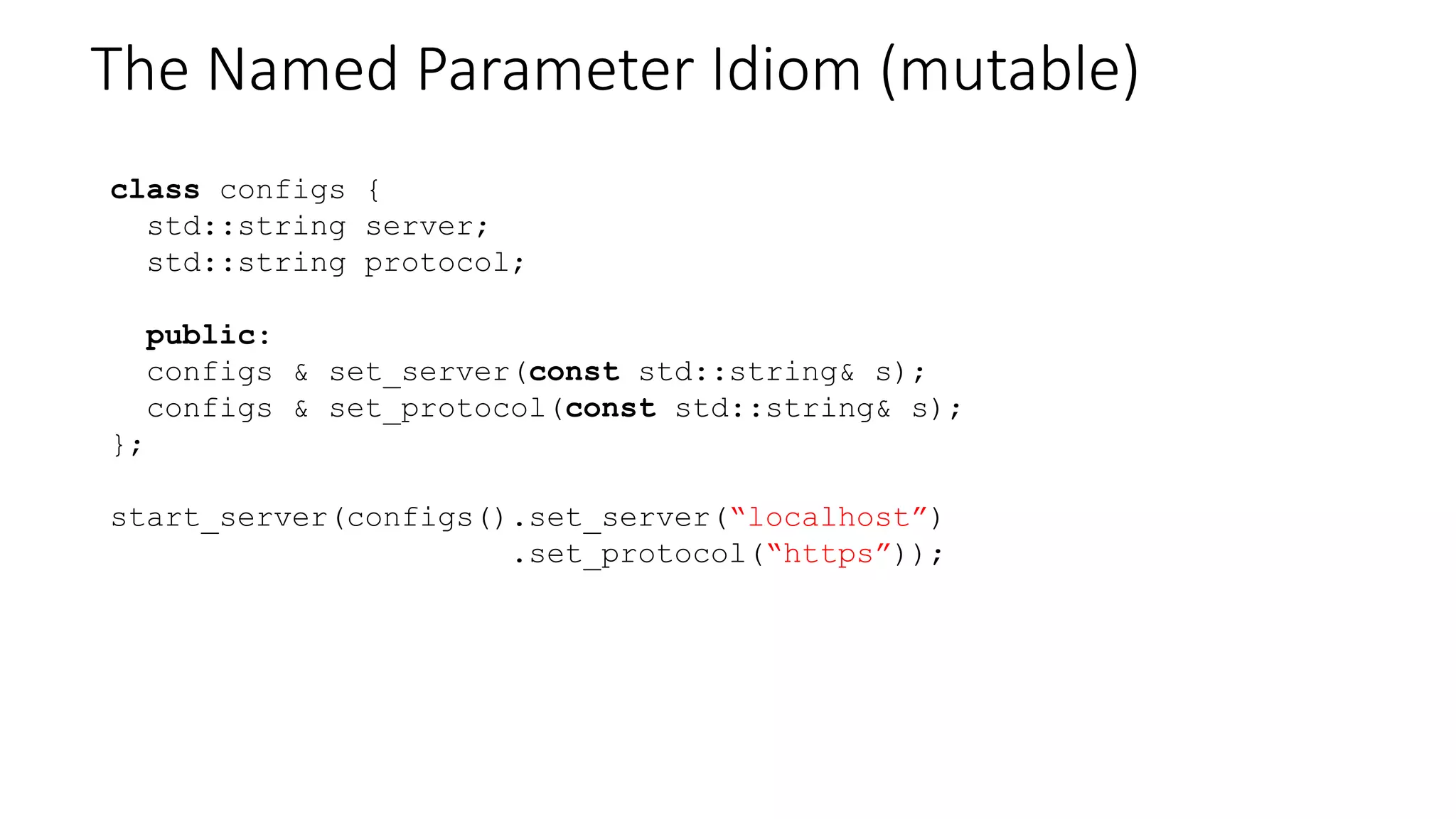
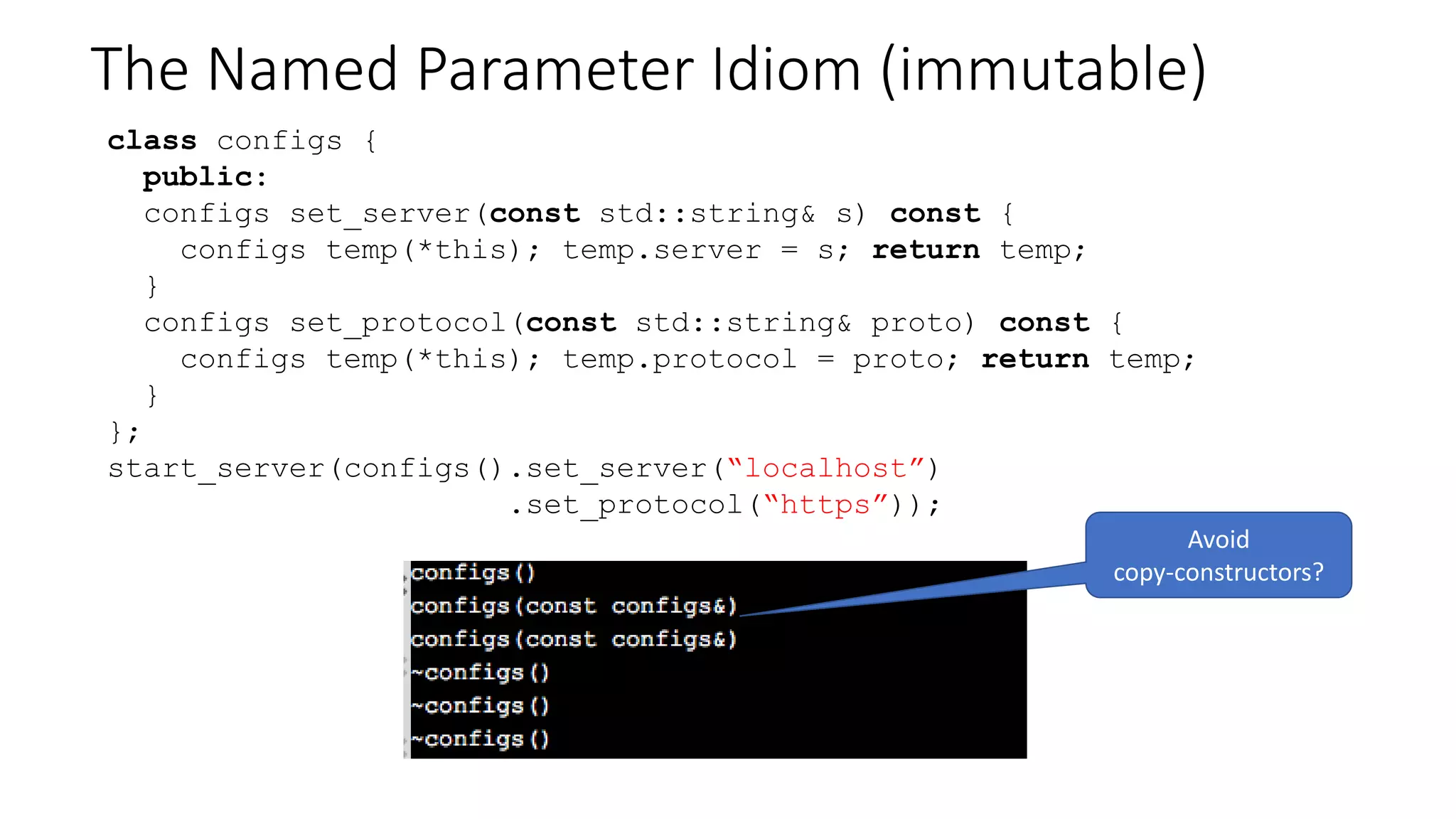
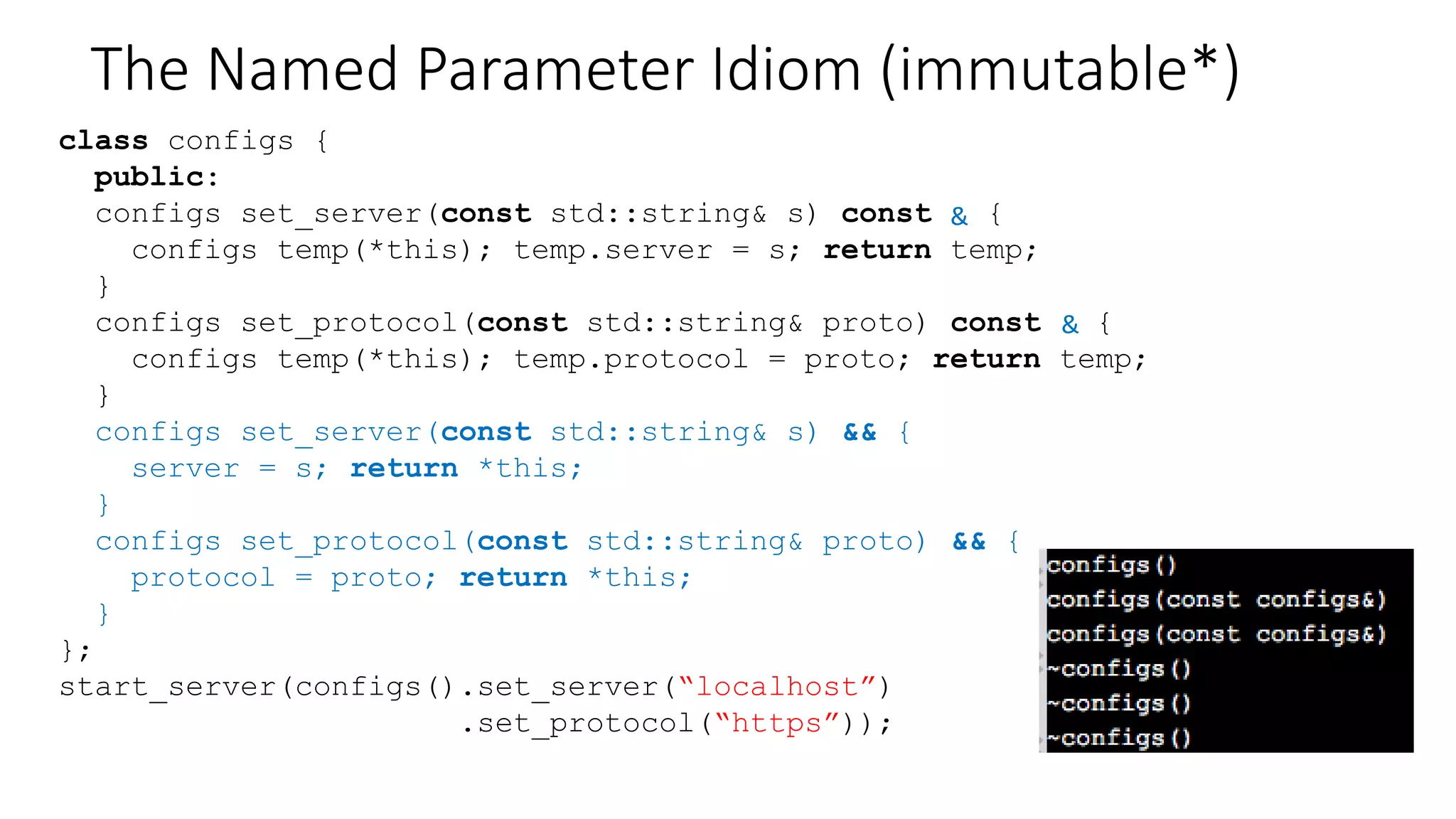
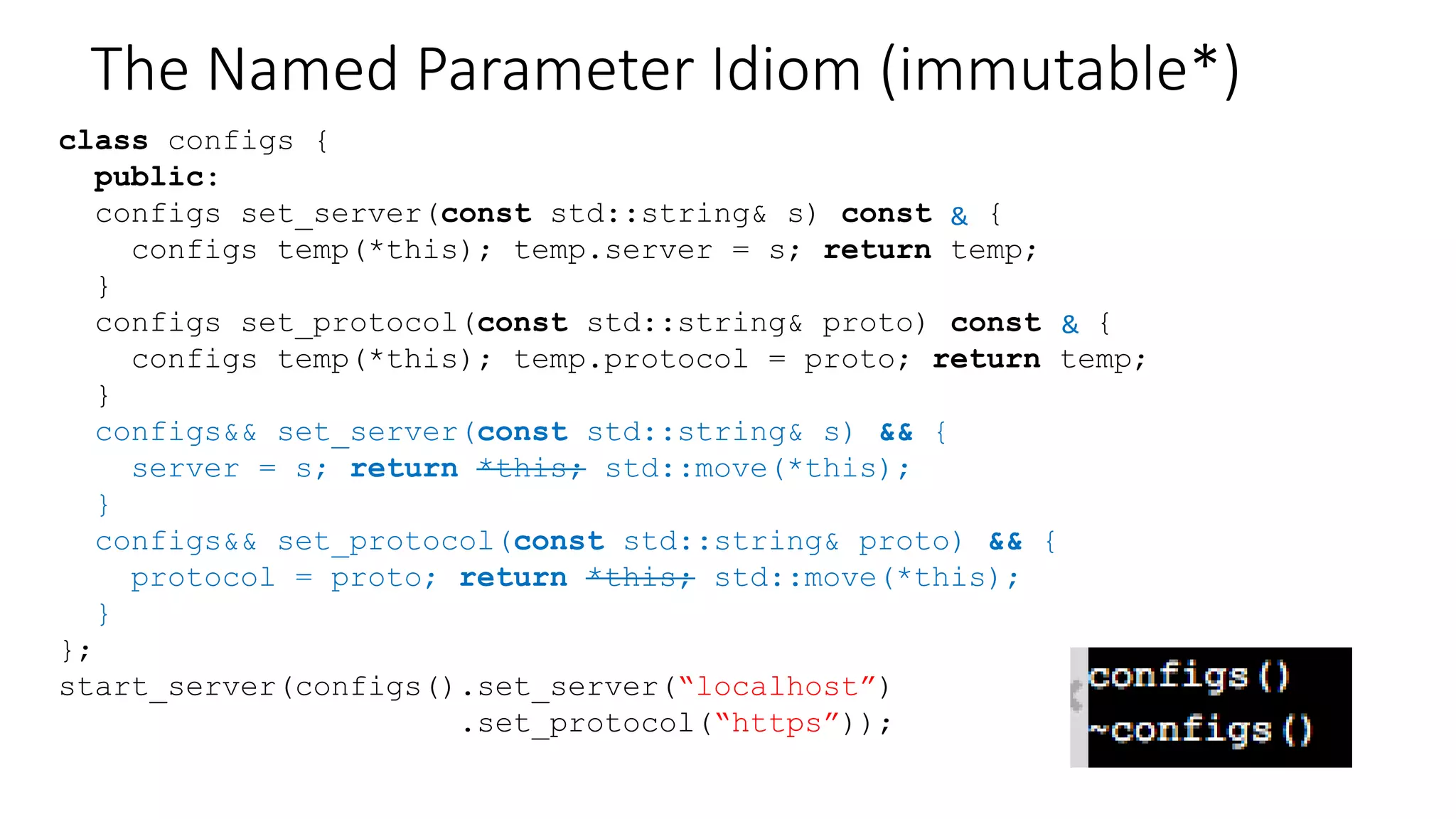
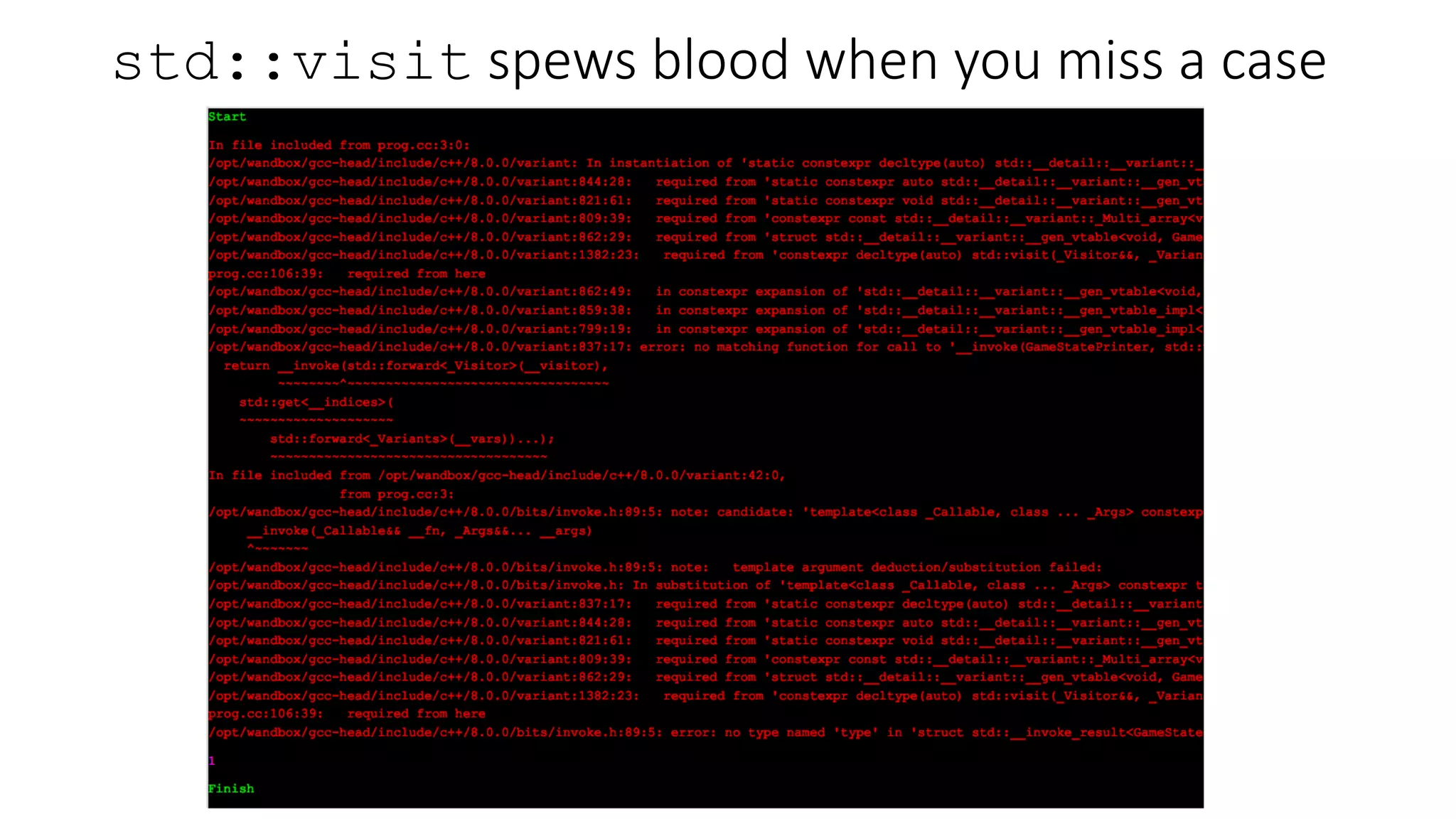
The document discusses advanced functional programming techniques in C++ using std::variant for modeling game states in tennis scoring. It demonstrates various implementations, including different score states and algorithms for transitioning between them while comparing inheritance with std::variant for state management. The document also covers deep immutability and the named parameter idiom to enhance code clarity and maintainability.






![Print GameState (std::variant)
struct GameStatePrinter {
std::ostream &o;
explicit GameStatePrinter(std::ostream& out) : o(out) {}
void operator ()(const NormalScore& ns) const {
o << "NormalScore[" << ns.p1 << ns.p2 << ns.p1_score << ns.p2_score << "]";
}
void operator ()(const DeuceScore& ds) const {
o << "DeuceScore[" << ds.p1 << "," << ds.p2 << "]";
}
void operator ()(const AdvantageScore& as) const {
o << "AdvantageScore[" << as.lead << "," << as.lagging << "]";
}
void operator ()(const GameCompleteScore& gc) const {
o << "GameComplete[" << gc.winner << gc.loser << gc.loser_score << "]";
}
};
std::ostream & operator << (std::ostream& o, const GameState& game) {
std::visit(GameStatePrinter(o), game);
return o;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-7-2048.jpg)
 {
o << "NormalScore" << ns.p1 << ns.p2 << ns.p1_score << ns.p2_score;
},
[&](const DeuceScore& gc) {
o << "DeuceScore[" << ds.p1 << "," << ds.p2 << "]";
},
[&](const AdvantageScore& as) {
o << "AdvantageScore[" << as.lead << "," << as.lagging << "]";
},
[&](const GameCompleteScore& gc) {
o << "GameComplete[" << gc.winner << gc.loser << gc.loser_score << "]";
}
}, game);
return o;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-9-2048.jpg)
 {
o << "NormalScore" << ns.p1 << ns.p2 << ns.p1_score << ns.p2_score;
},
[&](const DeuceScore& gc, const auto& other) {
o << "DeuceScore[" << ds.p1 << "," << ds.p2 << "]";
},
[&](const AdvantageScore& as, const auto& other) {
o << "AdvantageScore[" << as.lead << "," << as.lagging << "]";
},
[&](const GameCompleteScore& gc, const auto& other) {
o << "GameComplete[" << gc.winner << gc.loser << gc.loser_score << "]";
}
}, game, someother_variant);
return o;
}
There can be arbitrary number of arbitrary variant types.
The visitor must cover all cases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-10-2048.jpg)

 -> GameState {
if (ds.p1 == who_scored)
return AdvantageScore{ds.p1, ds.p2};
else
return AdvantageScore{ds.p2, ds.p1};
},
[&](const AdvantageScore& as) -> GameState {
if (as.lead == who_scored)
return GameCompleteScore{as.lead, as.lagging, 40};
else
return DeuceScore{as.lead, as.lagging};
},
[&](const GameCompleteScore &) -> GameState {
throw "Illegal State";
},
[&](const NormalScore& ns) -> GameState {
if (ns.p1 == who_scored) {
switch (ns.p1_score) {
case 0: return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, 15, ns.p2_score};
case 15: return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, 30, ns.p2_score};
case 30: if (ns.p2_score < 40)
return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, 40, ns.p2_score};
else
return DeuceScore{ns.p1, ns.p2};
case 40: return GameCompleteScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, ns.p2_score};
default: throw "Makes no sense!";
}
}
else {
switch (ns.p2_score) {
case 0: return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, ns.p1_score, 15};
case 15: return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, ns.p1_score, 30};
case 30: if (ns.p1_score < 40)
return NormalScore{ns.p1, ns.p2, ns.p1_score, 40};
else
return DeuceScore{ns.p1, ns.p2};
case 40: return GameCompleteScore{ns.p2, ns.p1, ns.p1_score};
default: throw "Makes no sense!";
}
}
}
}, now);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-12-2048.jpg)


 {
return s.who_is_serving();
}, state);
Player who_is_serving = state.who_is_serving();
ceremony!
struct NormalScore {
Player p1, p2;
int p1_score, p2_score;
int serving_player;
Player & who_is_serving();
};
struct DeuceScore {
Player p1, p2;
int serving_player;
Player & who_is_serving();
};
struct AdvantageScore {
Player lead, lagging;
int serving_player;
Player & who_is_serving();
};
struct GameCompleteScore {
Player winner, loser;
int loser_score;
int serving_player;
Player & who_is_serving();
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-15-2048.jpg)
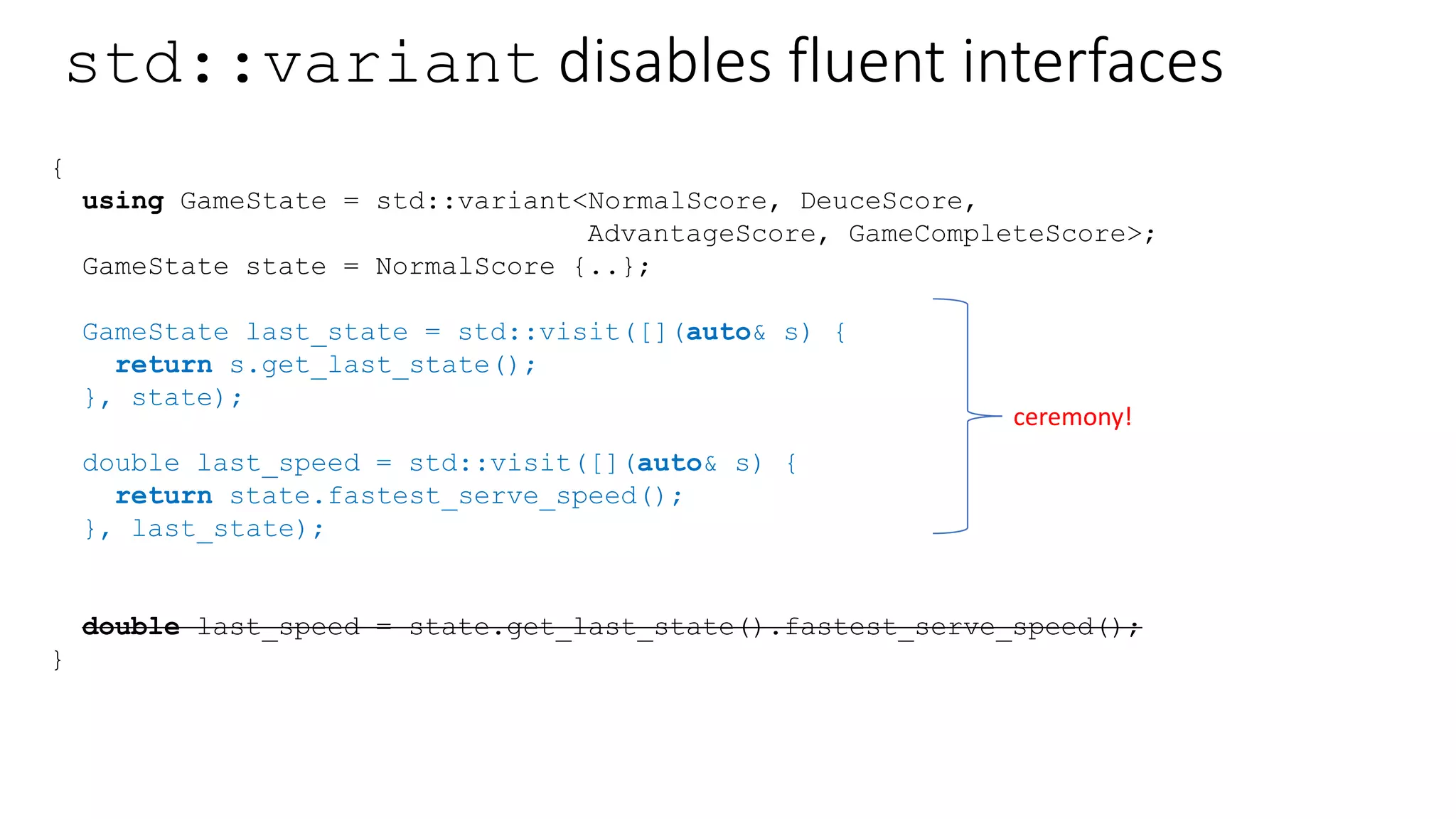
 {
return s.get_last_state();
}, state);
double last_speed = std::visit([](auto& s) {
return state.fastest_serve_speed();
}, last_state);
double last_speed = state.get_last_state().fastest_serve_speed();
}
ceremony!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-17-2048.jpg)
 {
return s.who_is_serving();
}, state);
Player who_is_serving = state.who_is_serving();
}
SharedGameState
who_is_serving()
NormalScore_v2 DeuceScore_v2 AdvantageScore_v2 GameCompleteScore_v2
ceremony!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsforamorefunctionalc-170929153923/75/New-Tools-for-a-More-Functional-C-18-2048.jpg)