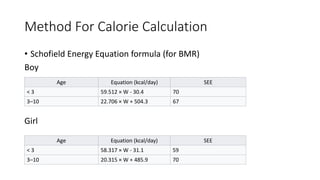
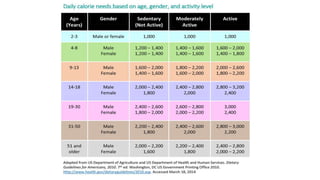
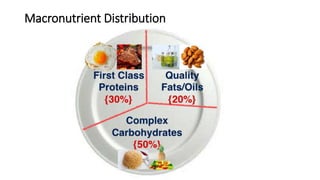
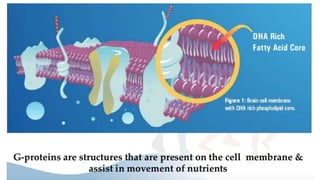
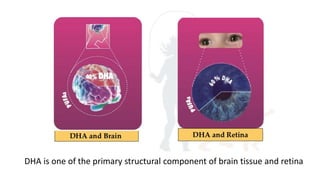
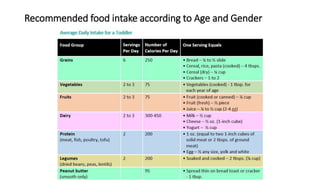
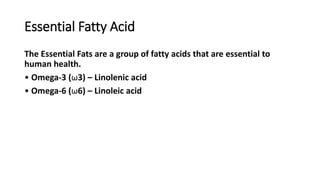This document provides nutrition guidelines for toddlers ages 1 to 3. It discusses calorie needs, which range from 1000-1400 calories per day depending on age, size and activity level. Protein requirements are 1.05 grams per kg per day. Important micronutrients discussed include zinc (RDA 3-5 mg), iron (RDA 7-10 mg), calcium (RDA 700 mg), and vitamin D (RDA 10 mcg or 400 IU). Food sources for these nutrients are provided. The document also discusses essential fatty acids, DHA needs, portion sizes, choking prevention tips, and maintaining a balanced diet for toddlers.