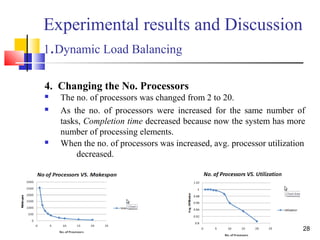
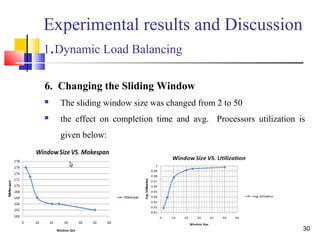
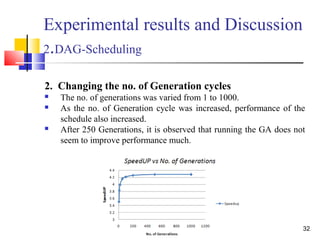
The document discusses a thesis focused on two main research projects: scheduling tasks using a genetic algorithm on heterogeneous systems represented as directed acyclic graphs (DAG) and dynamic load balancing using genetic algorithms. The proposed algorithms aim to minimize completion time and optimize processor utilization, with experimental results indicating significant performance improvements in both cases as processor numbers and generations increase. The results demonstrate high average processor utilization and effective scheduling, particularly when tasks are abundant.



![5
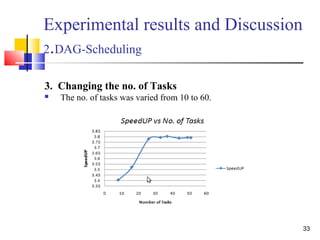
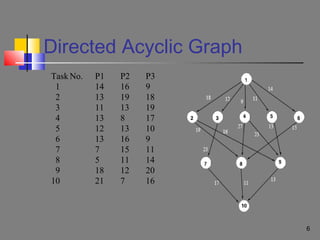
Directed Acyclic Graph
A process or an application can be broken down into a set of tasks
we represent these tasks in the form of a directed acyclic graph
(DAG)
A parallel program with n tasks can be represented by a 4-tuple (T, E,
D, [Ai])
1) T = {tl, t2, . . , tn} is the set of tasks.
2) E the edges, represents the communication between tasks
3) D is an n x n matrix, where the element dij of D is the data volume
which ti should transmit into tj.
4) Ai, 1 <= i <= n, is a vector [eil, ei2, . . . , eiu,], where eiu, is the execution
time of ti on pu.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/observationsondagschedulinganddynamic-load-balancingusinggeneticalgorithm-130622021121-phpapp01/85/Observations-on-dag-scheduling-and-dynamic-load-balancing-using-genetic-algorithm-5-320.jpg)


![9
DAG-Scheduling
2. Scheduling Encoding (Chromosome)
A string is a candidate solution for the problem. String consists of
several lists. Each list is associated with a processor.
Lets for any application of 10 tasks the generated schedule is:
• 1th Processor : t3 t4 t8
• 2th Processor : t5 t7 t9
• 3th Processor : t0 t1 t2 t6
Then the chromosome can be represented as matrix of size[No. of
Task x No. of Processors]
P1 P2 P3
t3 t5 t0
t4 t7 t1
t8 t9 t2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/observationsondagschedulinganddynamic-load-balancingusinggeneticalgorithm-130622021121-phpapp01/85/Observations-on-dag-scheduling-and-dynamic-load-balancing-using-genetic-algorithm-9-320.jpg)

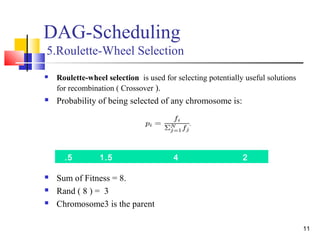
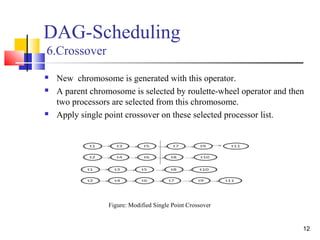
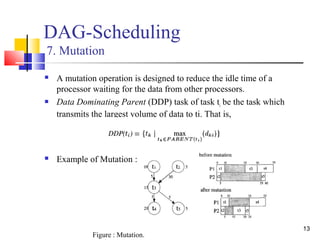


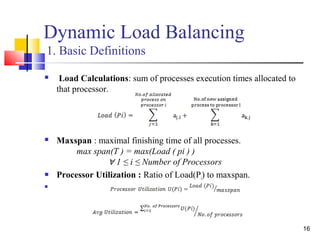

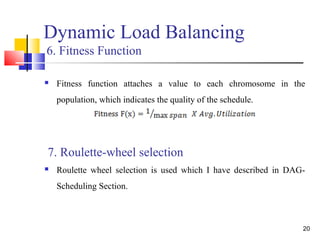
![19
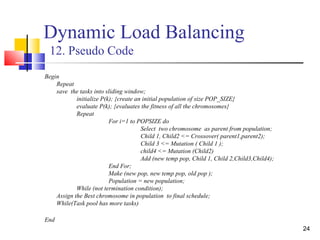
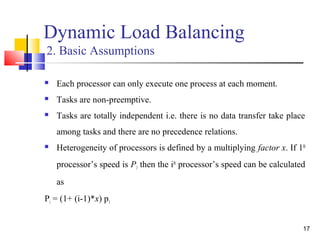
Dynamic Load Balancing
4. Scheduling Encoding (Chromosome)
This is a 2D matrix of size[no. of processors x size of sliding
window].
Figure: Chromosome Representation
5. Initialization
Population of size POP_SIZE is initialized by randomly assigning
tasks to processors.
P1 P2 P3
3 5 0
4 7 1
8 9 2
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/observationsondagschedulinganddynamic-load-balancingusinggeneticalgorithm-130622021121-phpapp01/85/Observations-on-dag-scheduling-and-dynamic-load-balancing-using-genetic-algorithm-19-320.jpg)