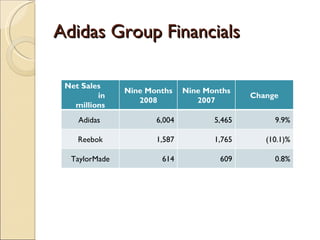
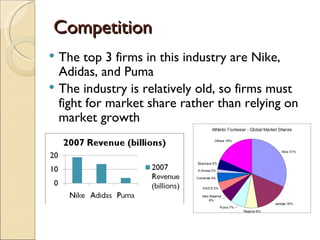
This document provides an analysis of the sports footwear and apparel industry, with a focus on Nike Corporation. It defines the industry as operating within sports footwear and apparel and discusses Nike's expansion beyond running shoes into a wide range of sports and leisure wear. The document also examines Nike's largest competitor Adidas Group, industry structure factors like threats of new entrants and substitutes, and how the industry and Nike are impacted by economic, social, and technological changes.