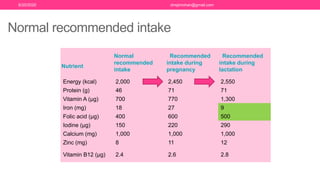
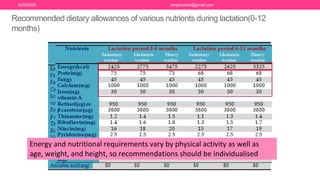
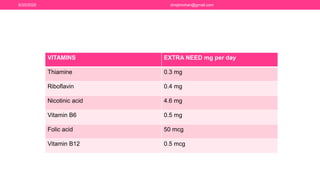
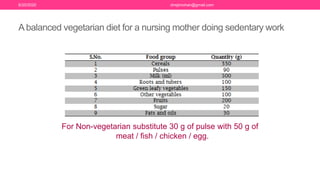
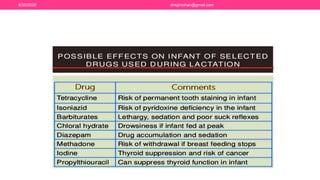
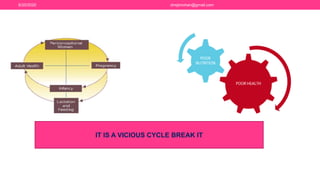
The document discusses nutritional support for breastfeeding mothers and contraindications for breastfeeding. It provides guidelines on the extra calorie and nutrient needs during lactation. These include an additional 300-450 kcal/day during pregnancy and 600 kcal in the first 6 months of lactation. Certain medical conditions like HIV, active tuberculosis, and illnesses with risk of transmission to the infant are contraindications for breastfeeding. Most medications are secreted in breastmilk, so their use during lactation requires careful consideration and medical supervision. Maintaining good nutrition is important for a mother's health and sufficient milk production.