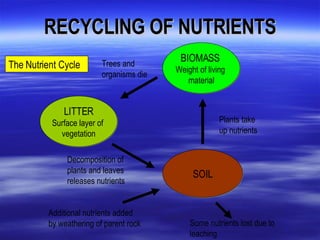
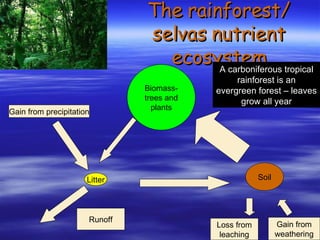
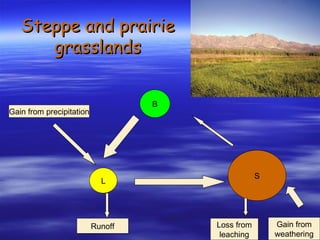
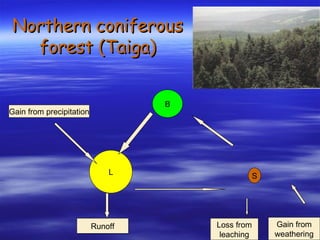
The document discusses nutrient cycles in different ecosystems. Nutrients cycle between biomass, litter, and soil and are gained through precipitation, weathering, and decomposition or lost through leaching and runoff. It specifically examines the nutrient cycles in tropical rainforests, prairies/grasslands, and northern coniferous forests (taiga).