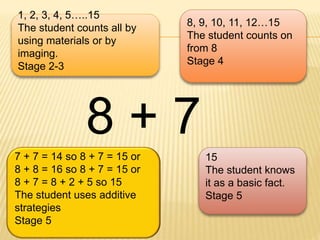
This document discusses key changes in how mathematics is taught today including multi-level teaching to meet different needs, small group teaching, and encouraging the use of equipment like fingers. It defines numeracy as involving number knowledge and mental strategies. It outlines the different numeracy stages children progress through and provides examples of word problems to show how children at different stages would solve them. Finally, it provides tips for supporting children's math learning at home through positive engagement, everyday activities, and interactive games.