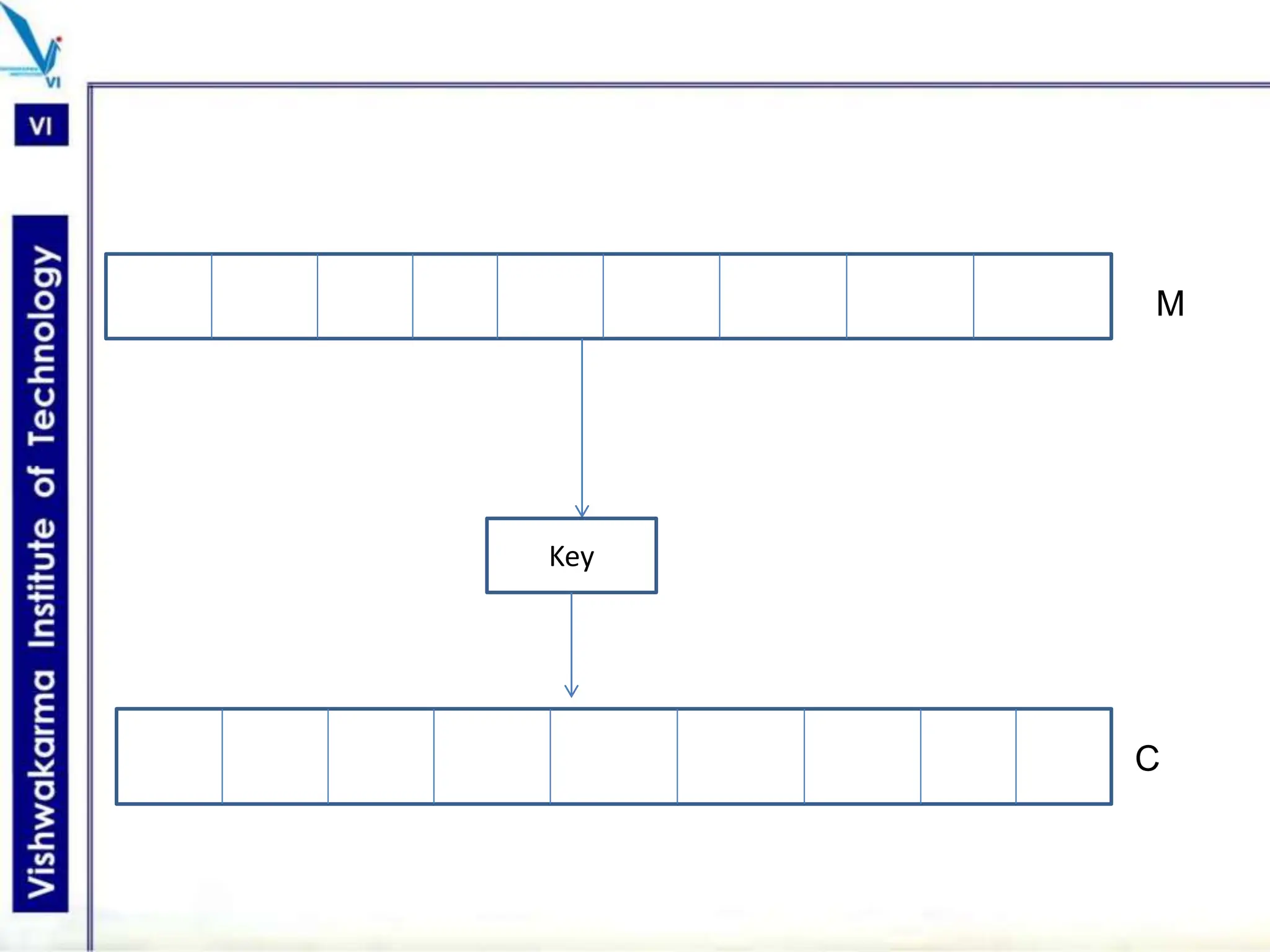
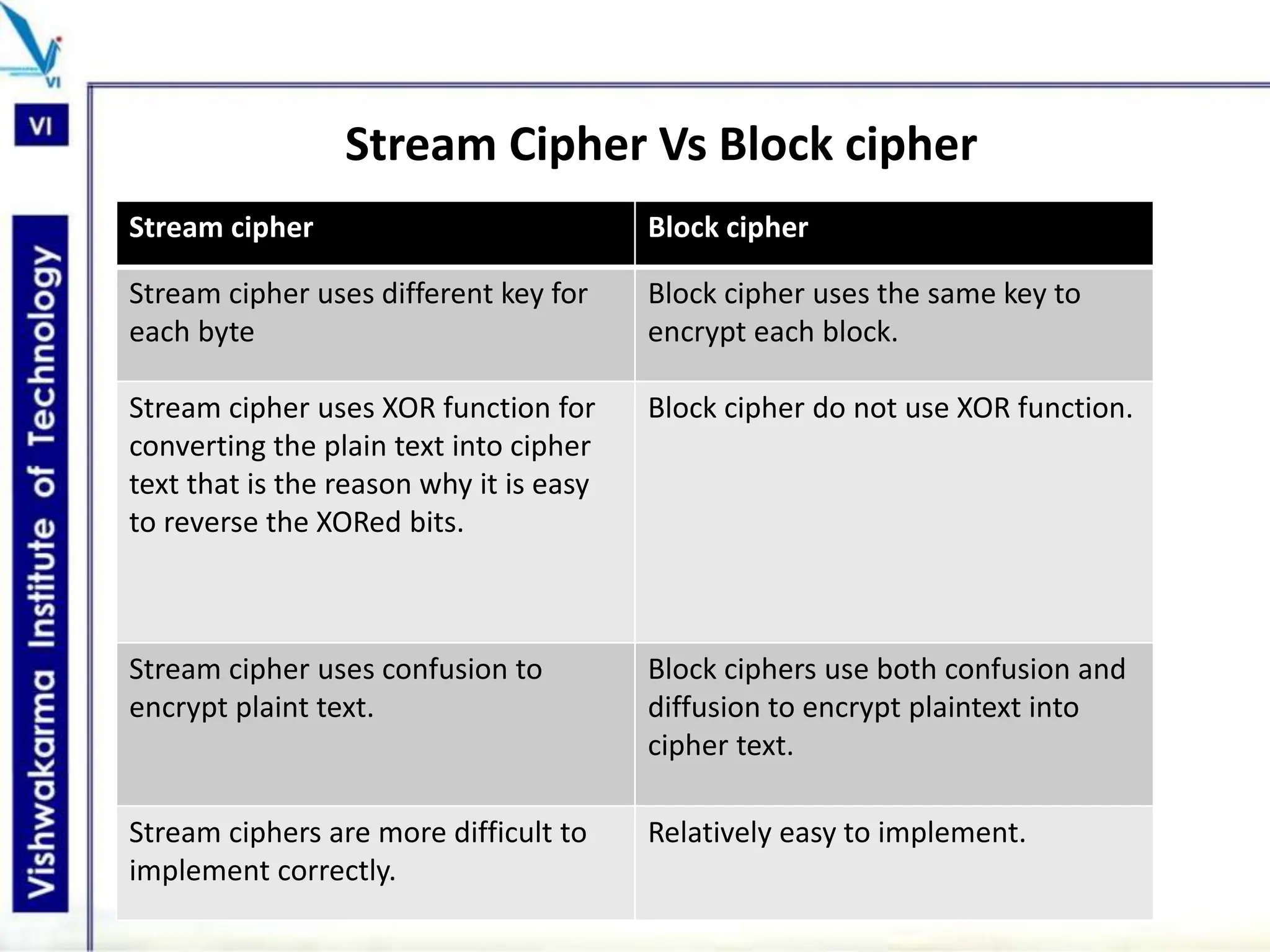
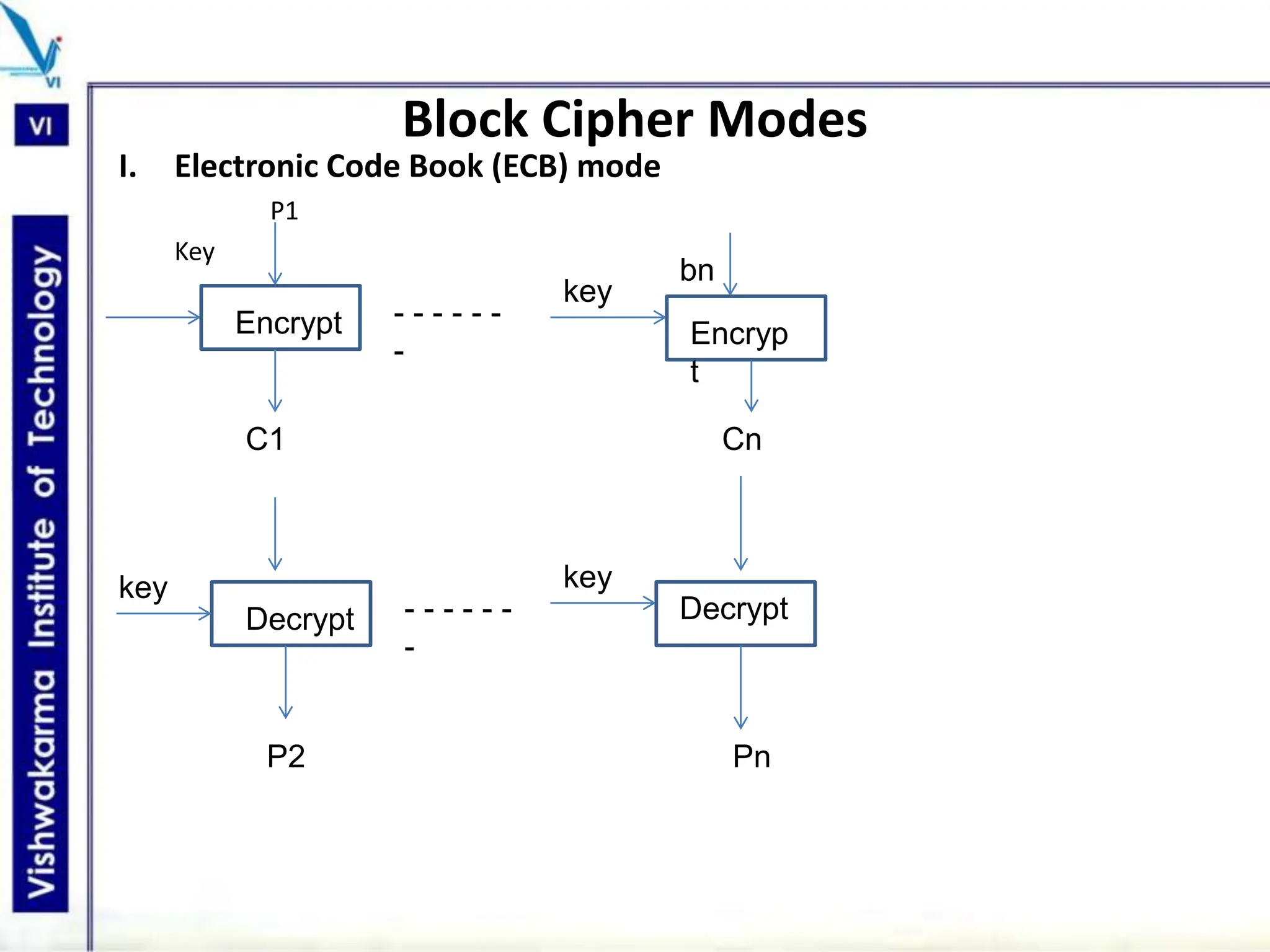
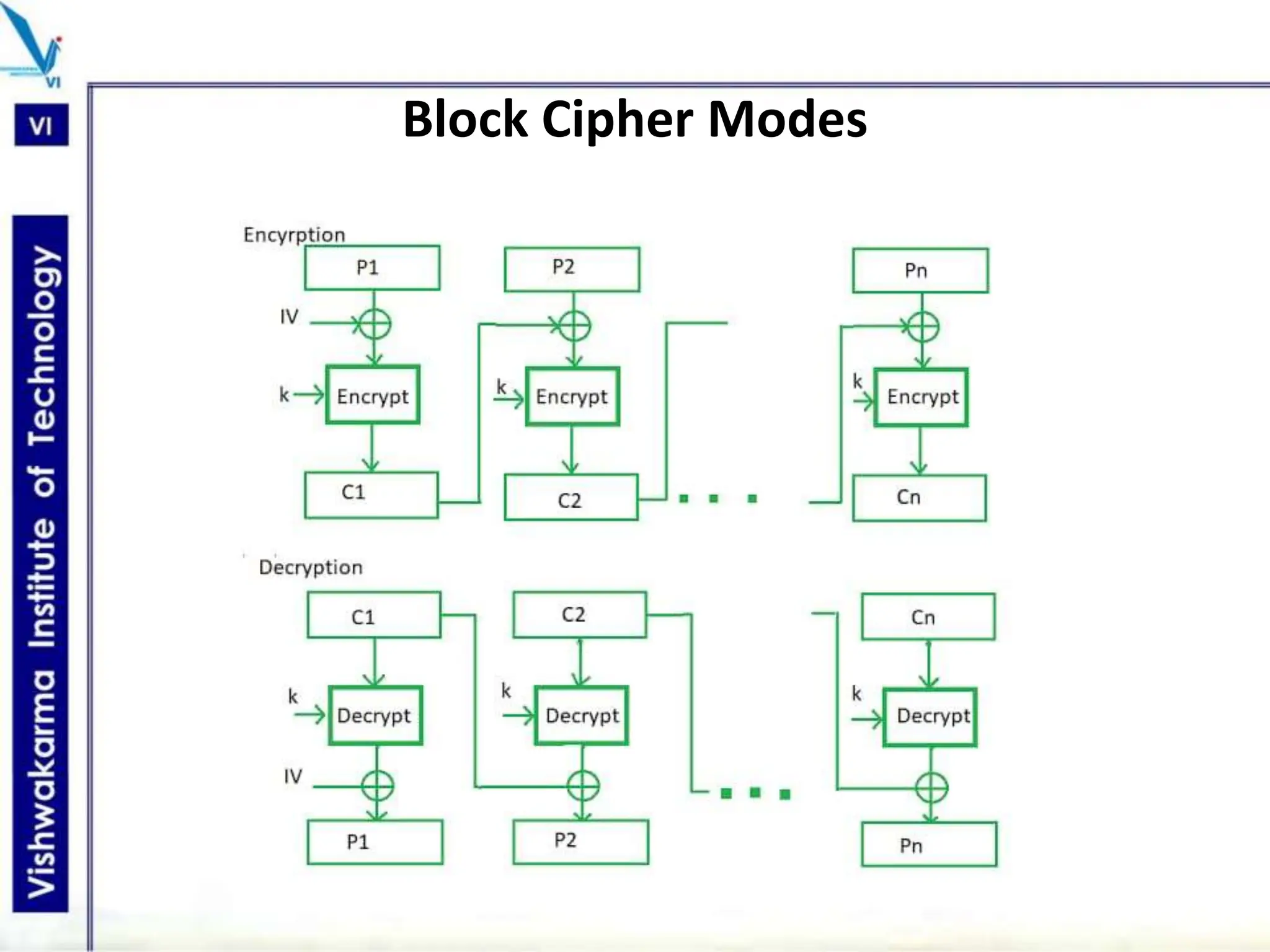
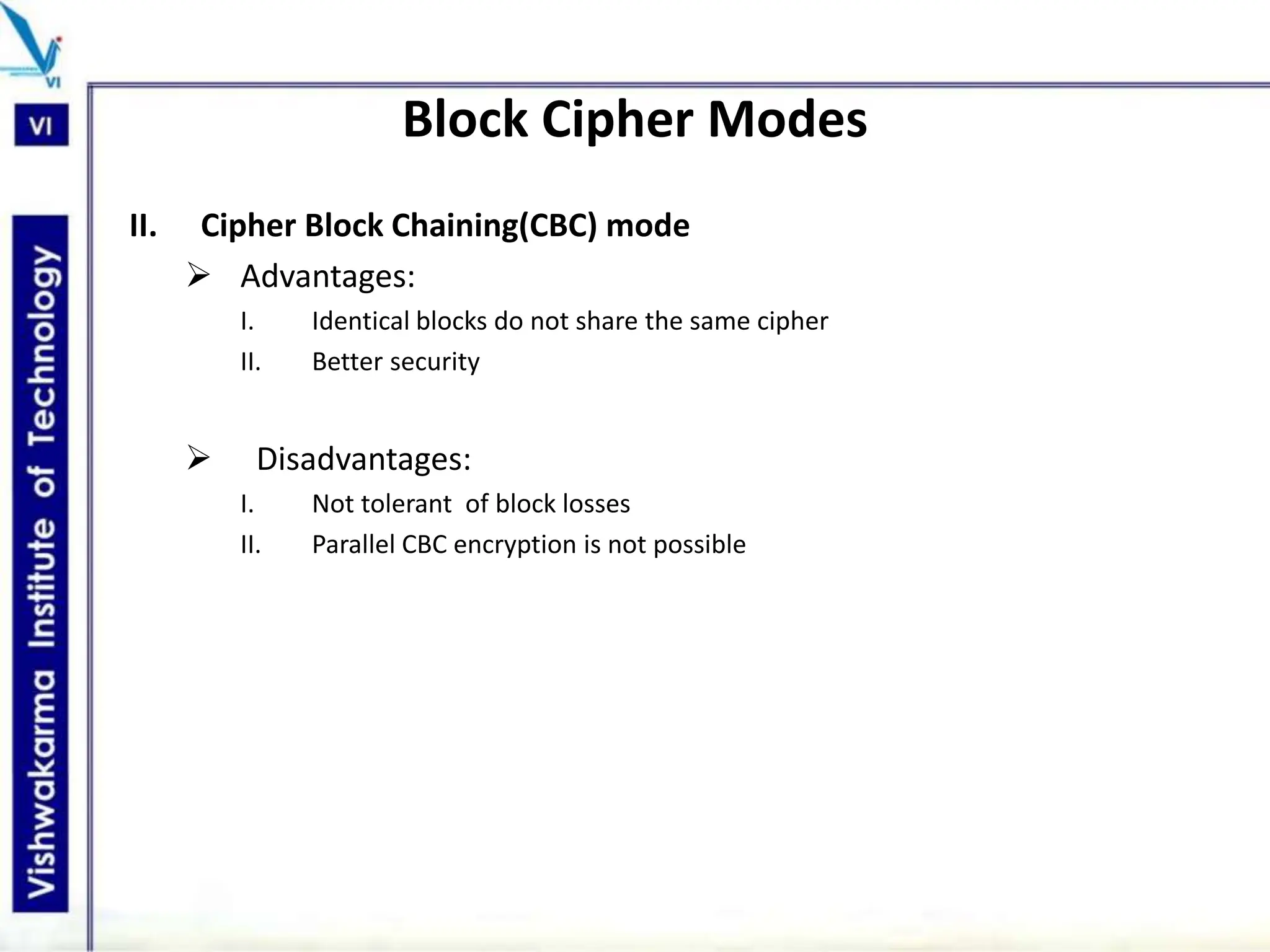
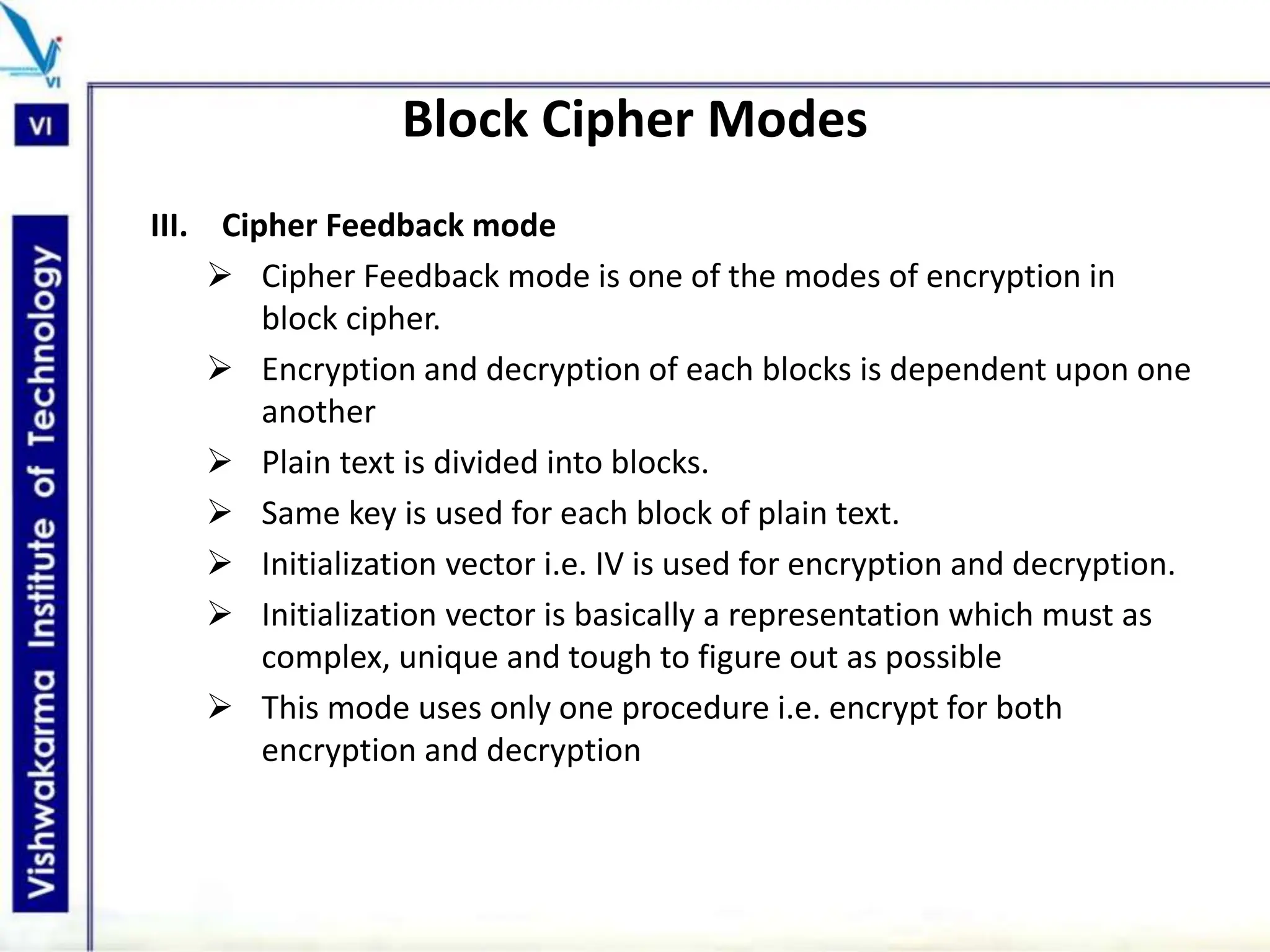
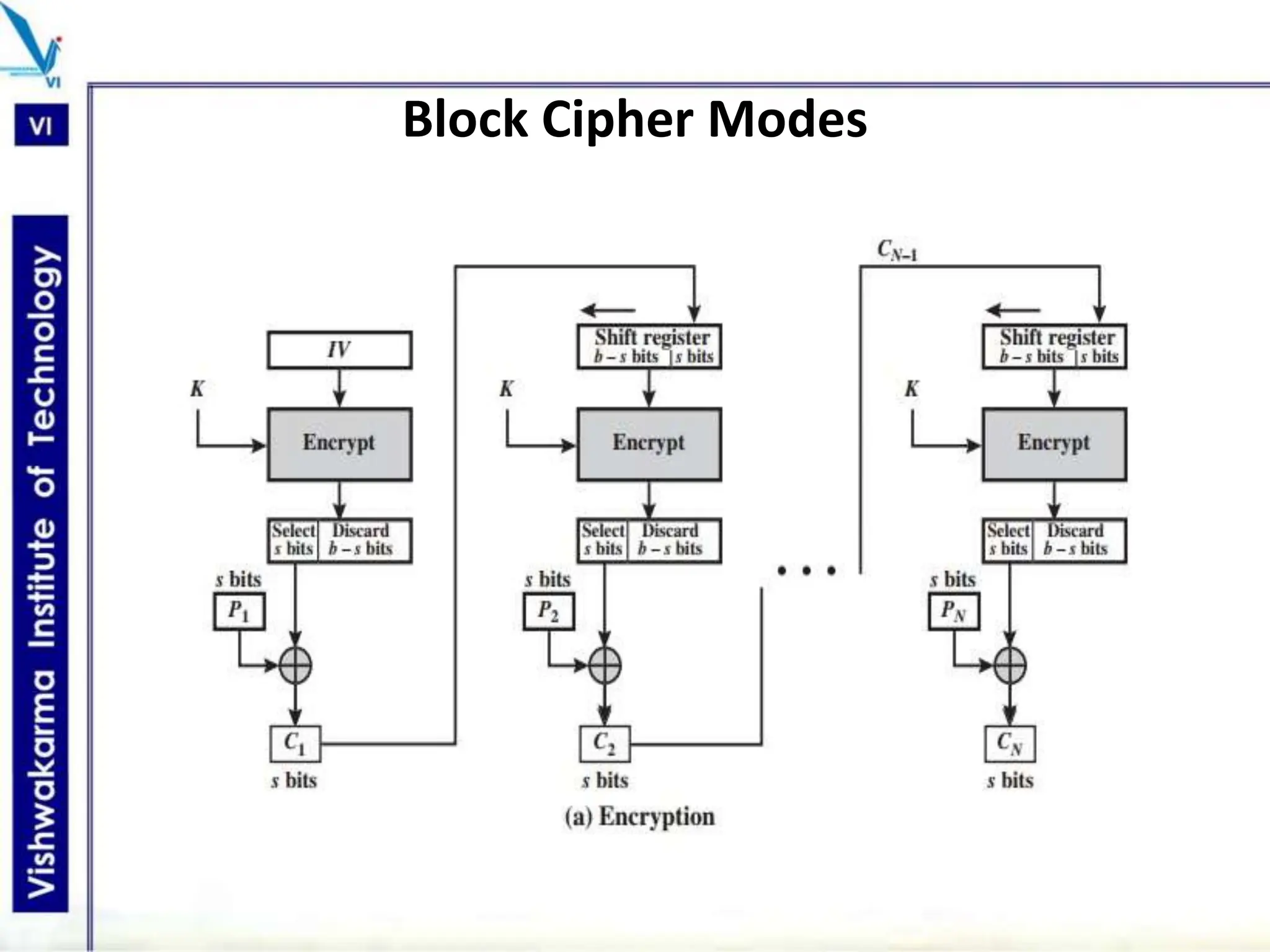
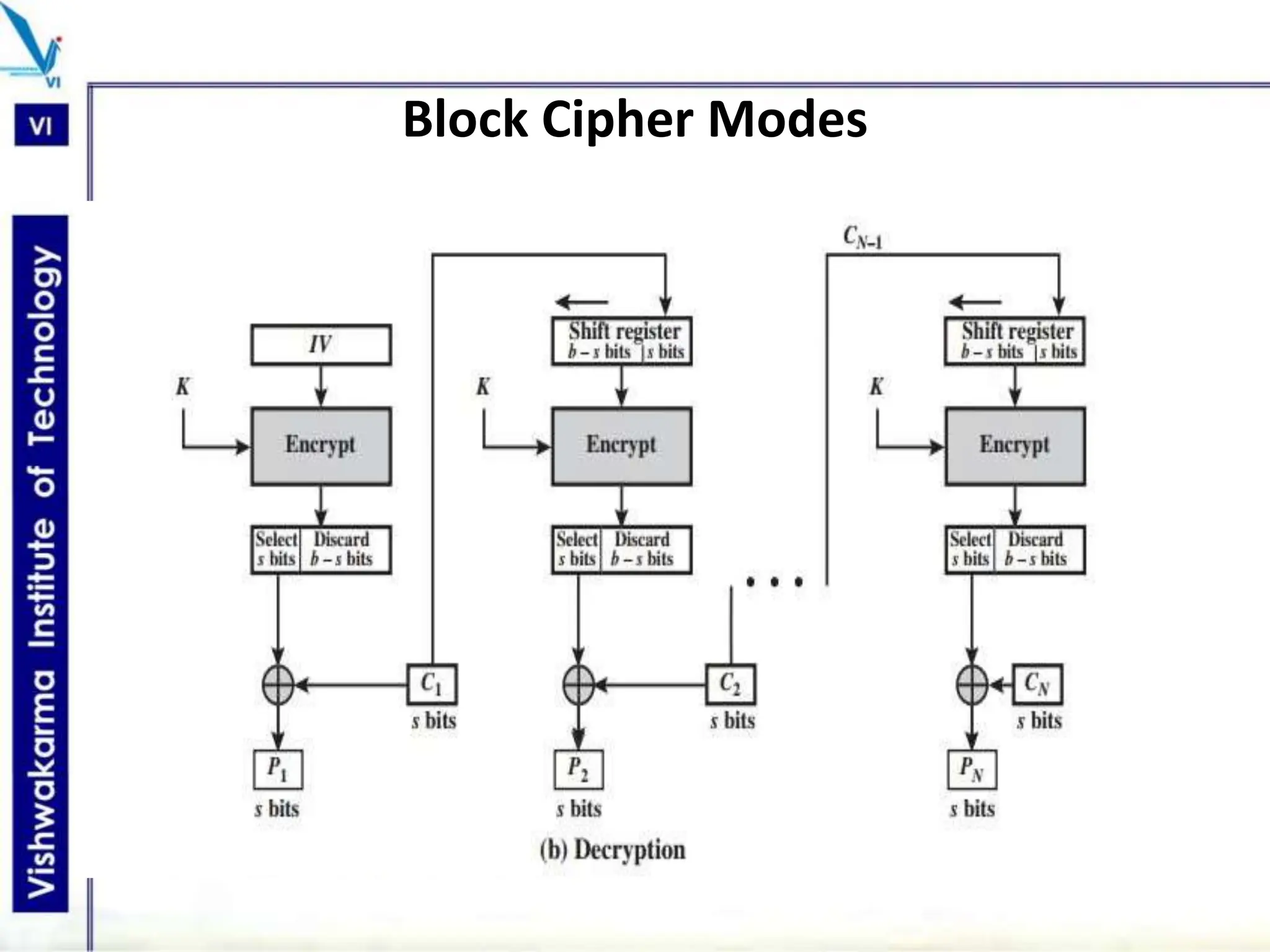
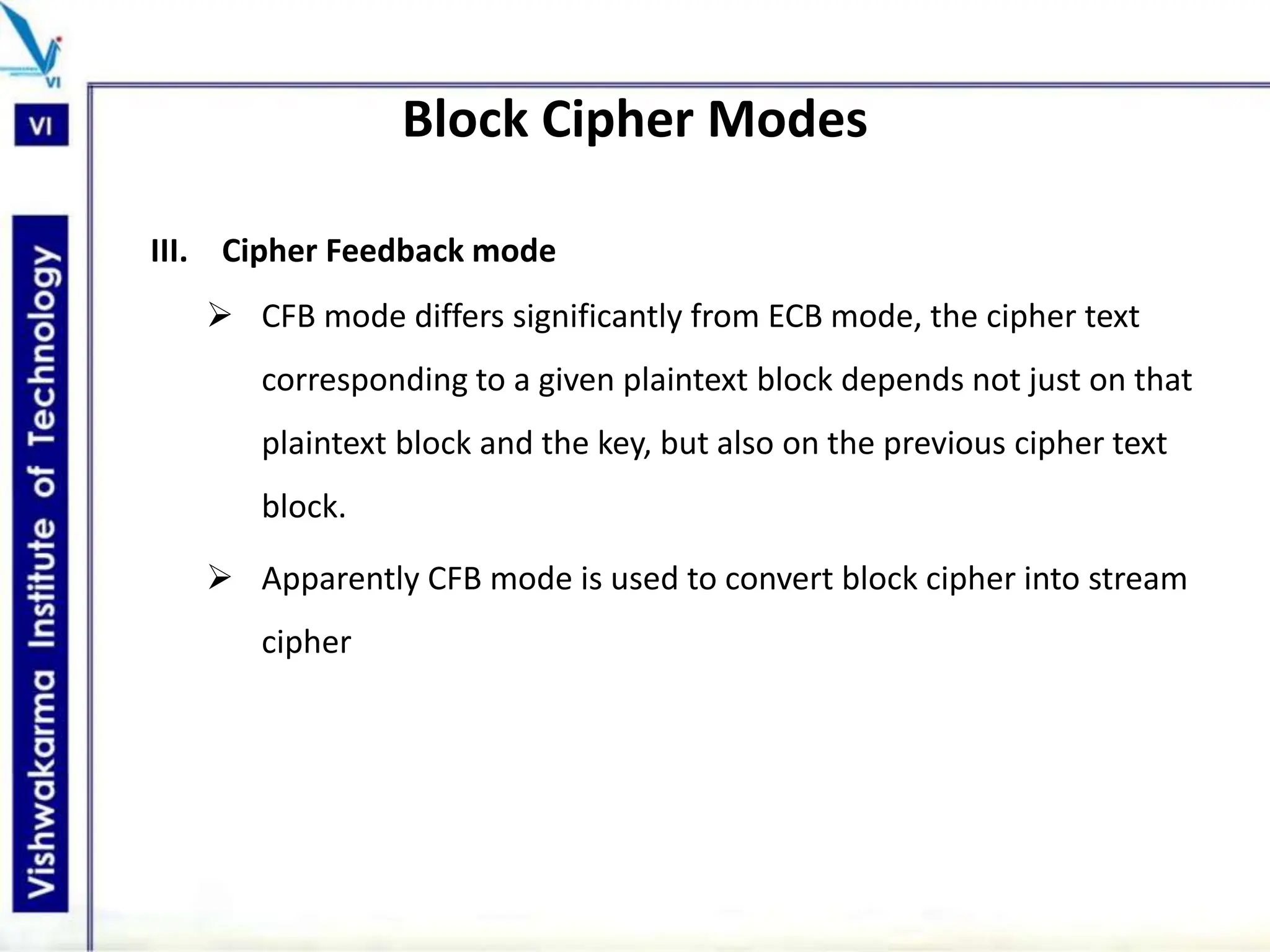
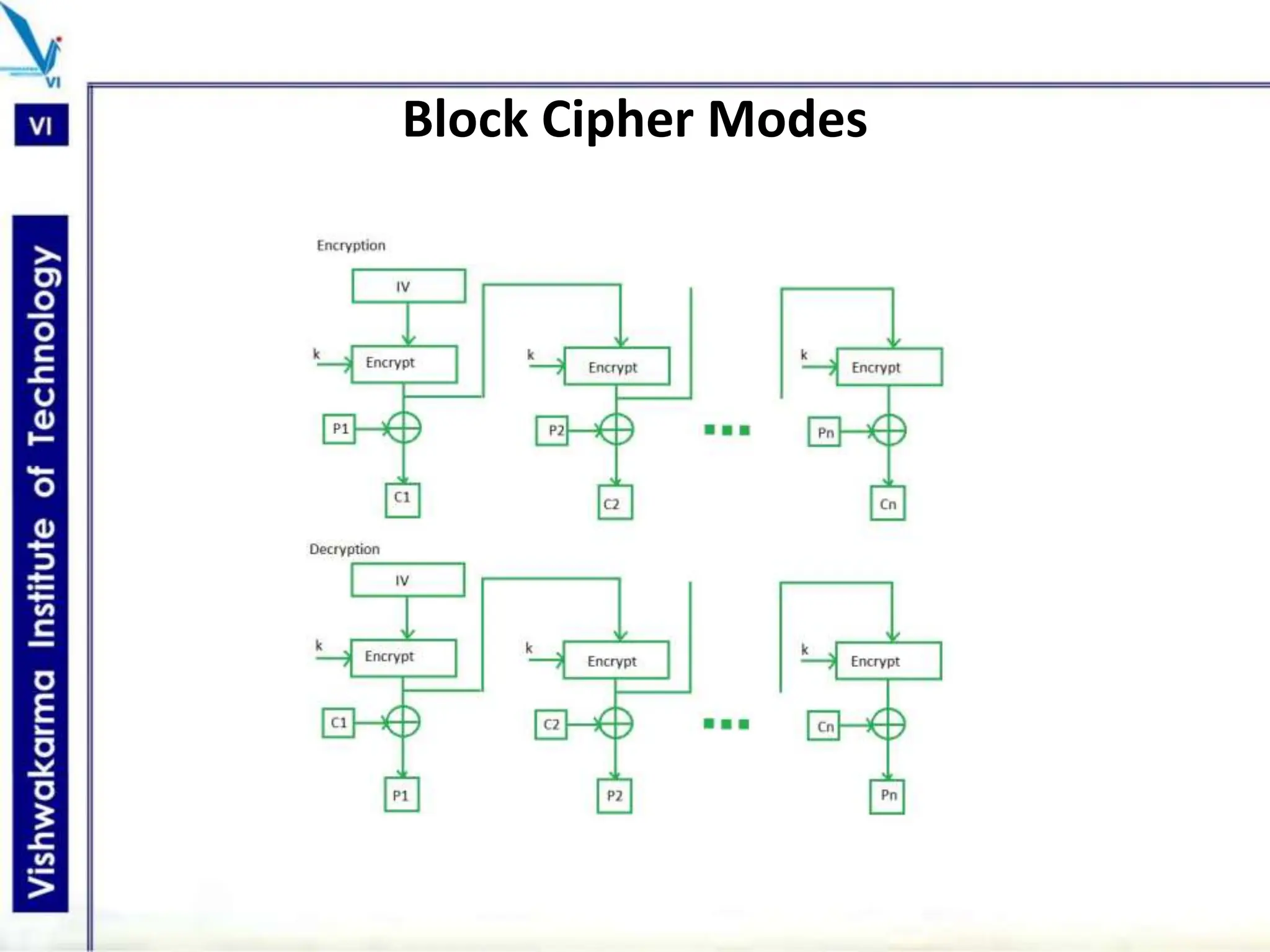
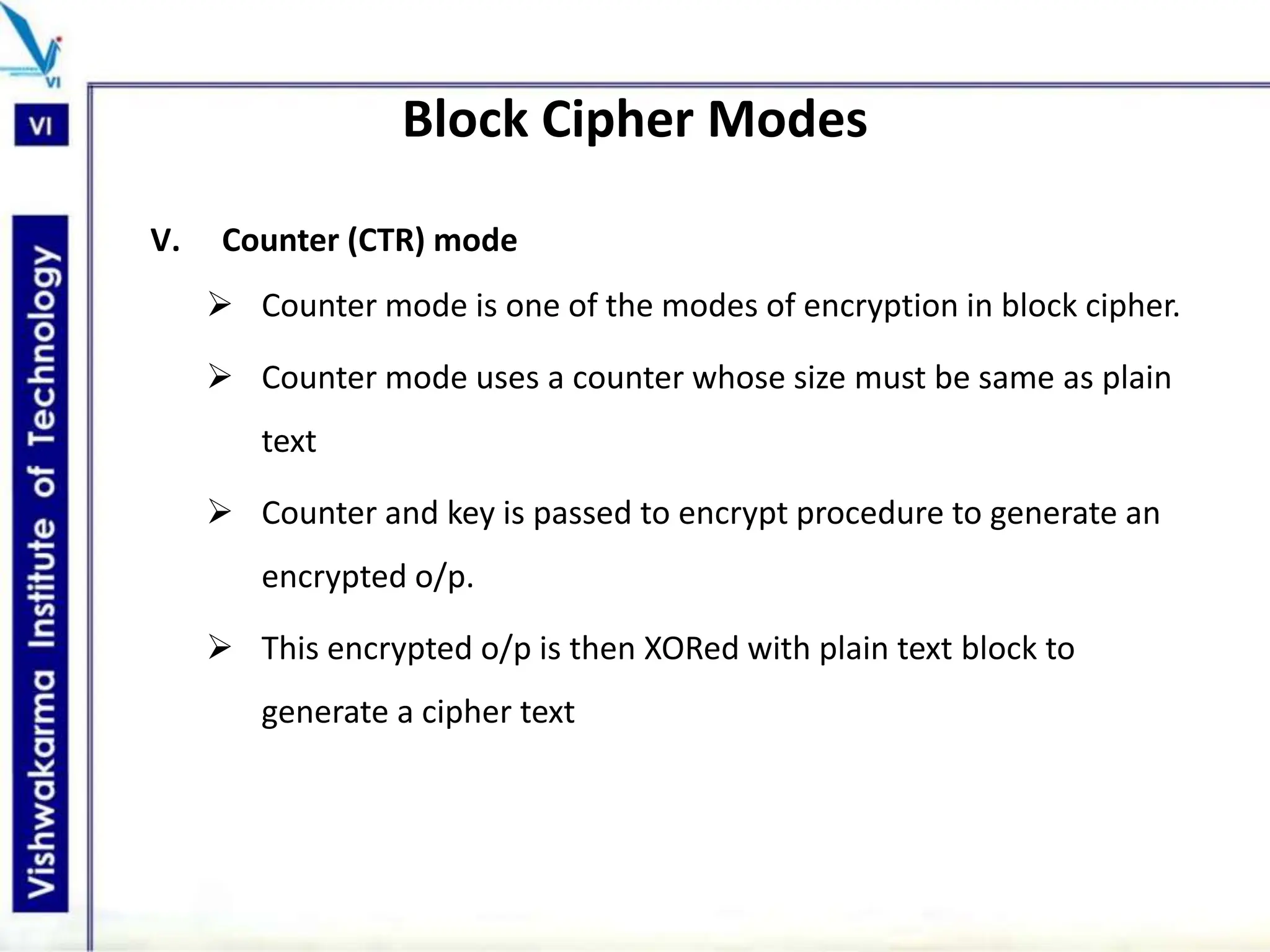
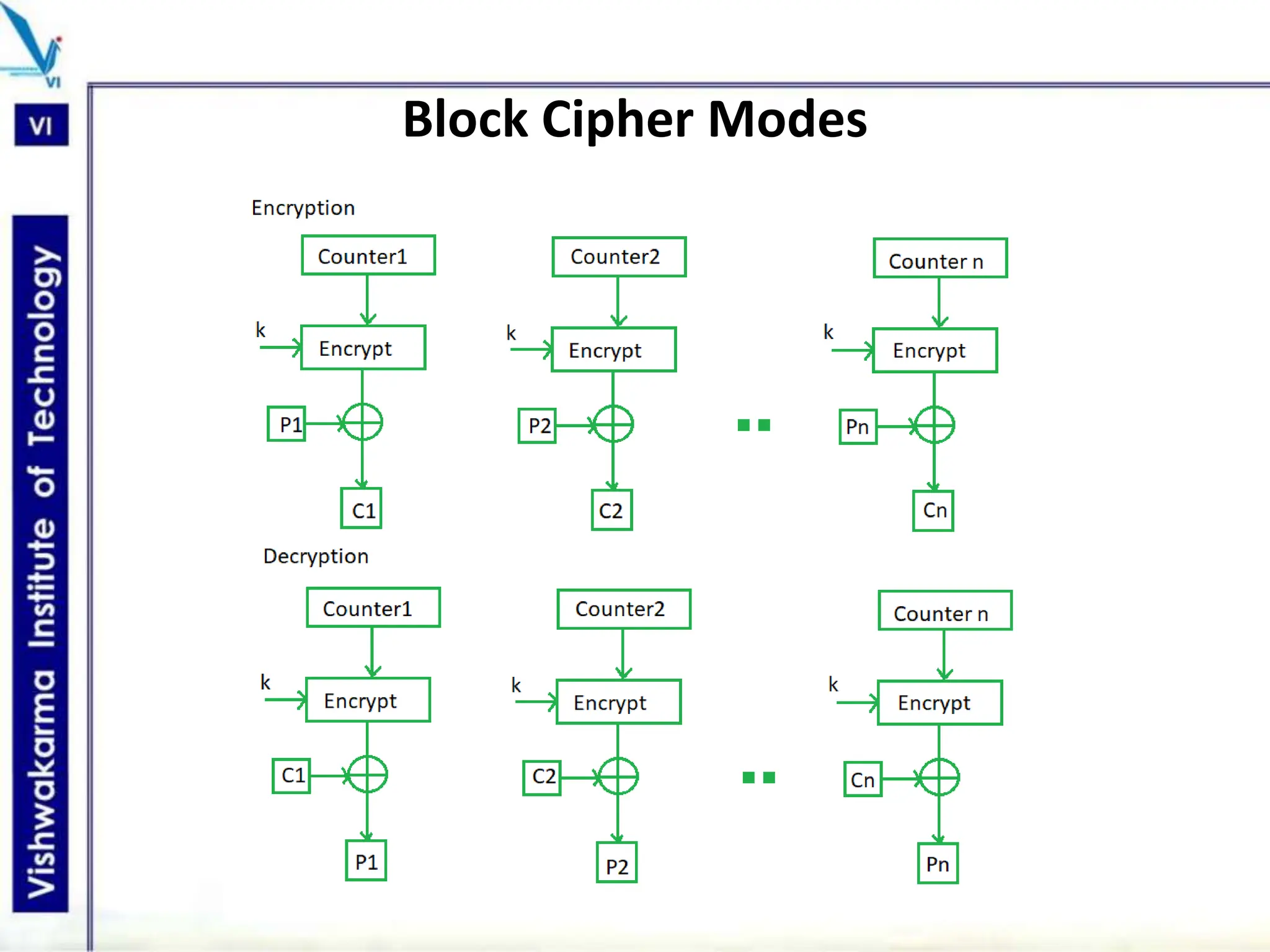
The document discusses block ciphers, a data encryption method that encrypts data divided into blocks using a symmetric key, comparing it with stream ciphers. It outlines various block cipher modes such as Electronic Code Book (ECB), Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Cipher Feedback (CFB), Output Feedback (OFB), and Counter (CTR) modes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The conclusion emphasizes the operational efficiency and use of different modes in converting block cipher into stream cipher, showcasing the versatility of the block cipher technique.