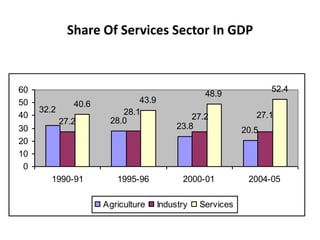
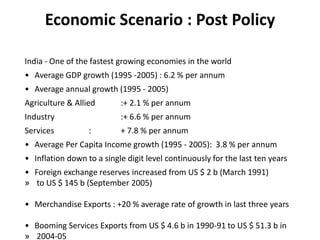
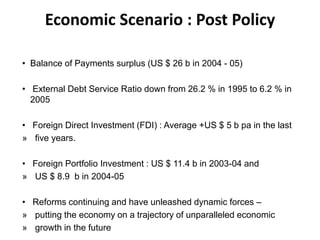
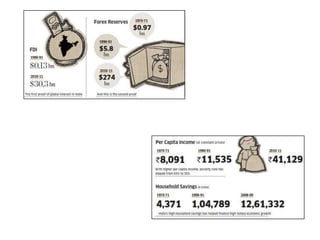
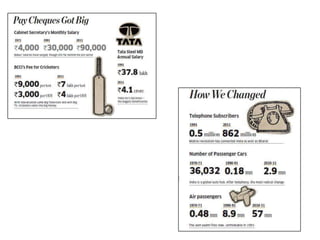
The document summarizes the economic situation in India before and after the 1991 economic reforms. Before 1991, India followed socialist policies and imposed licenses and restrictions on private investment and imports. This led to high inflation, currency volatility, and increasing debt. The 1991 reforms introduced liberalization, privatization, and globalization policies. This included industrial deregulation, trade liberalization, and foreign investment reforms. After 1991, India's economy grew rapidly, with GDP quadrupling, foreign exchange reserves surging, and exports increasing substantially. However, the reforms also led to rising inequality, unemployment, and poverty remained an issue.