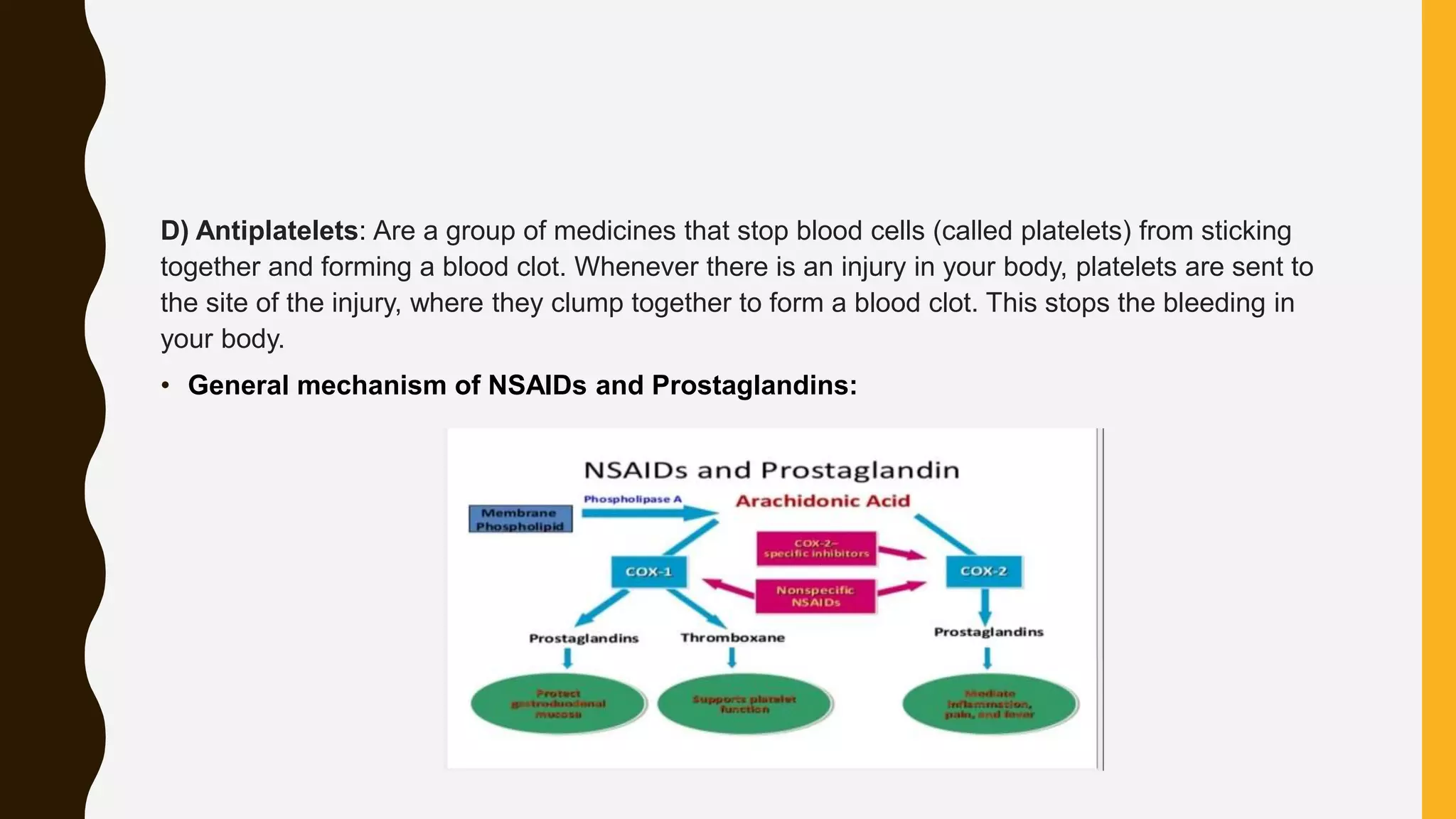
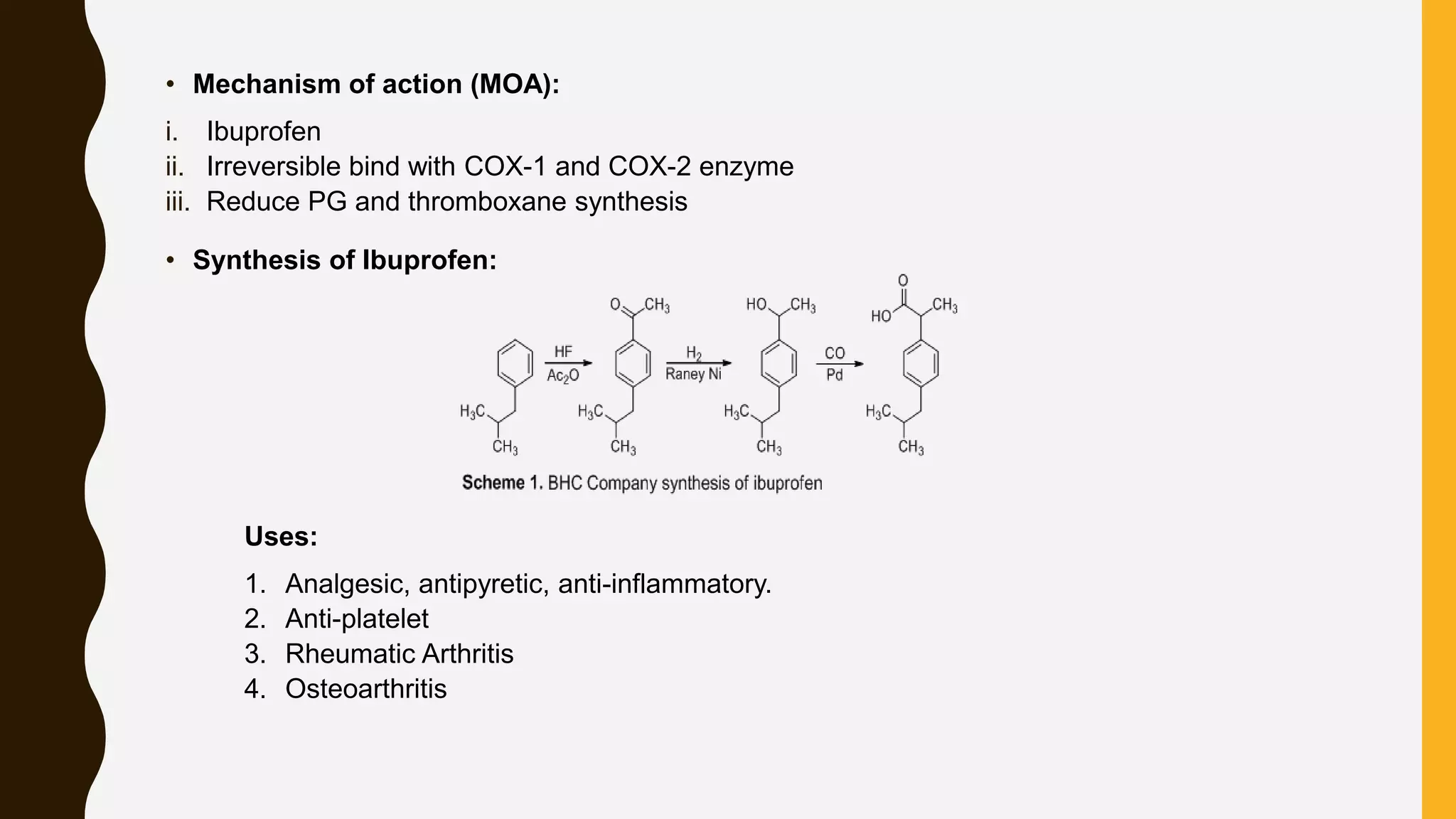
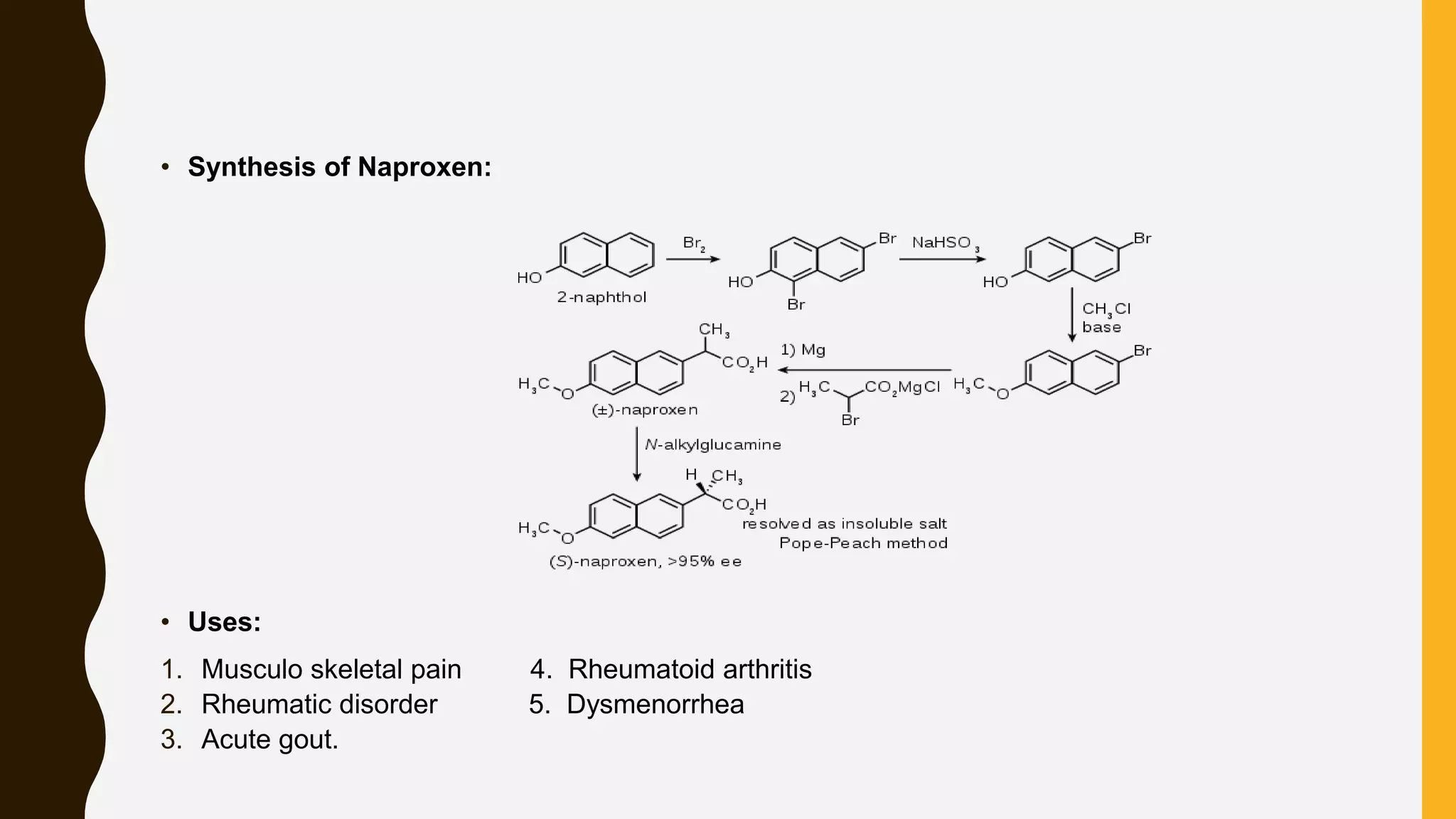
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications used to reduce pain, inflammation, and fever, including categories such as analgesics, antipyretics, anti-inflammatories, and antiplatelets. Common NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, each having specific mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. The document outlines the classification, structure-activity relationships, mechanisms of action, and synthesis processes for several NSAIDs.