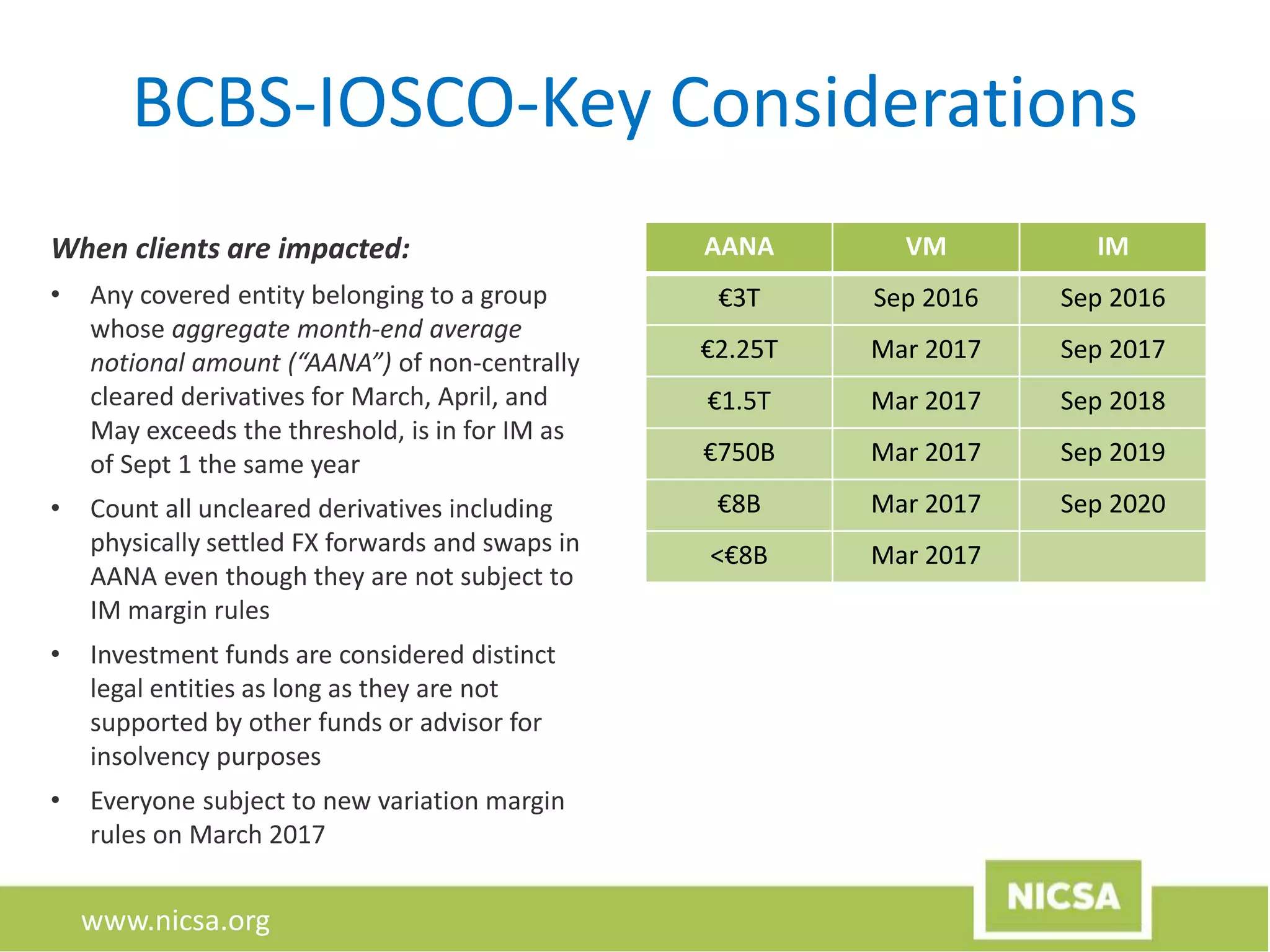
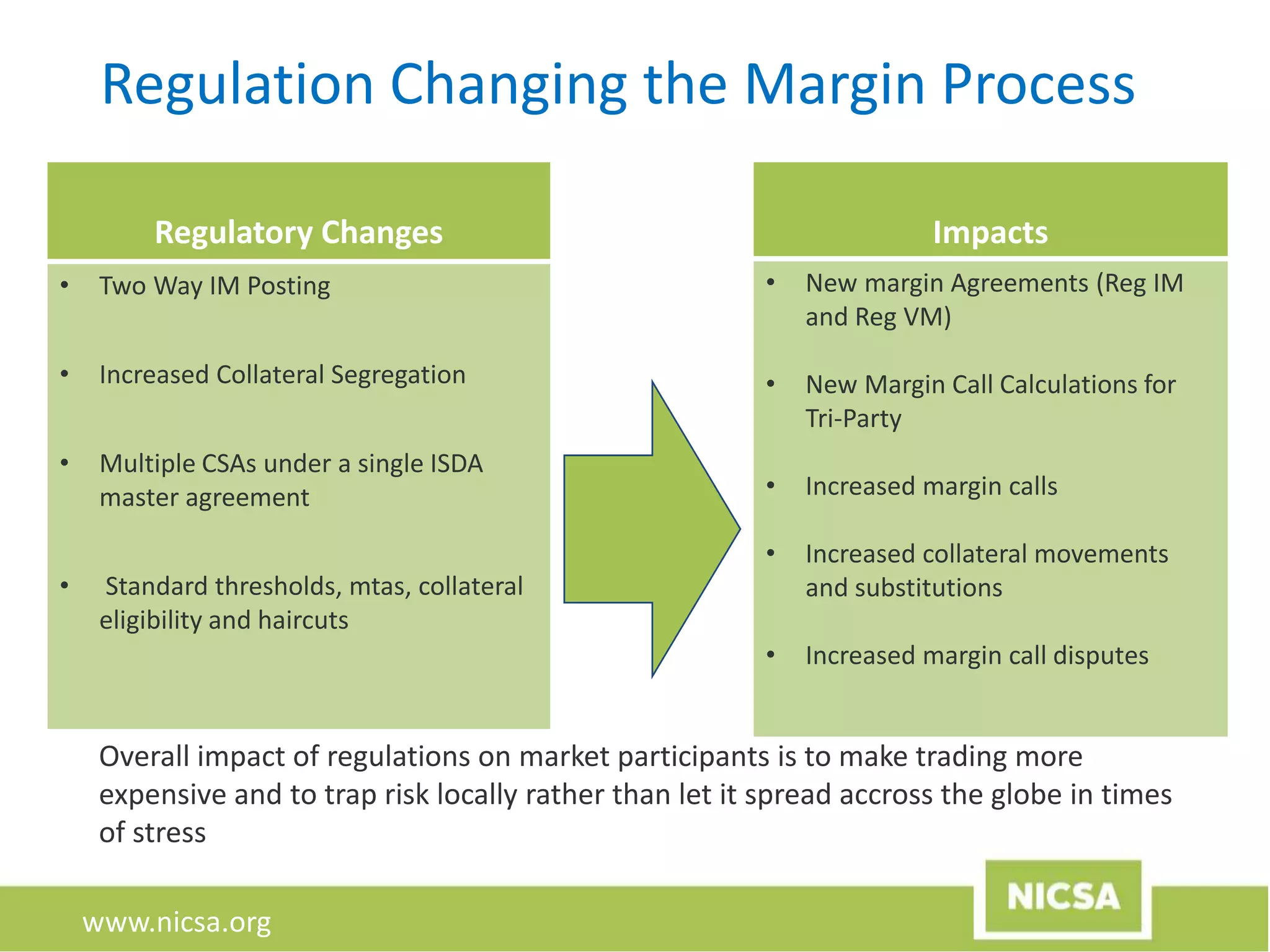
The document discusses the evolution of collateral management, focusing on its importance in the context of recent regulatory changes following the 2008 financial crisis. Key topics include margin call management, data requirements, and the impact of G20 regulations aimed at reducing systemic risk in OTC derivatives. The document highlights the introduction of initial and variation margin requirements, alongside the industry's response through standards and processes to ensure compliance and mitigate disputes.