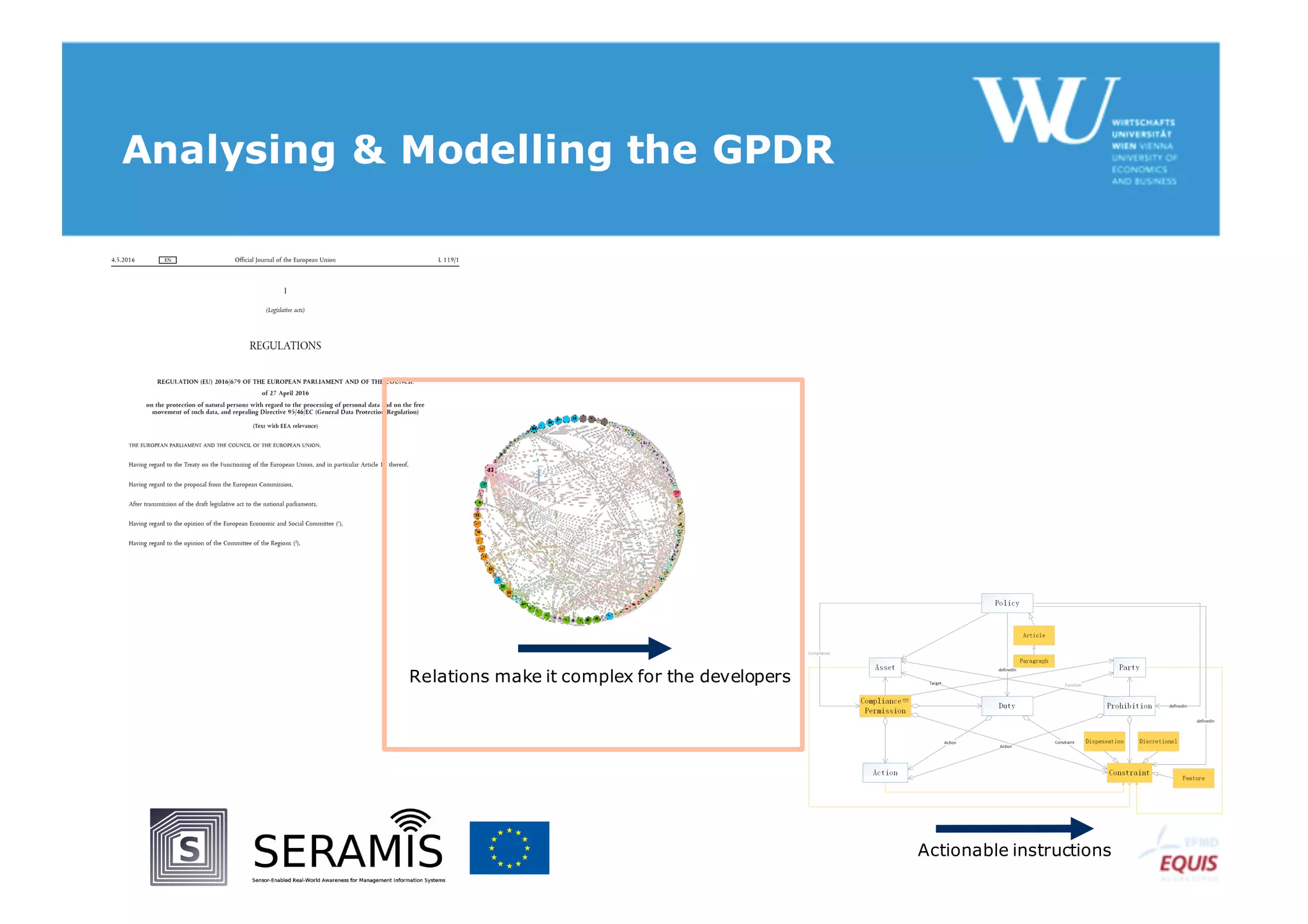
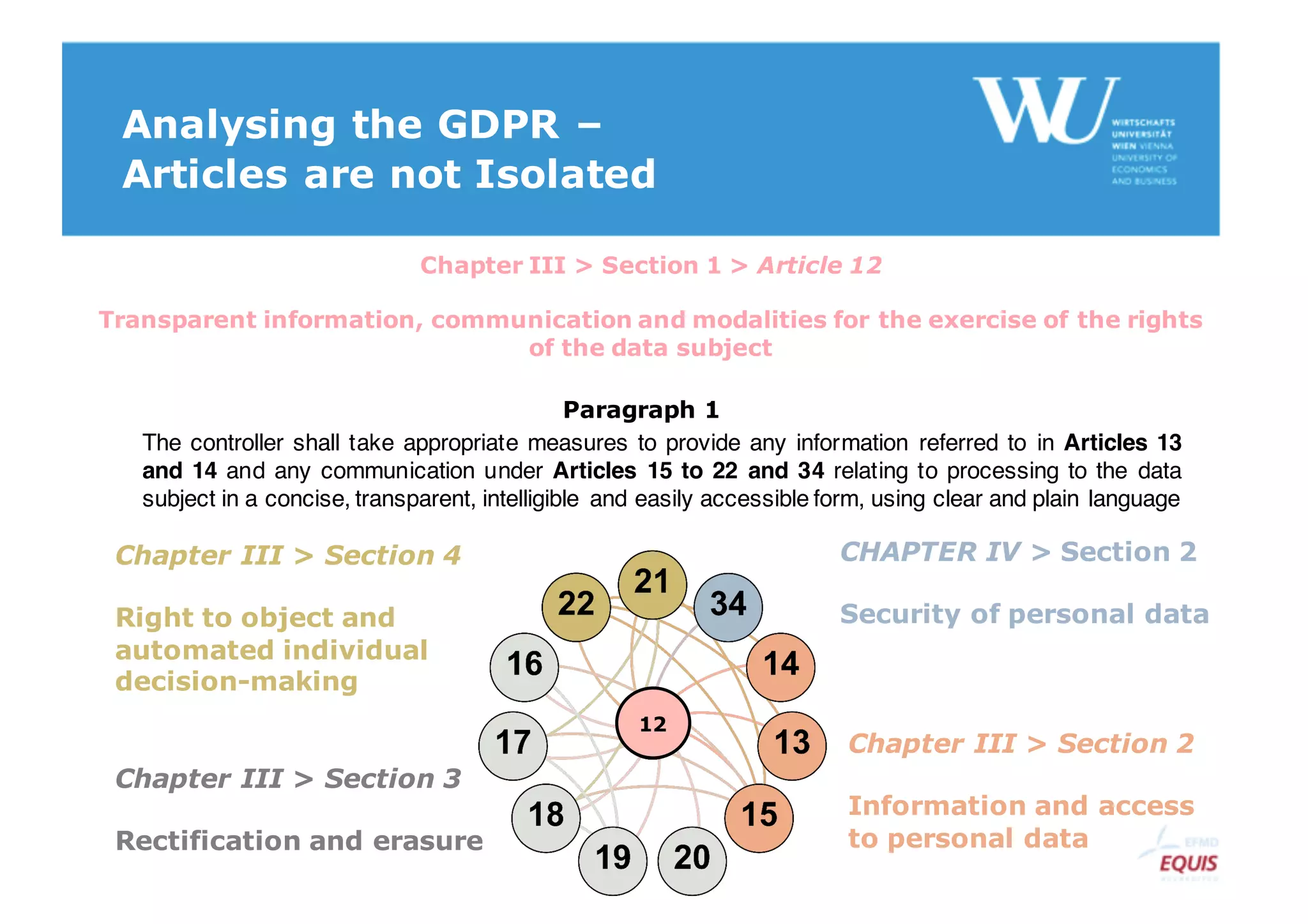
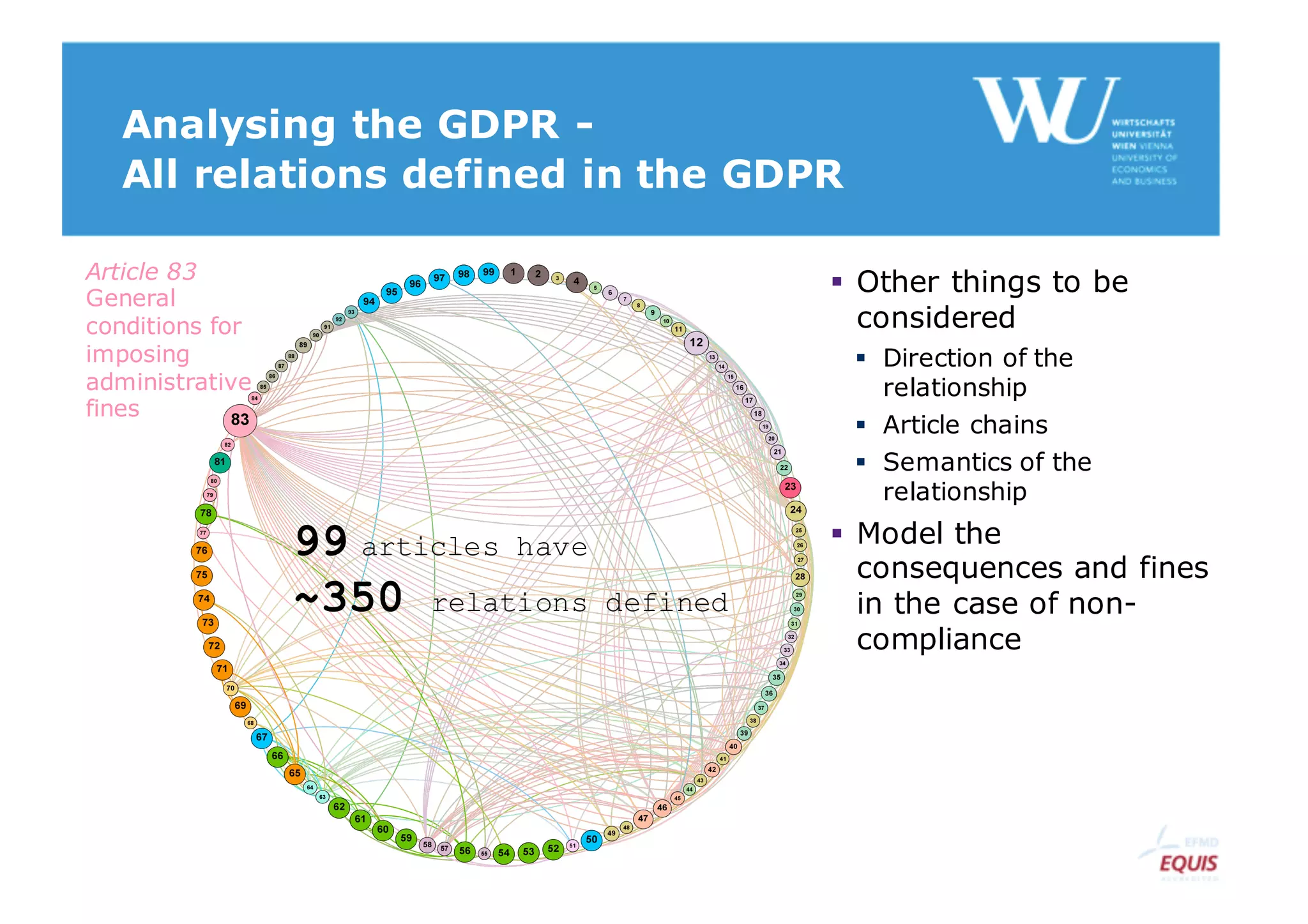
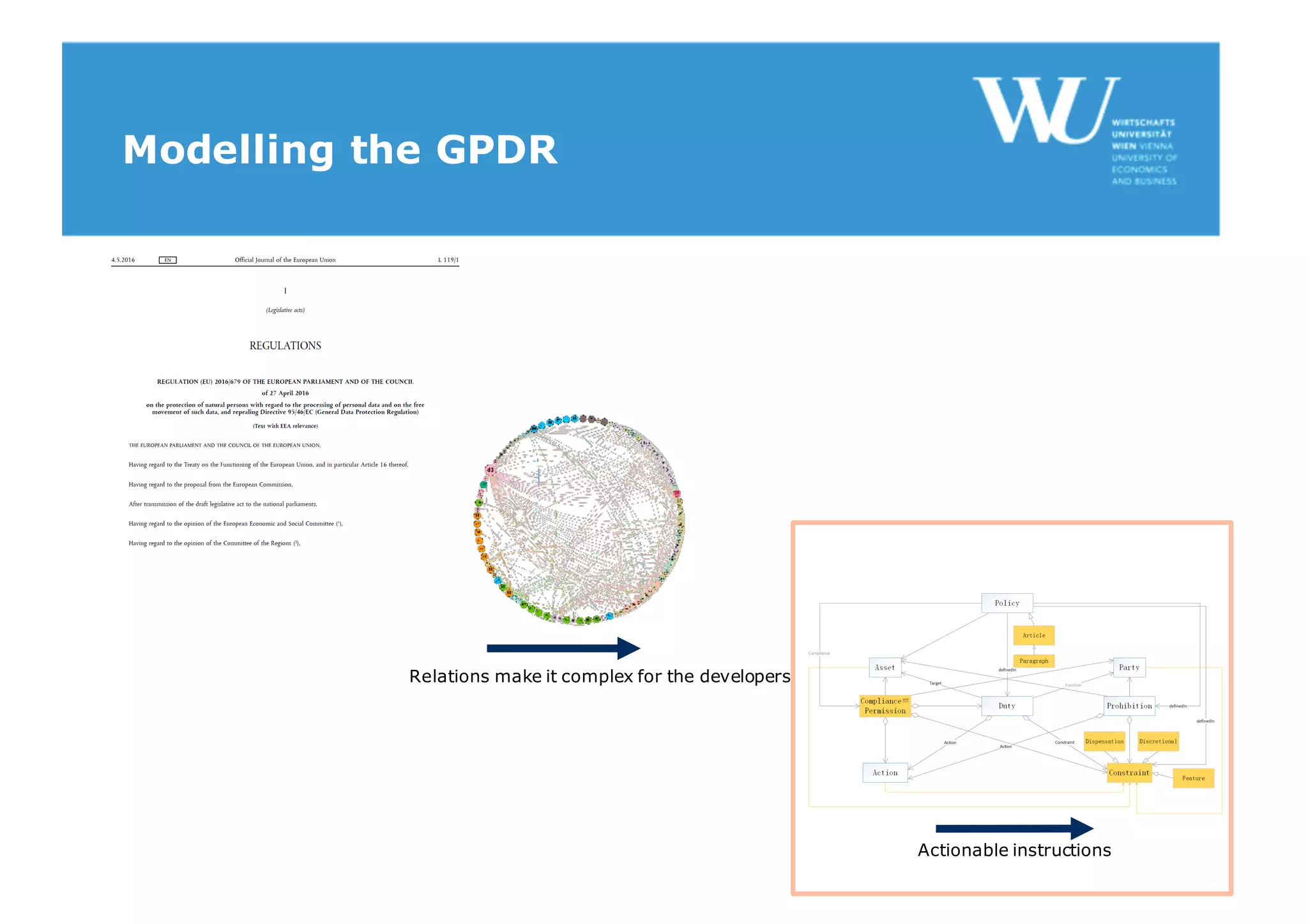
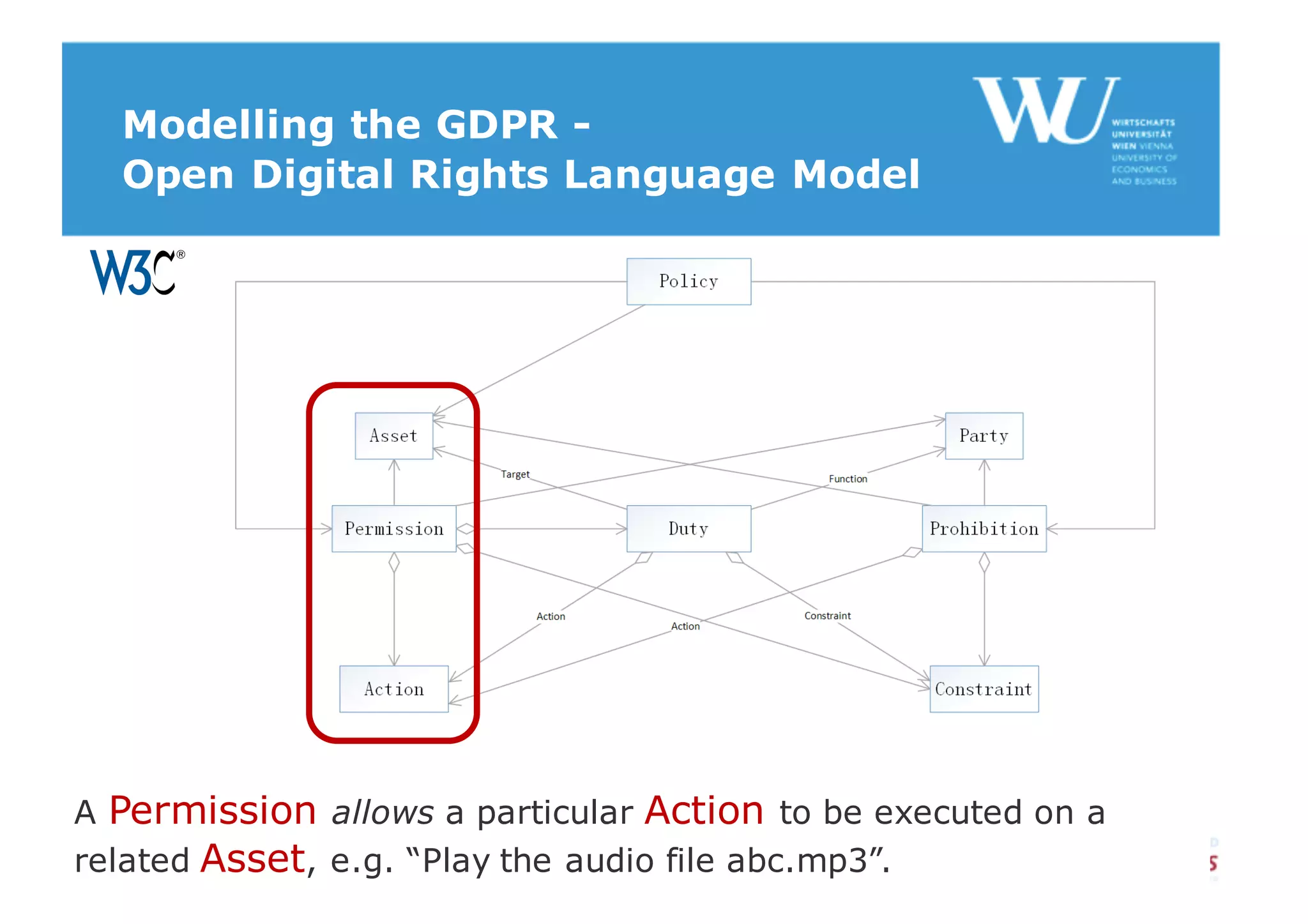
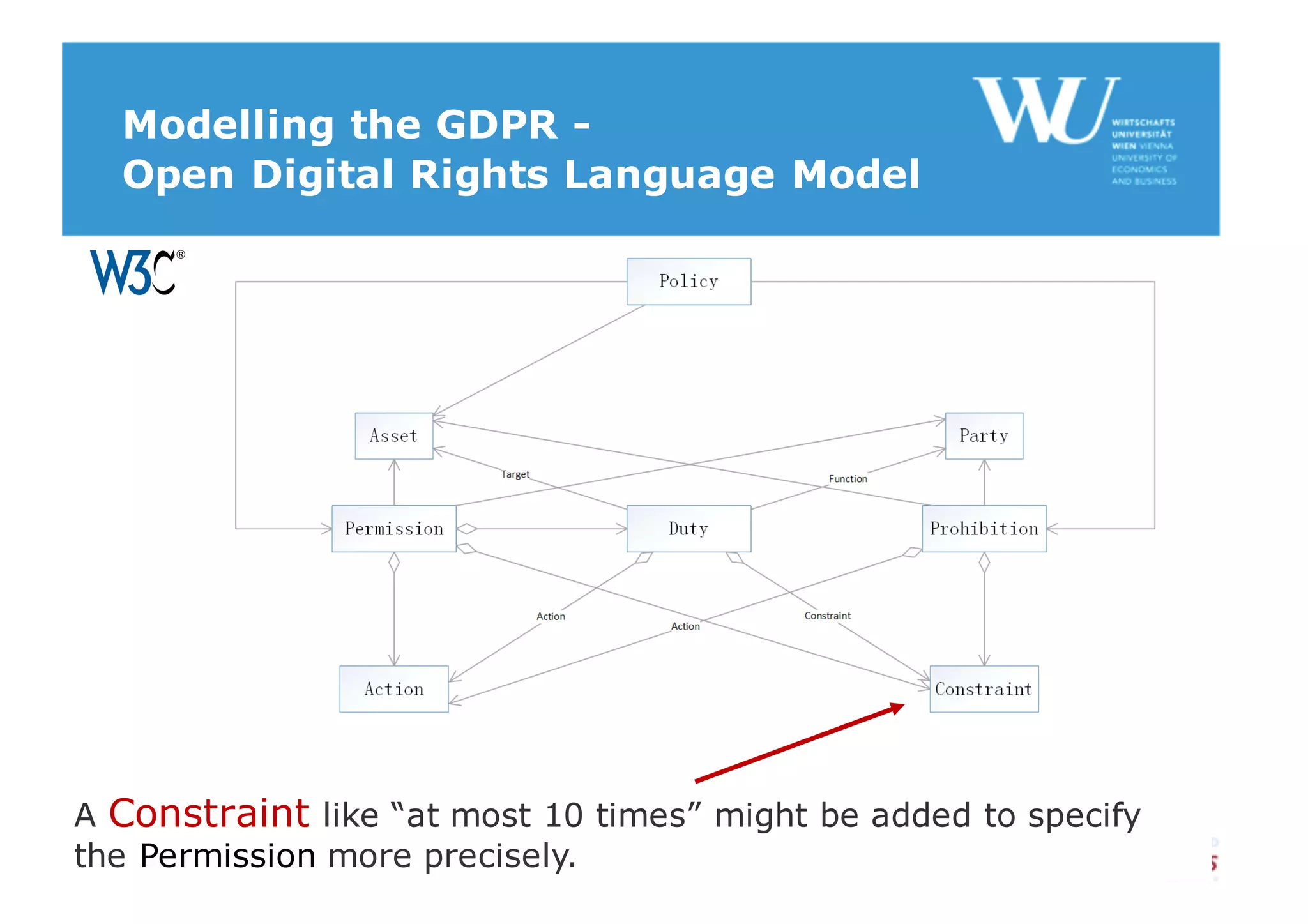
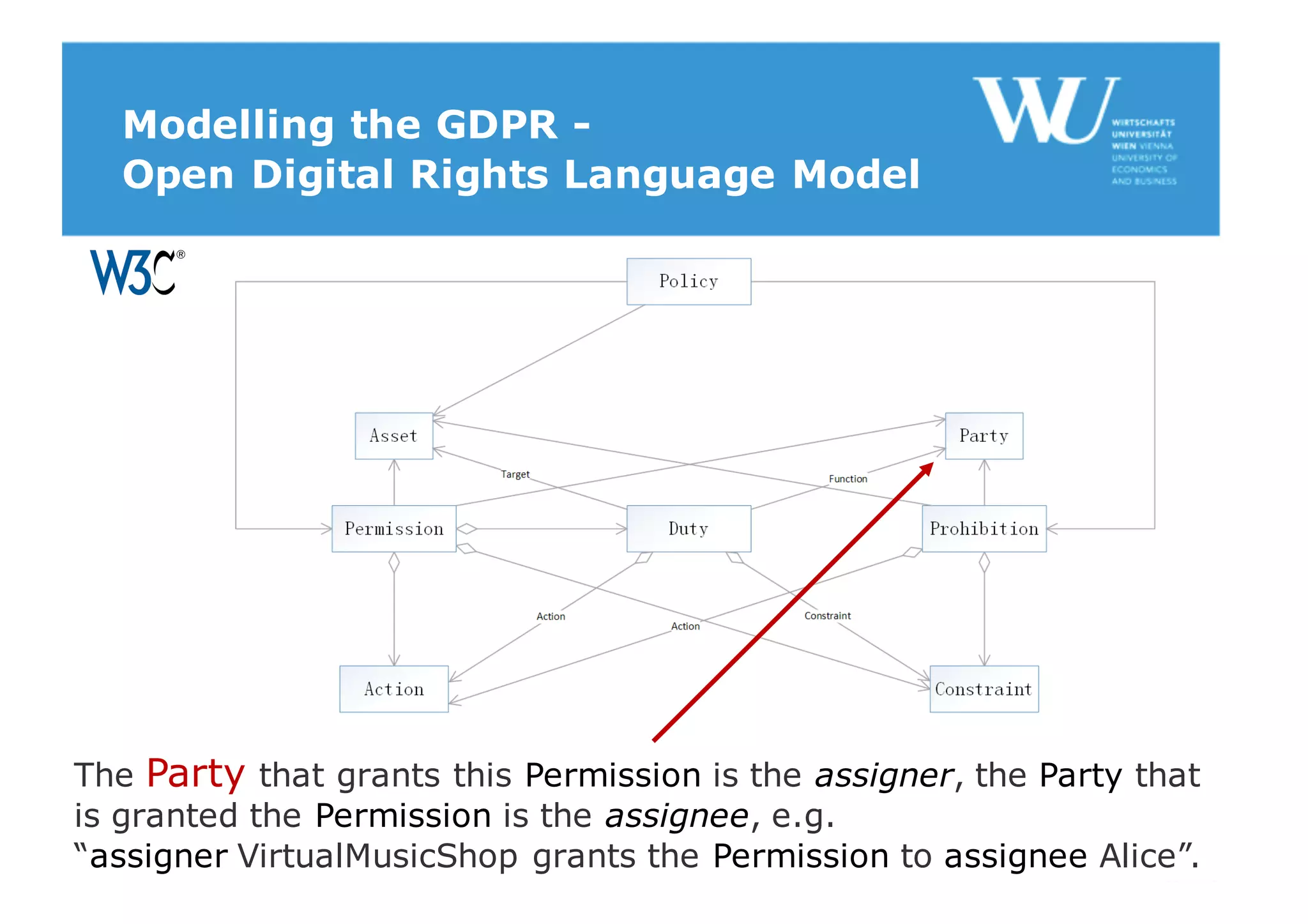
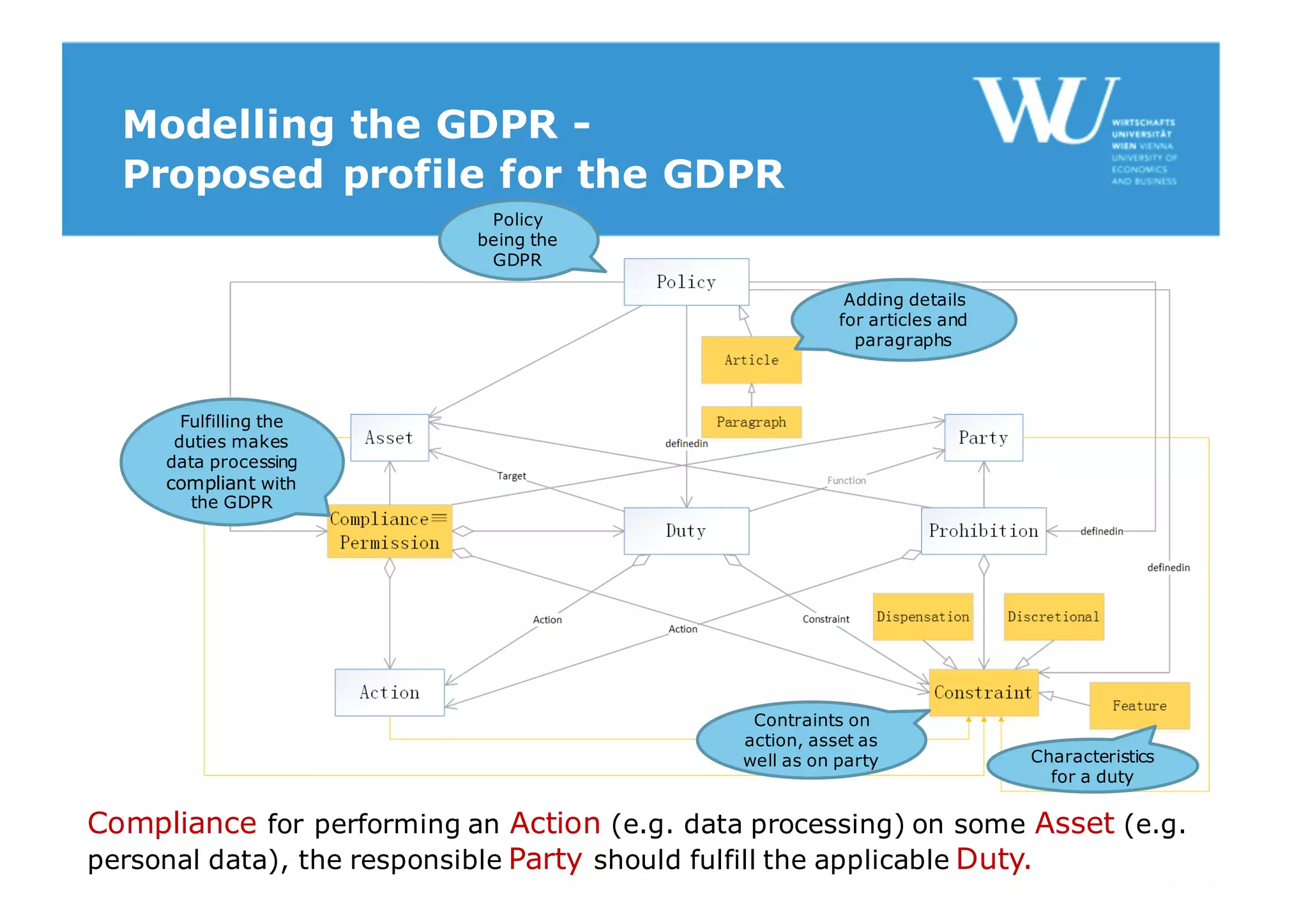
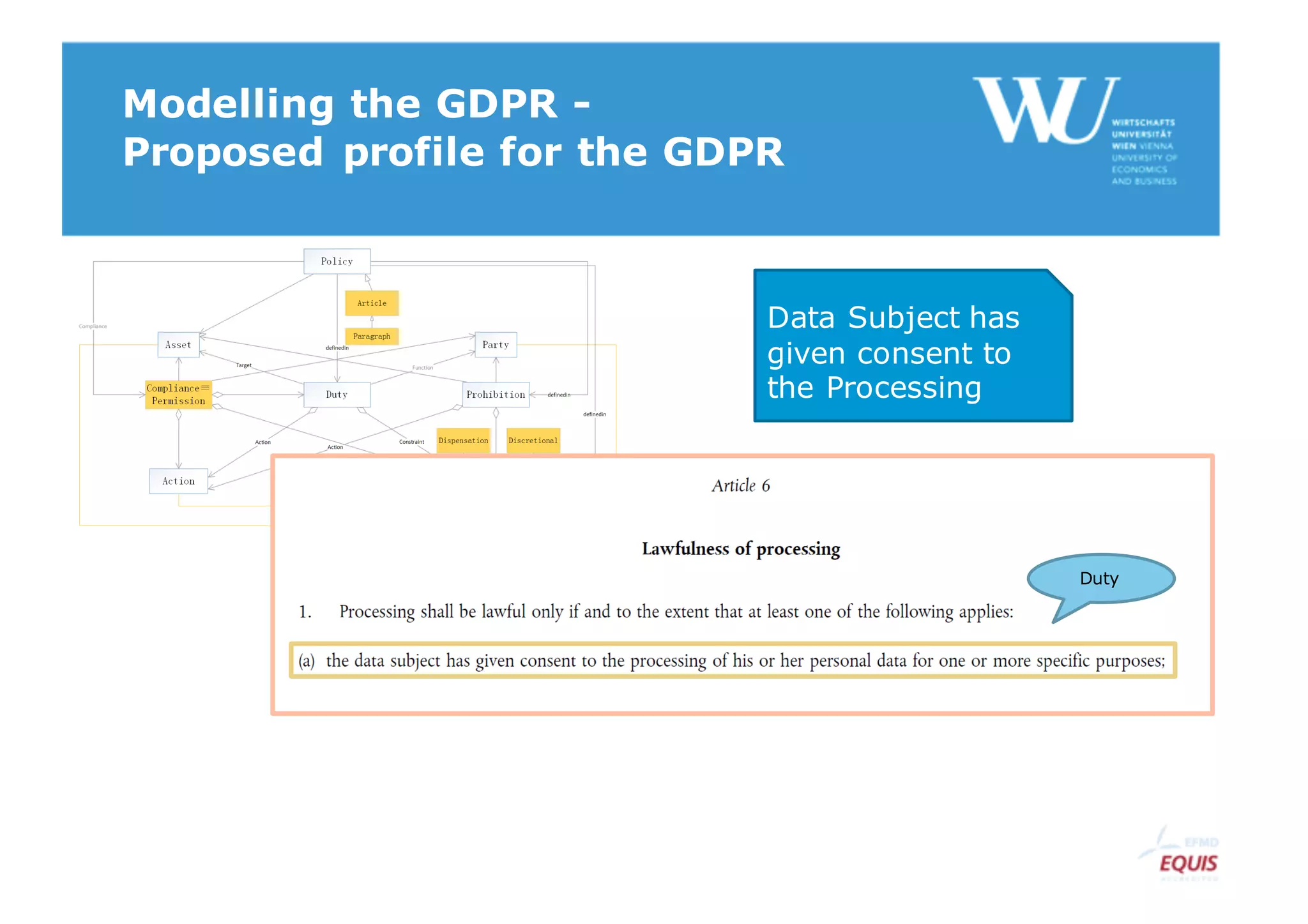
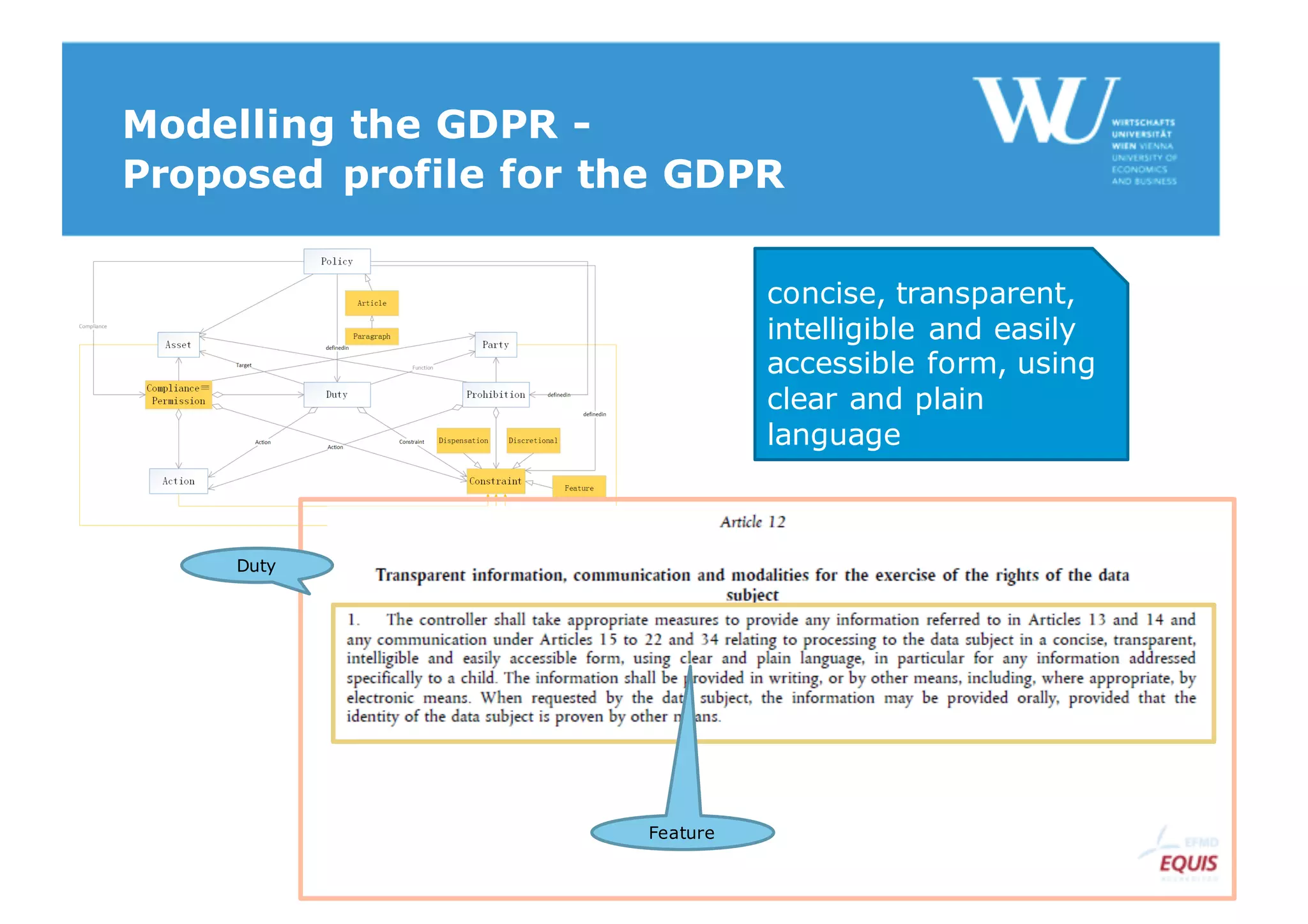
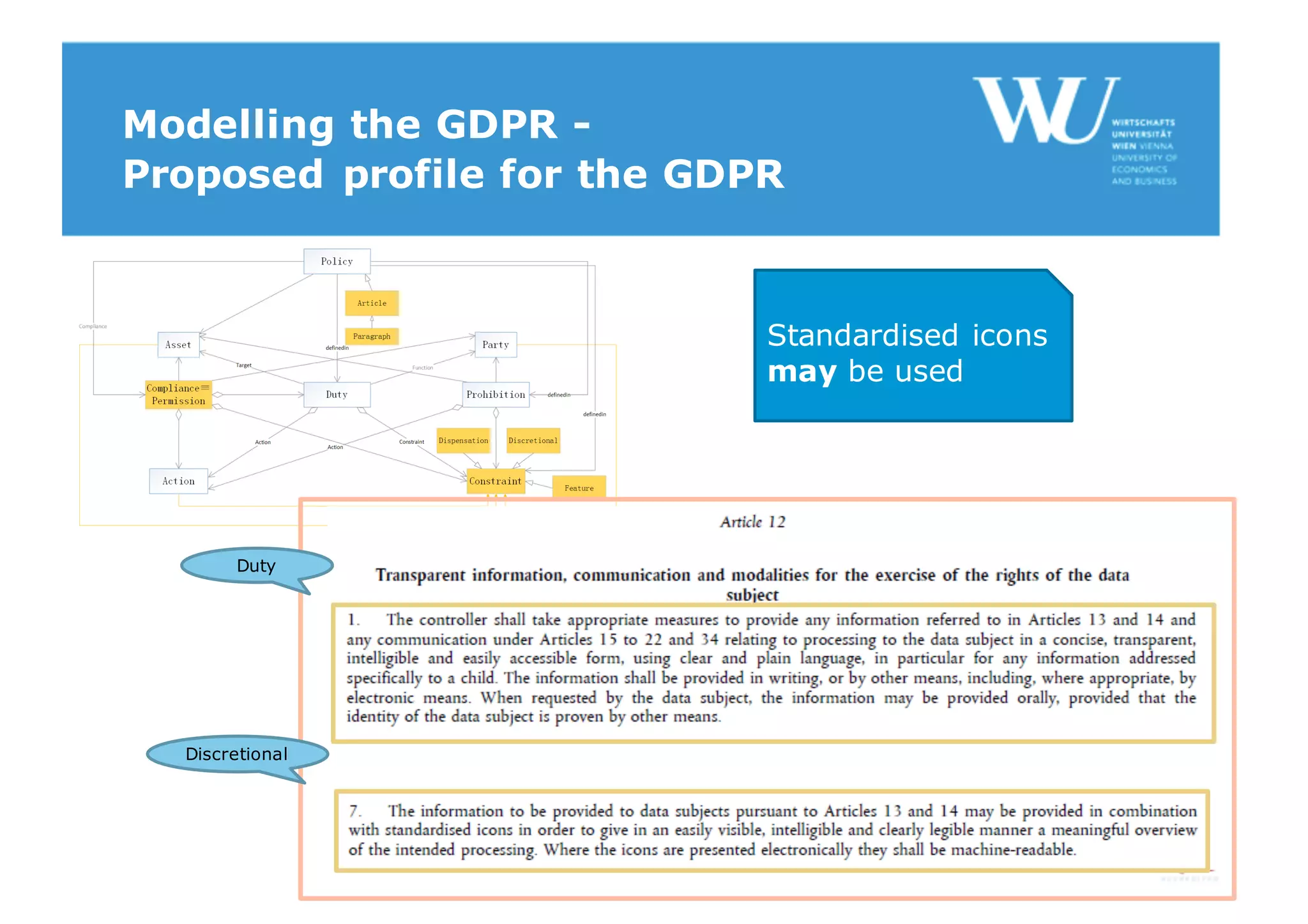
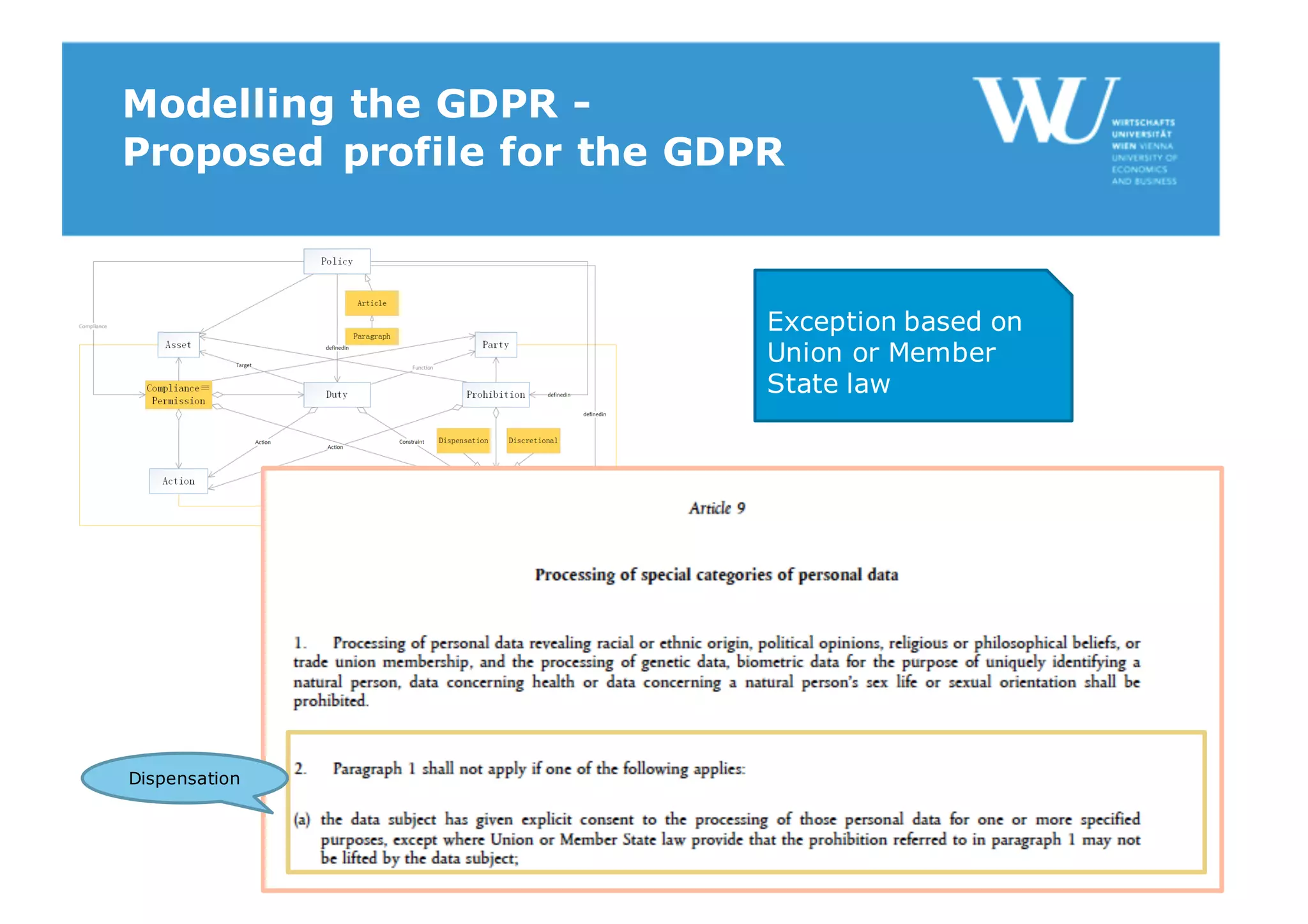
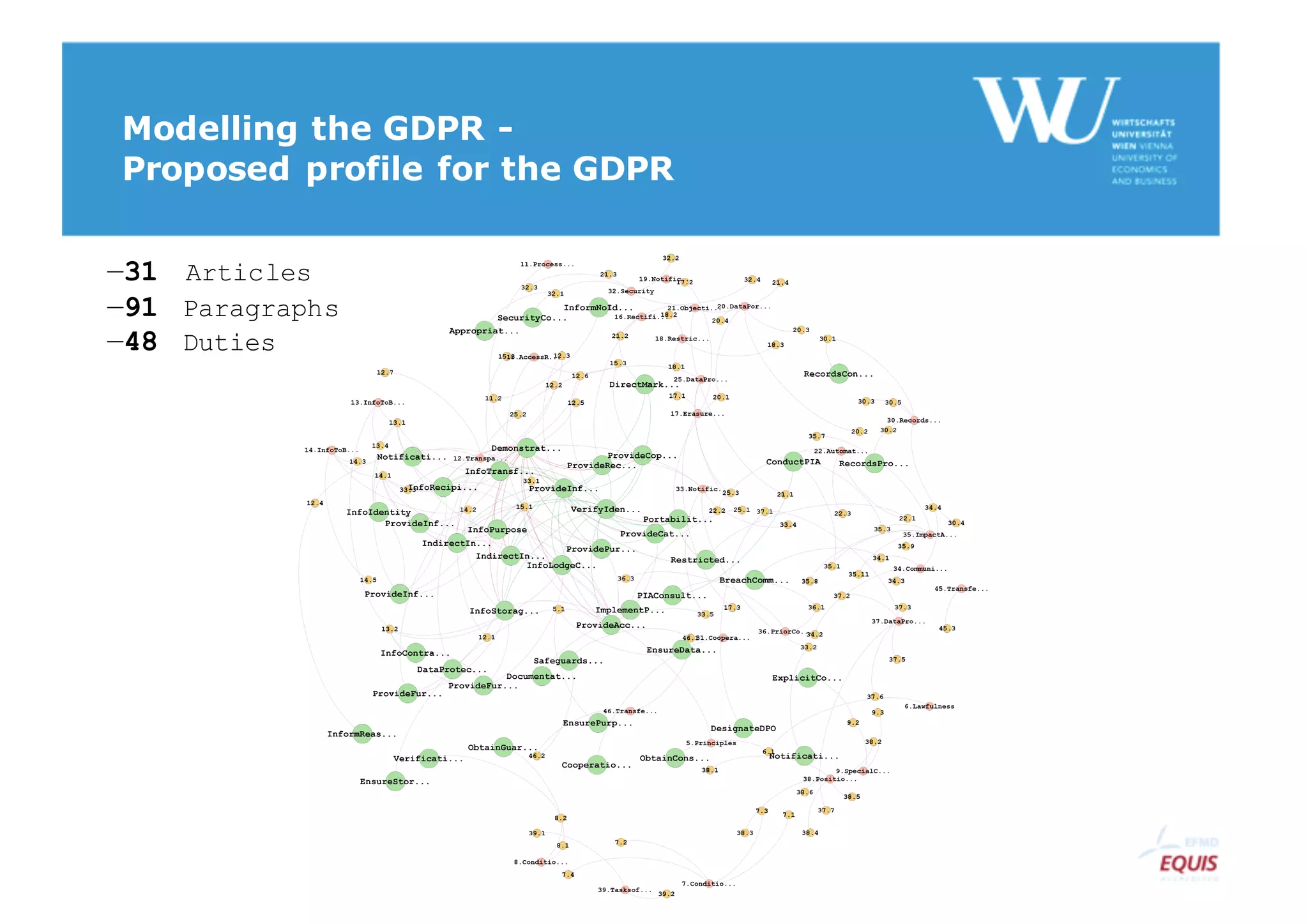
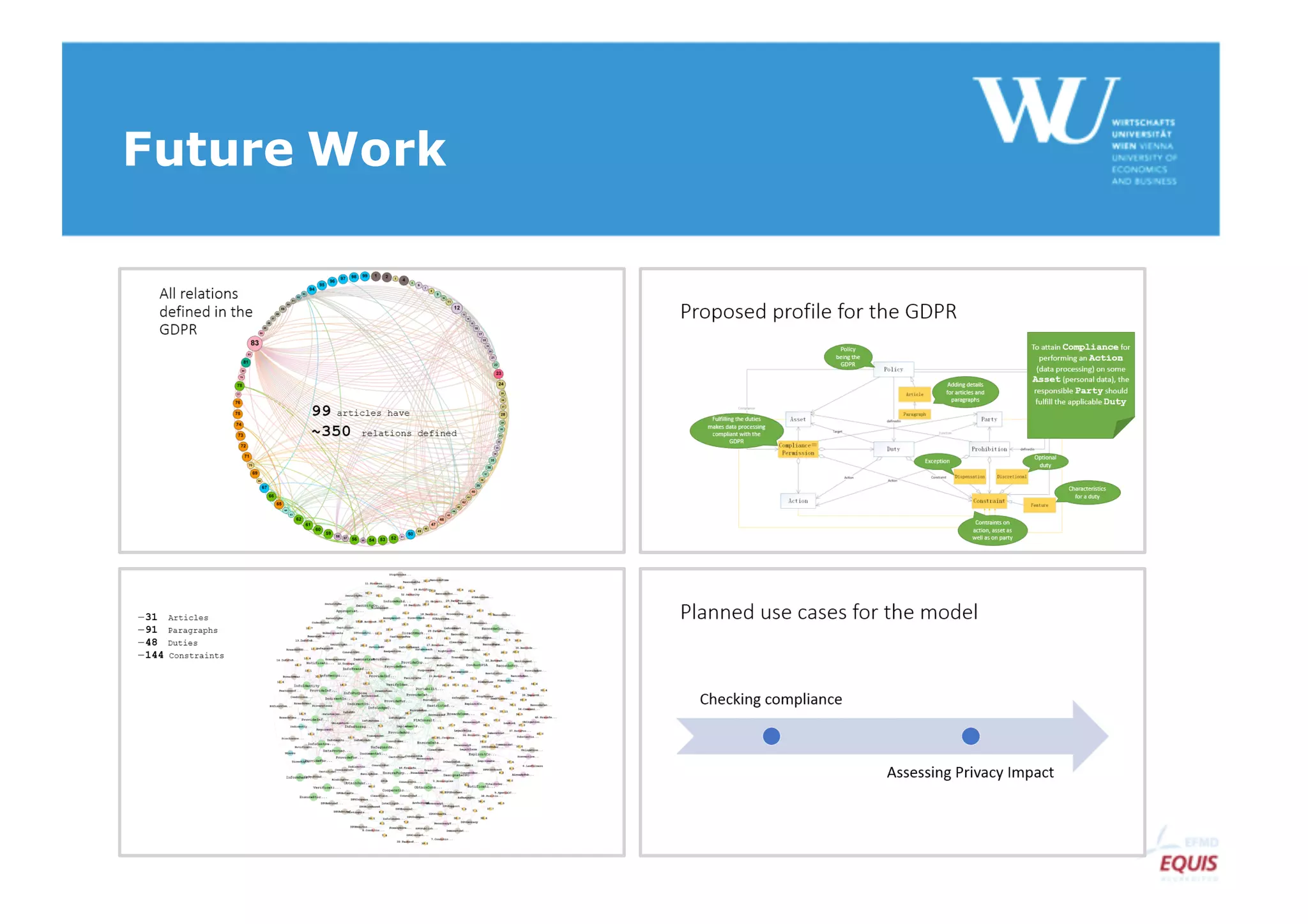
The document discusses modelling the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) using the Open Digital Rights Language (ODRL) model. It analyzes the 99 articles and ~350 relations defined in the GDPR. It then proposes using ODRL to model the GDPR as a policy, with duties, constraints, and other features represented as ODRL entities. Specifically, it models 31 articles, 91 paragraphs, and identifies 48 duties and 144 constraints that could be represented in this ODRL profile of the GDPR.