) ore deposits on the seafloor that contain valuable metals like copper, zinc, gold and silver. These deposits form from hydrothermal vents where superheated water and dissolved metals erupt from underwater volcanoes. While explored in the 1970s, the technology was not advanced enough to mine economically. However, with rising demand and limited new sources of critical metals, companies are again looking to mine these deep ocean deposits using new mining machines and ship-based processing. One project, Solwara 1 off Papua New Guinea, aims to extract over a million tons per year of high-grade copper and gold starting in 2013 at a depth of 1,600