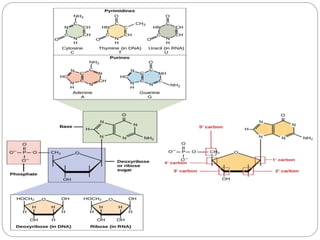
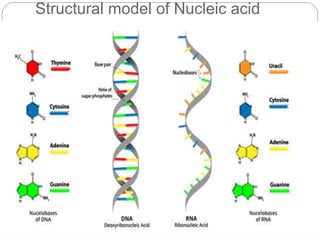
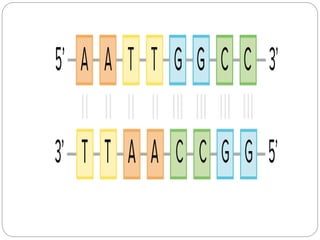
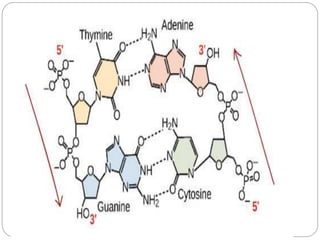
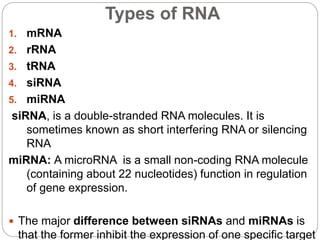
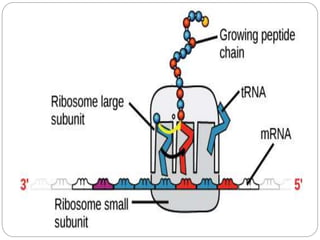
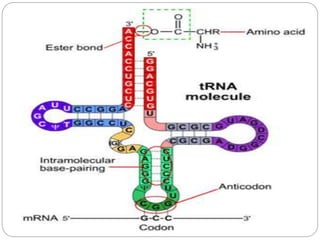
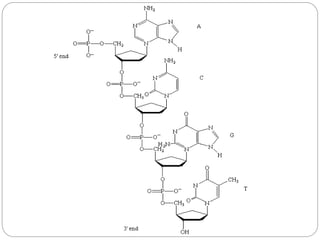
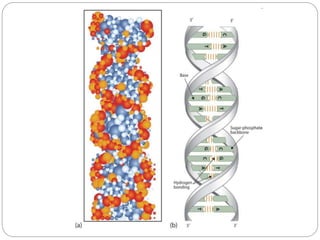
Nucleic acids are polymers found in cell nuclei that can be broken down into monomers called nucleotides. The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic material found in cells and organisms. It exists in various forms within cells and organisms. RNA also exists in several types that play important roles in gene expression and regulation. Nucleic acids have a primary structure defined by their sequence of nucleotides, and DNA exhibits a characteristic secondary structure as a double helix modelled by Watson and Crick.