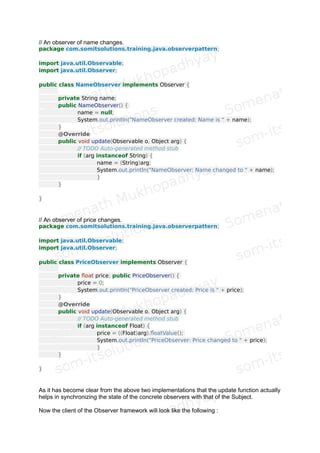
1. The document discusses the Observer pattern as implemented in Java through the Observer and Observable classes. The Observer pattern allows objects called observers to monitor changes to other objects called subjects.
2. When a subject's state changes, it notifies its observers. The observers then update themselves to match the new state of the subject. This keeps all observers synchronized with the subject.
3. As an example, the document describes how different views of a document can observe the document object. When the document changes, it notifies the views which then update themselves to reflect the new document state.




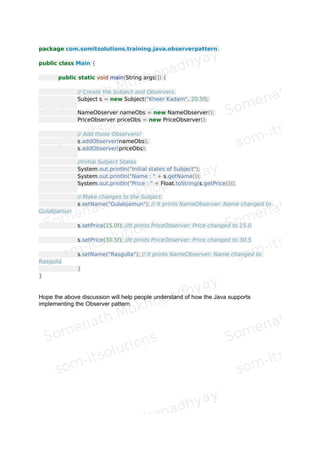

![package com.somitsolutions.training.java.observerpattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create the Subject and Observers.
Subject s = new Subject("Kheer Kadam", 20.5f);
NameObserver nameObs = new NameObserver();
PriceObserver priceObs = new PriceObserver();
// Add those Observers!
s.addObserver(nameObs);
s.addObserver(priceObs);
//Initial Subject States
System.out.println("Initial states of Subject");
System.out.println("Name : " + s.getName());
System.out.println("Price : " + Float.toString(s.getPrice()));
// Make changes to the Subject.
s.setName("Gulabjamun"); // It prints NameObserver: Name changed to
Gulabjamun
s.setPrice(15.0f); //It prints PriceObserver: Price changed to 15.0
s.setPrice(30.5f); //It prints PriceObserver: Price changed to 30.5
s.setName("Rasgulla"); // It prints NameObserver: Name changed to
Rasgulla
}
}
Hope the above discussion will help people understand of how the Java supports
implementing the Observer pattern.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/observerpattern-151012123143-lva1-app6891/85/Observer-pattern-8-320.jpg)