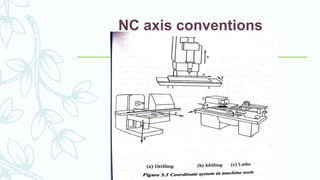
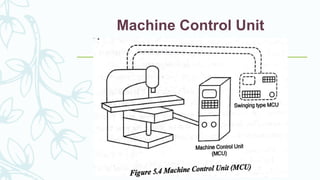
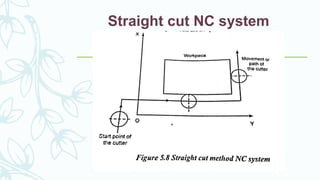
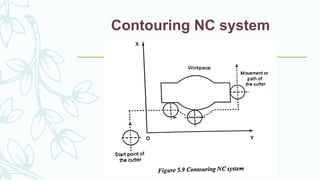
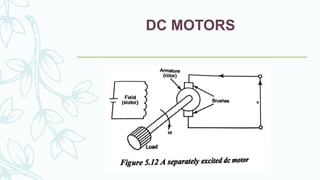
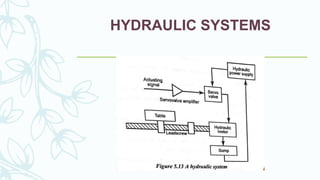
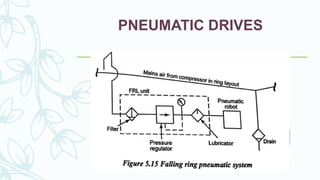
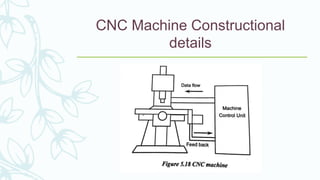
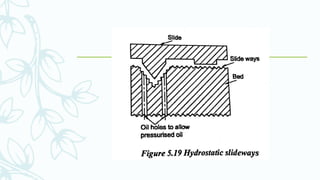
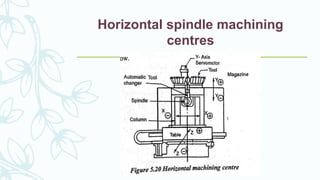
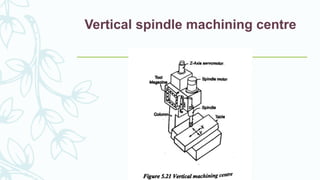
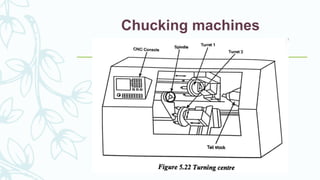
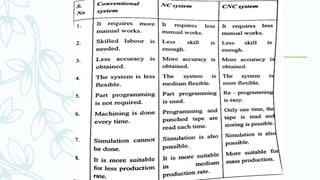
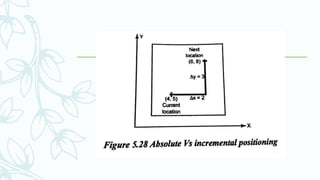
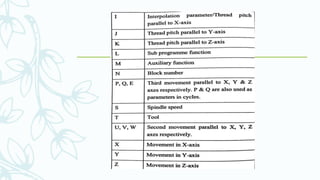
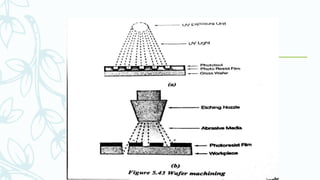
The document provides an overview of numerical control (NC) systems, detailing their types, components, and operational principles, as well as the differences between traditional NC and computer numerical control (CNC) systems. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of NC machines, various tooling systems, and the programming methods used to control these machines. Additionally, it covers the applications of NC machines in different industries, along with the concepts of part programming and micromachining techniques.