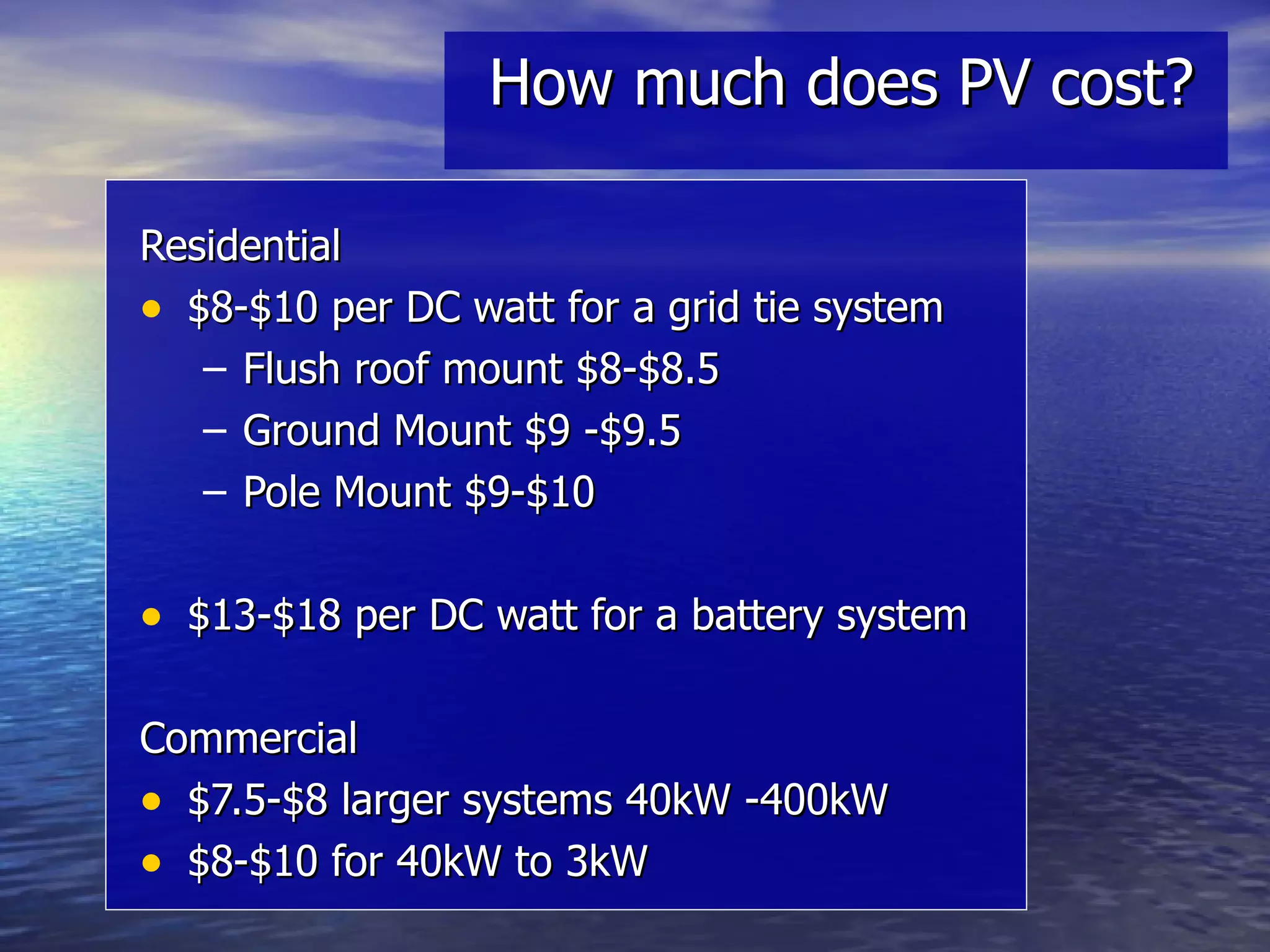
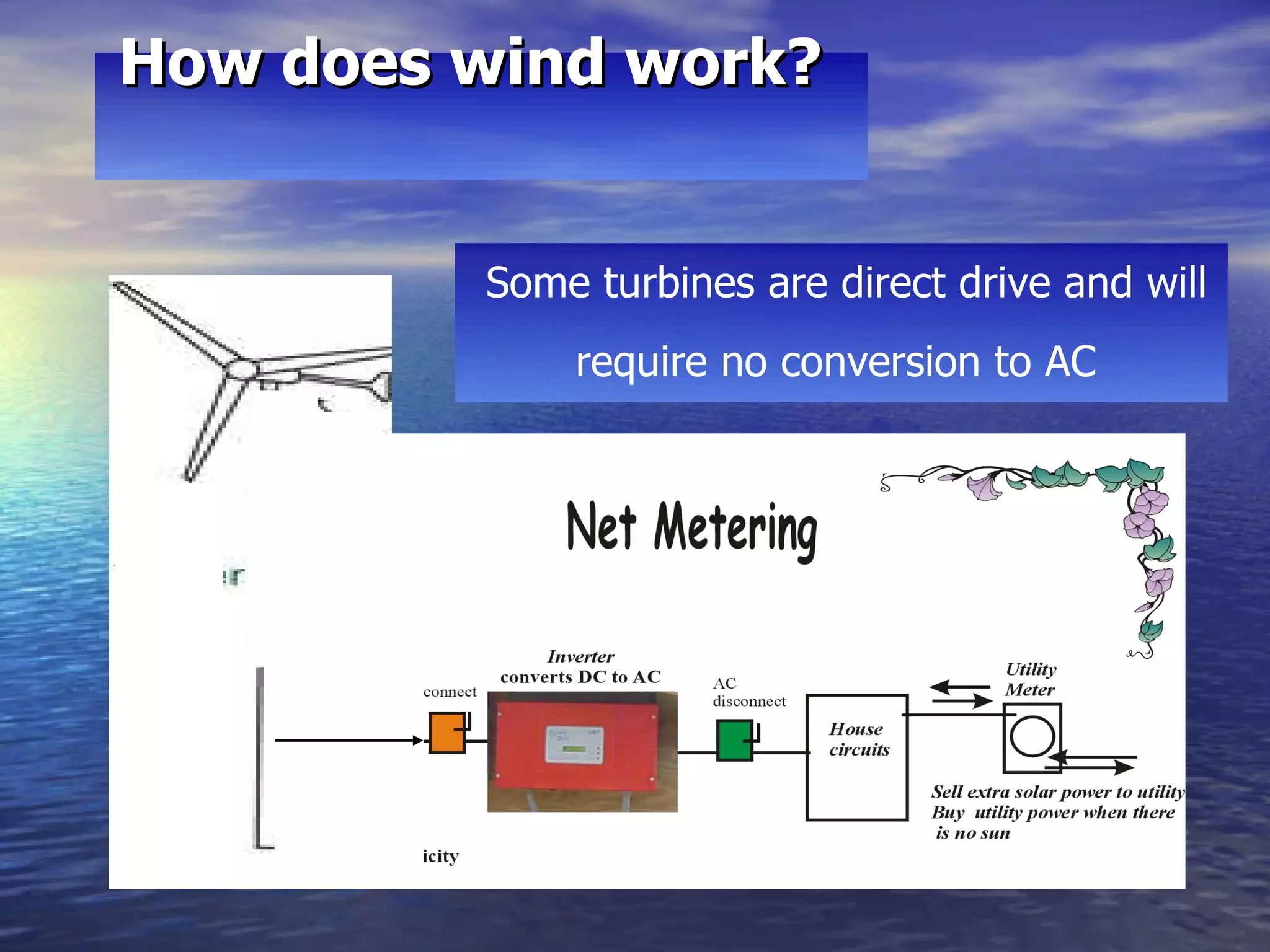
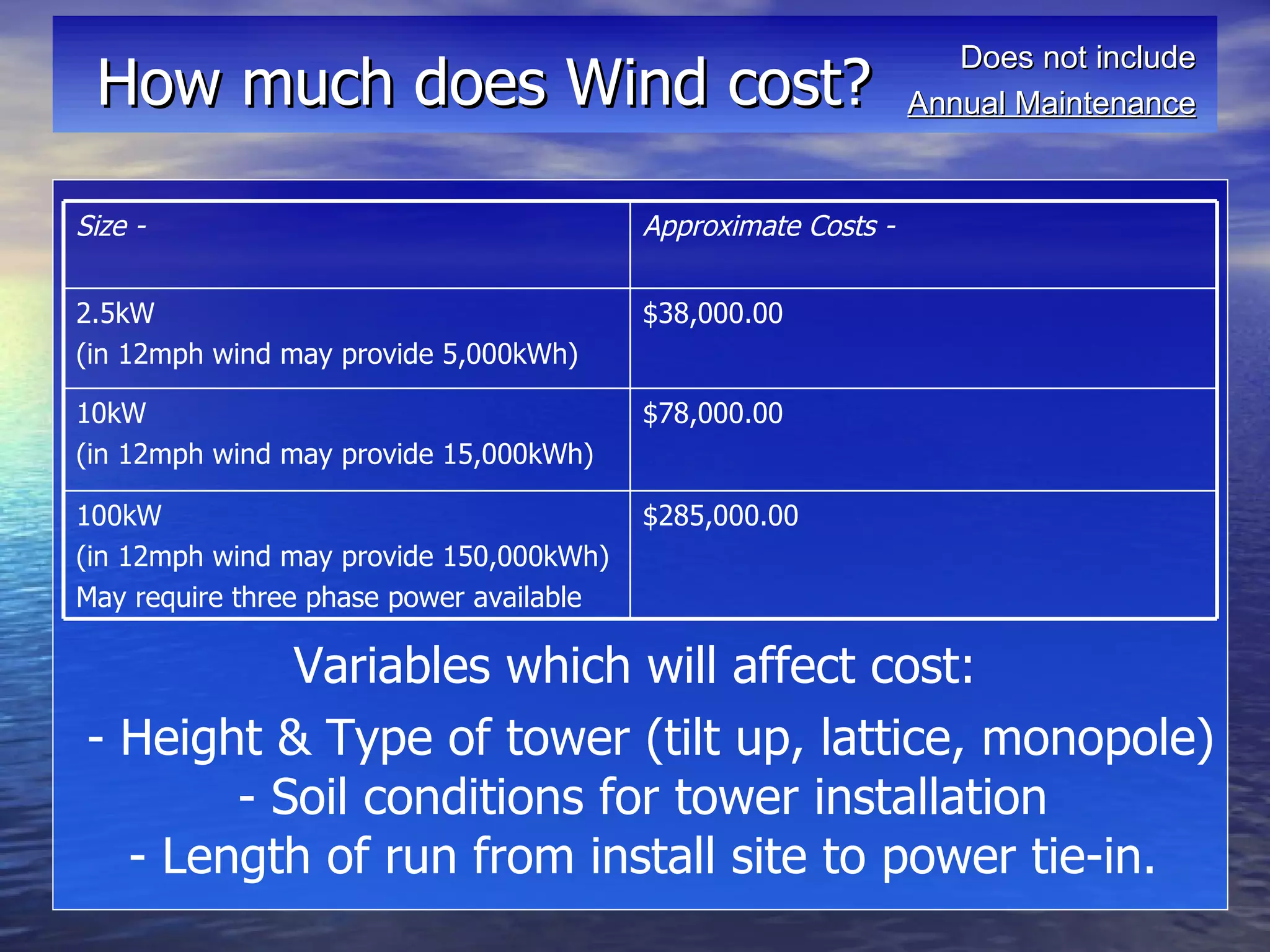
This presentation covers renewable energy options including solar thermal, photovoltaics, and wind. It discusses the basic technology behind each option, costs, financial incentives, and considerations for installation such as roof orientation and shading issues. Installation costs can be recouped in 5-7 years for solar thermal and wind may provide the quickest payback if installed in an appropriate location.


















































![Thank you for your time! Please contact Liz Argo for more information: 866-682-0514 [email_address] This concludes The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education Systems Program Questions?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newportcollaborativearchitectspresentation-100730124805-phpapp02/75/Newport-Collaborative-Architects-62-2048.jpg)
