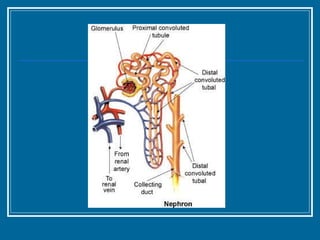
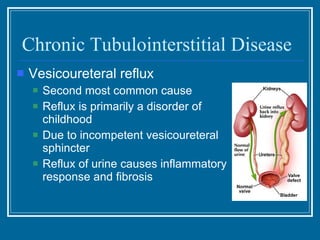
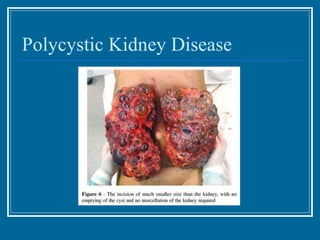
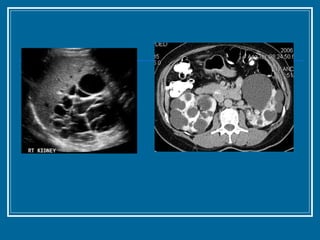
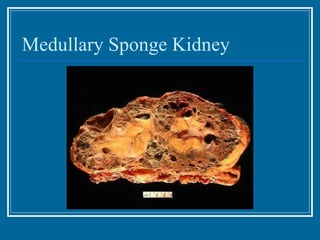
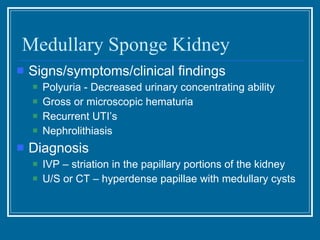
Tubulointerstitial nephropathy can be acute or chronic and is characterized by inflammation and scarring of the kidney tubules and surrounding tissue. Acute causes are often toxins or ischemia while chronic causes include obstructive uropathy, vesicoureteral reflux, analgesics, and heavy metals. Polycystic kidney disease is a common hereditary condition where numerous cysts develop in the kidneys, often leading to end-stage renal disease. Medullary sponge kidney is a benign condition present from birth that causes kidney cysts and issues like hematuria, urinary tract infections, and kidney stones.