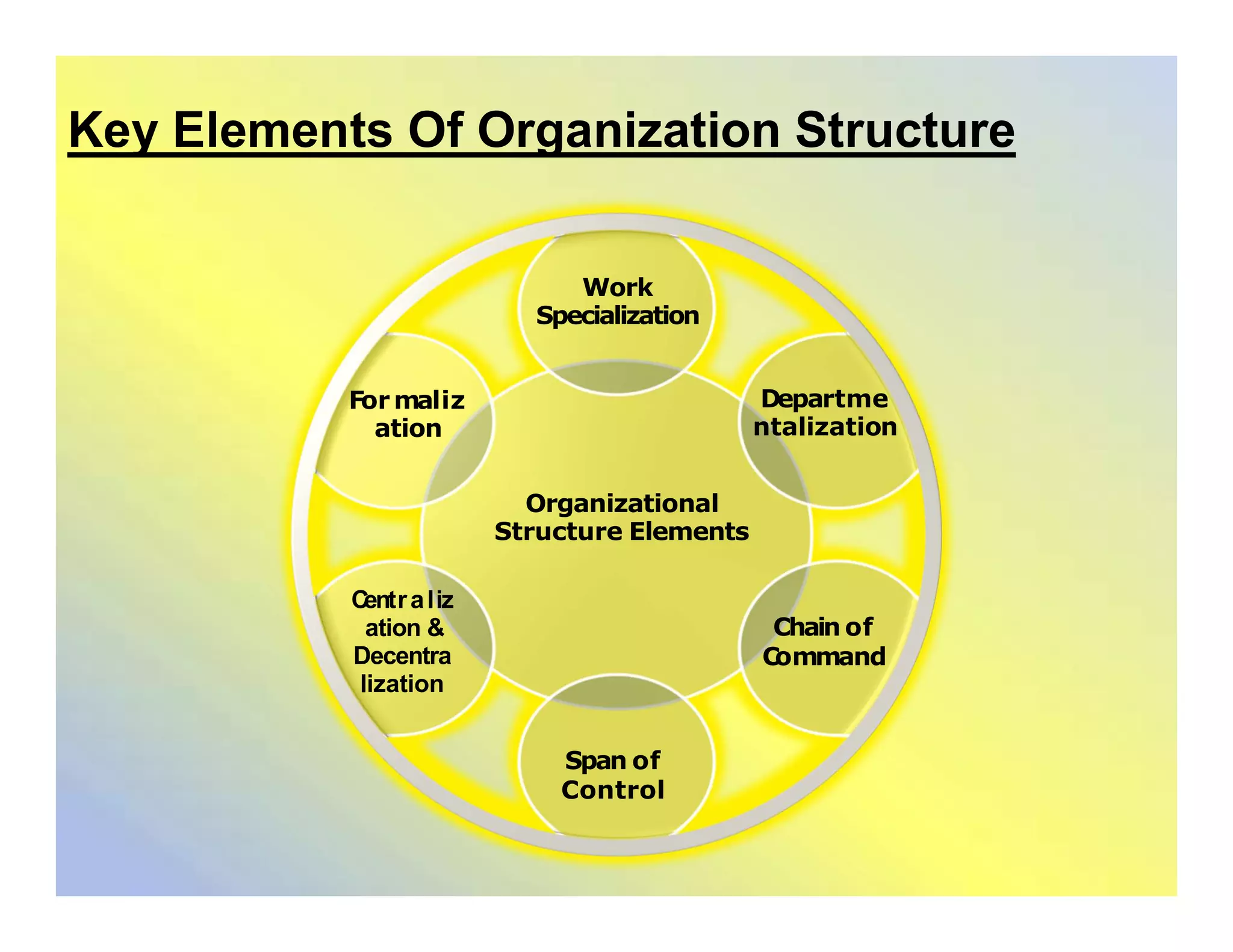
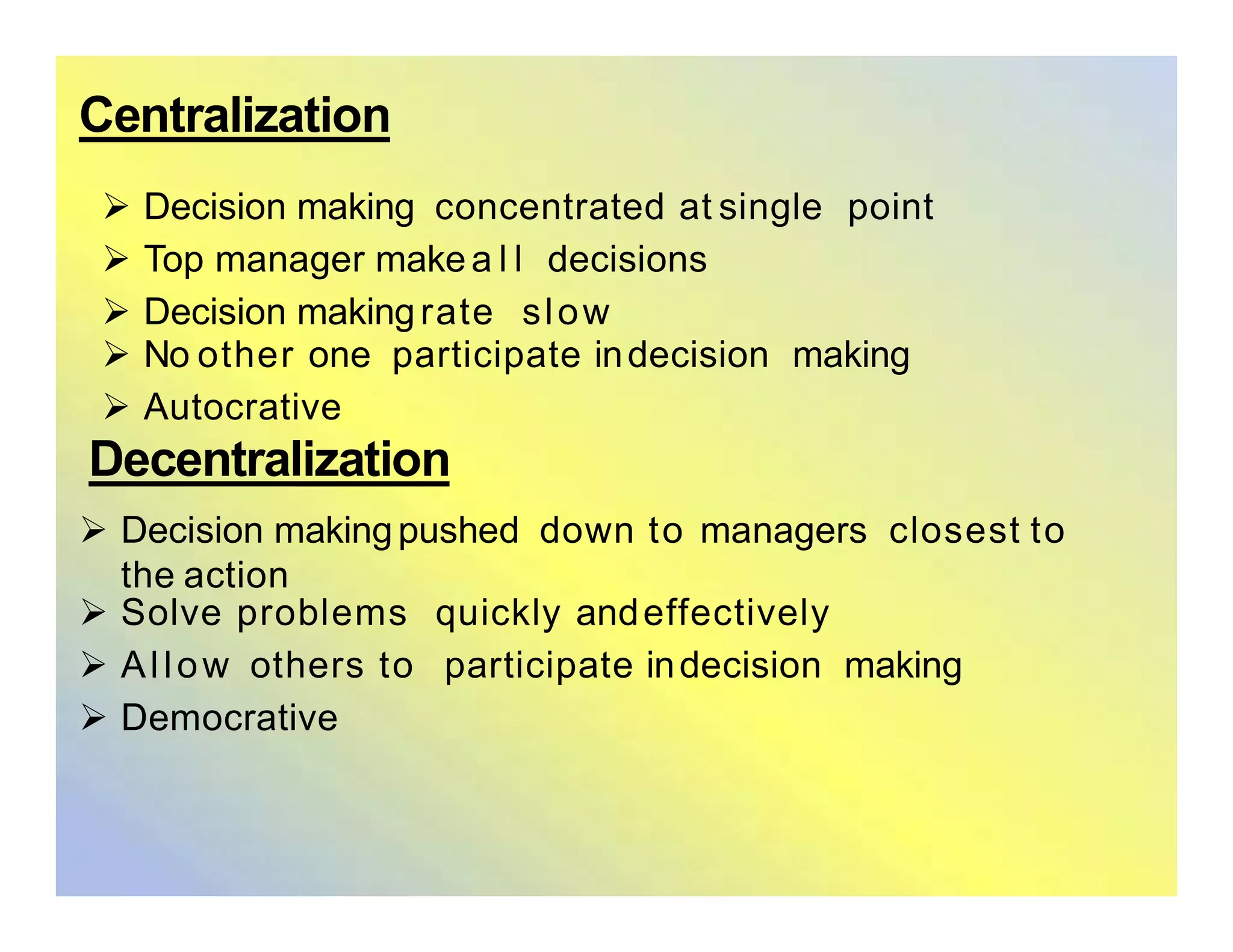
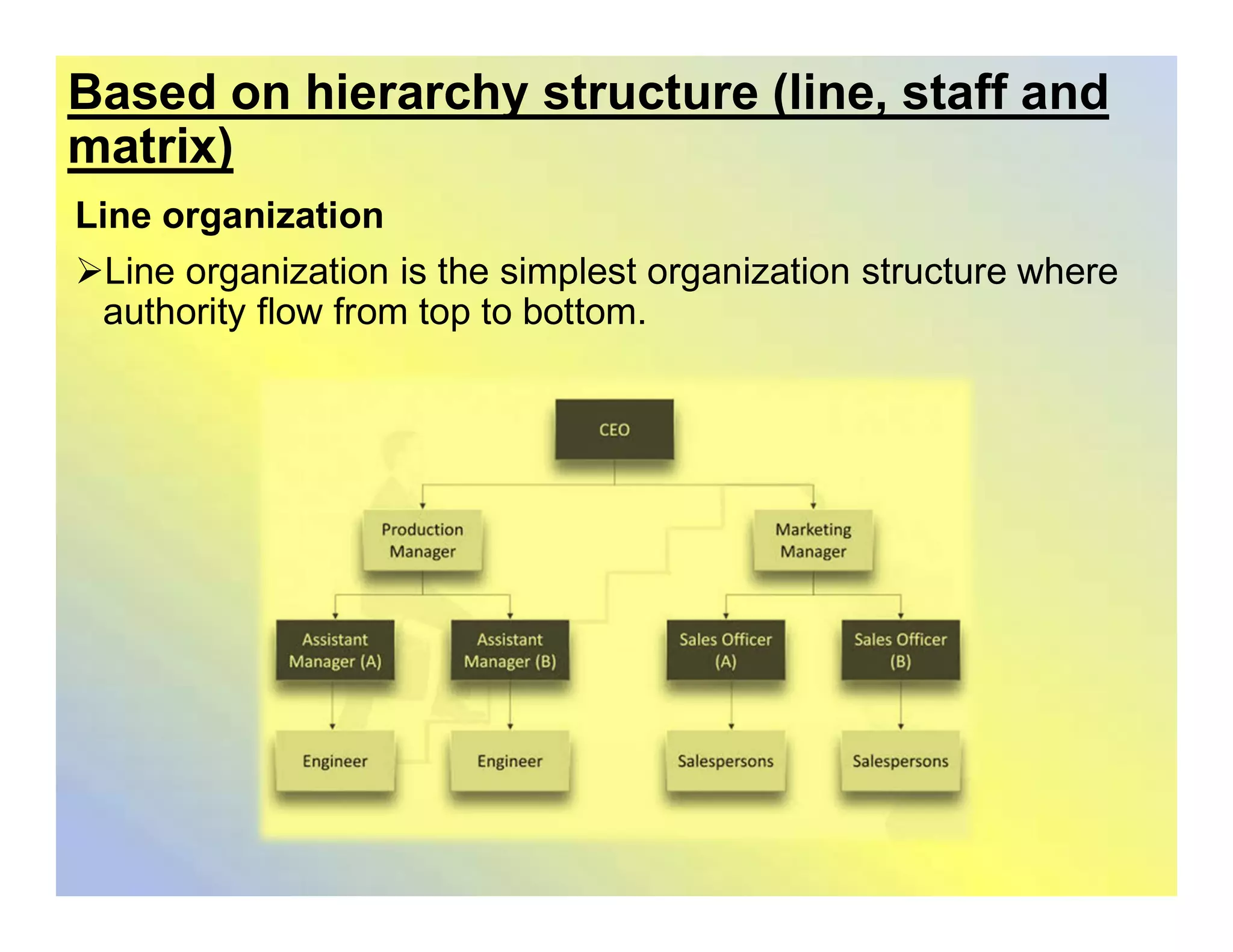
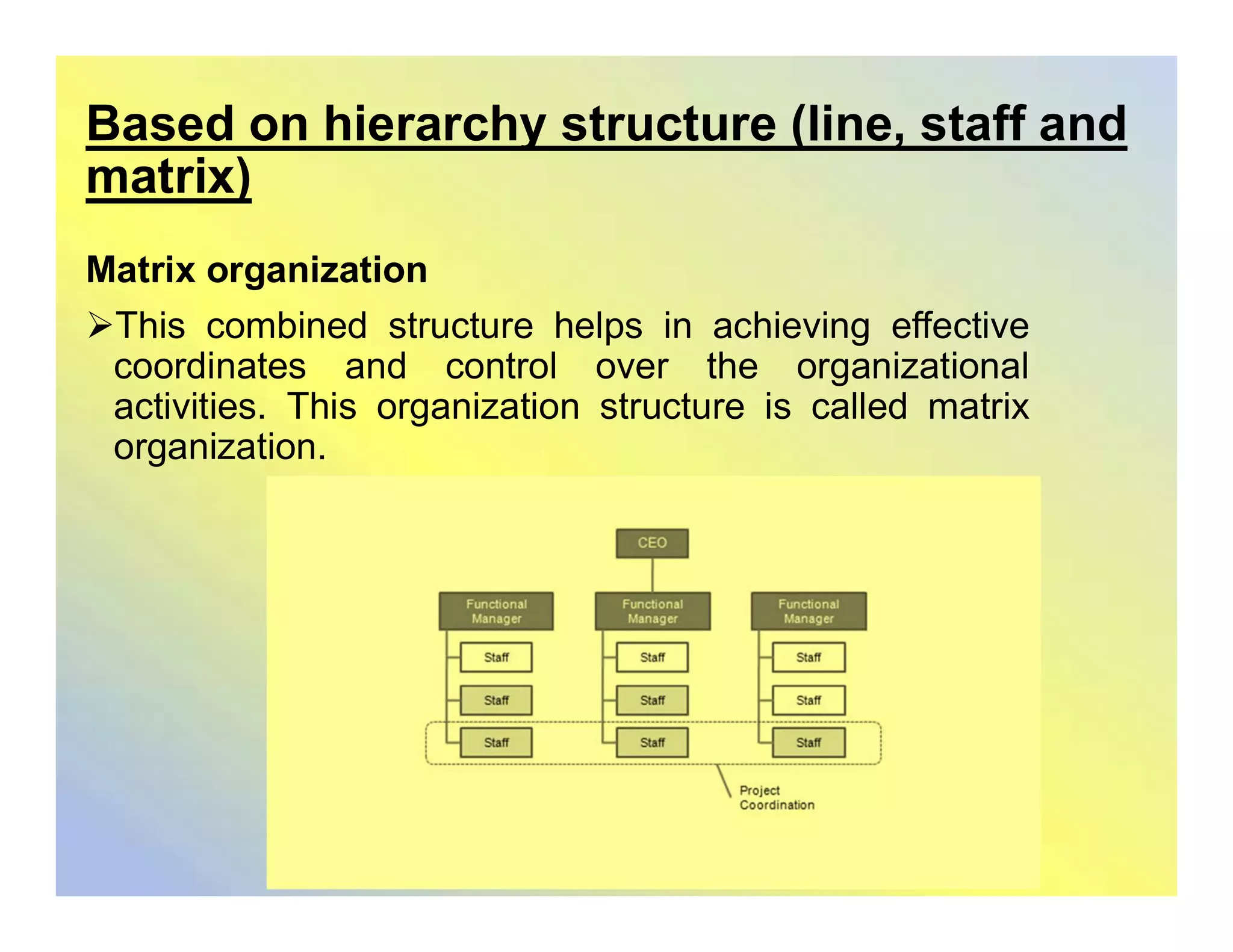
This document discusses organizational structures and group dynamics. It defines organizational structure as how activities are directed to achieve goals. Key elements of structure discussed include work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization/decentralization, and formalization. The document also examines group formation theories and types of groups, both formal and informal. It describes the punctuated equilibrium model of group formation and dynamics of formal work groups.