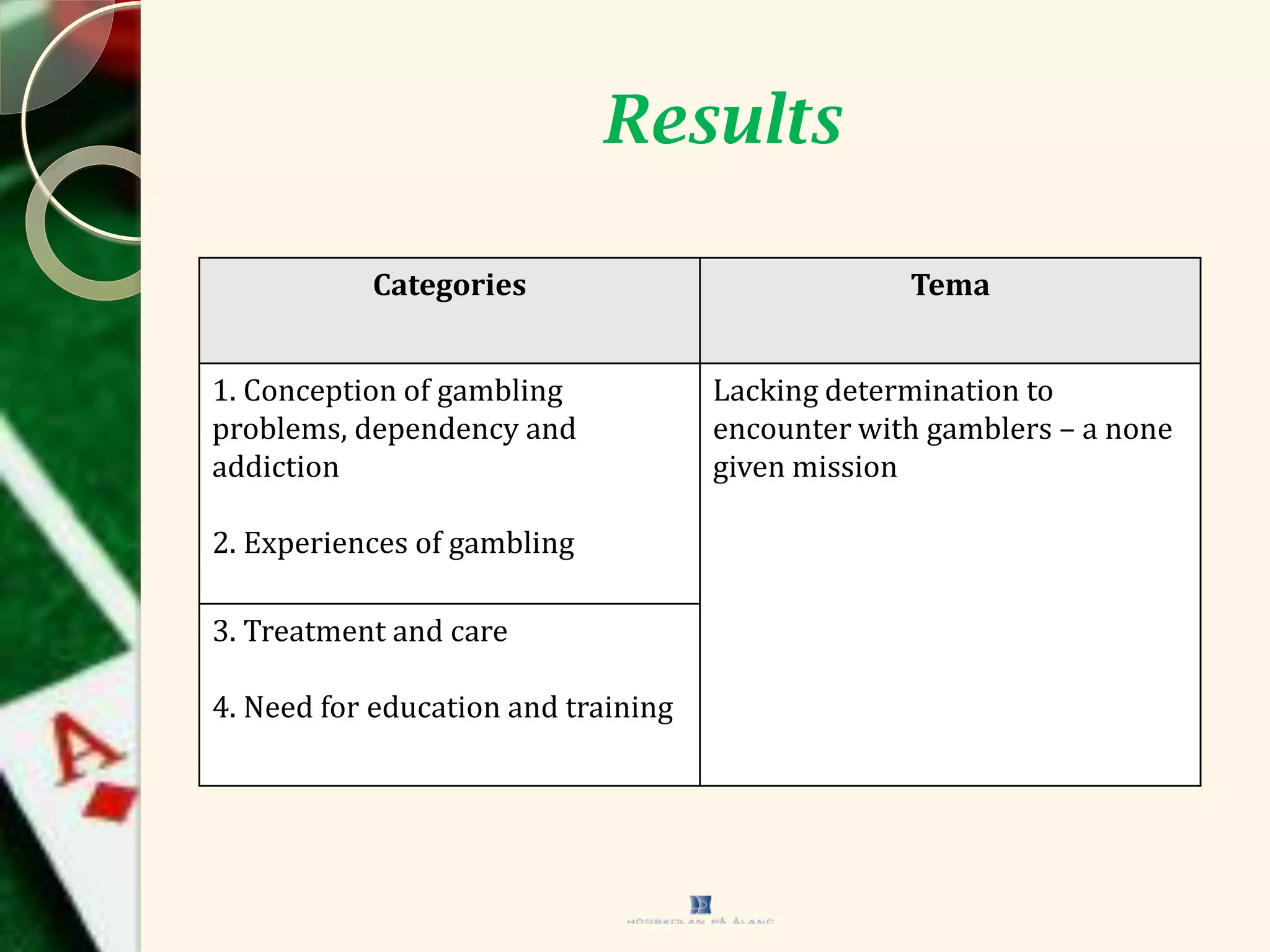
This document outlines a study conducted by researchers at Åland University, focusing on health professionals' experiences in treating gambling problems, addiction, and dependency. It highlights key themes such as definitions of gambling issues, treatment experiences, and the need for improved education and guidelines in handling gambling addiction. The results emphasize the necessity of enhancing resources and strategies in health and social services to better address these concerns.