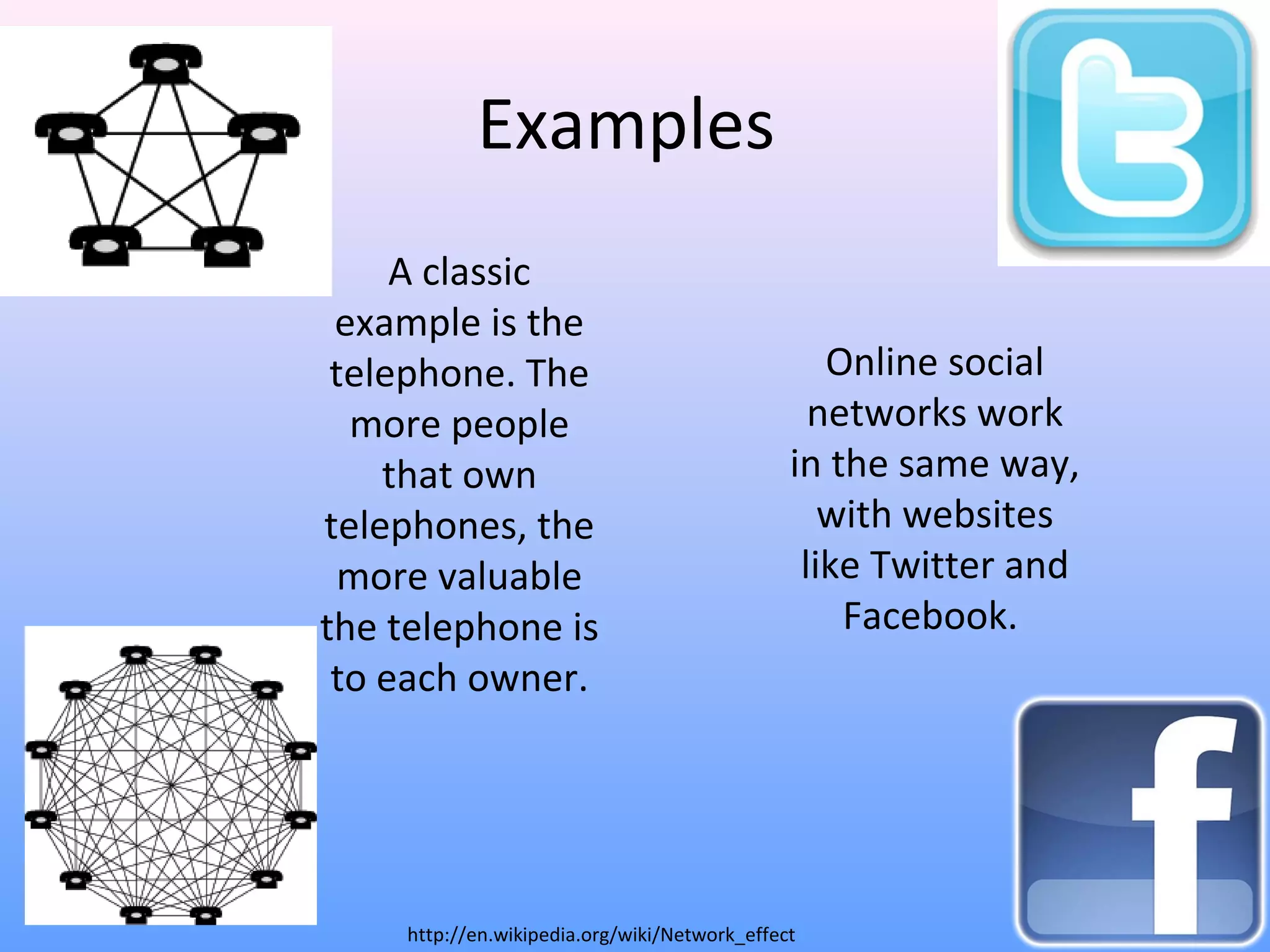
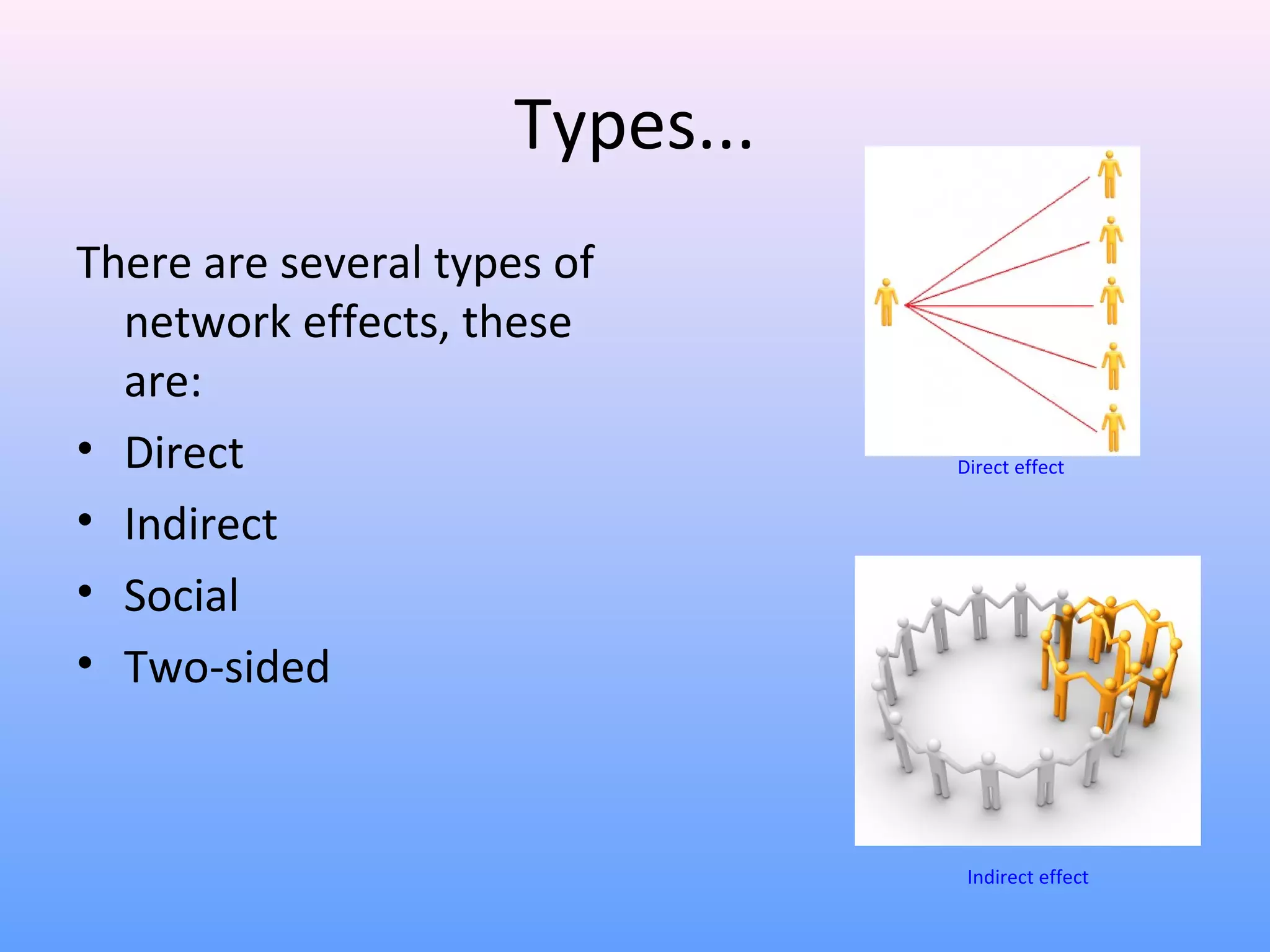
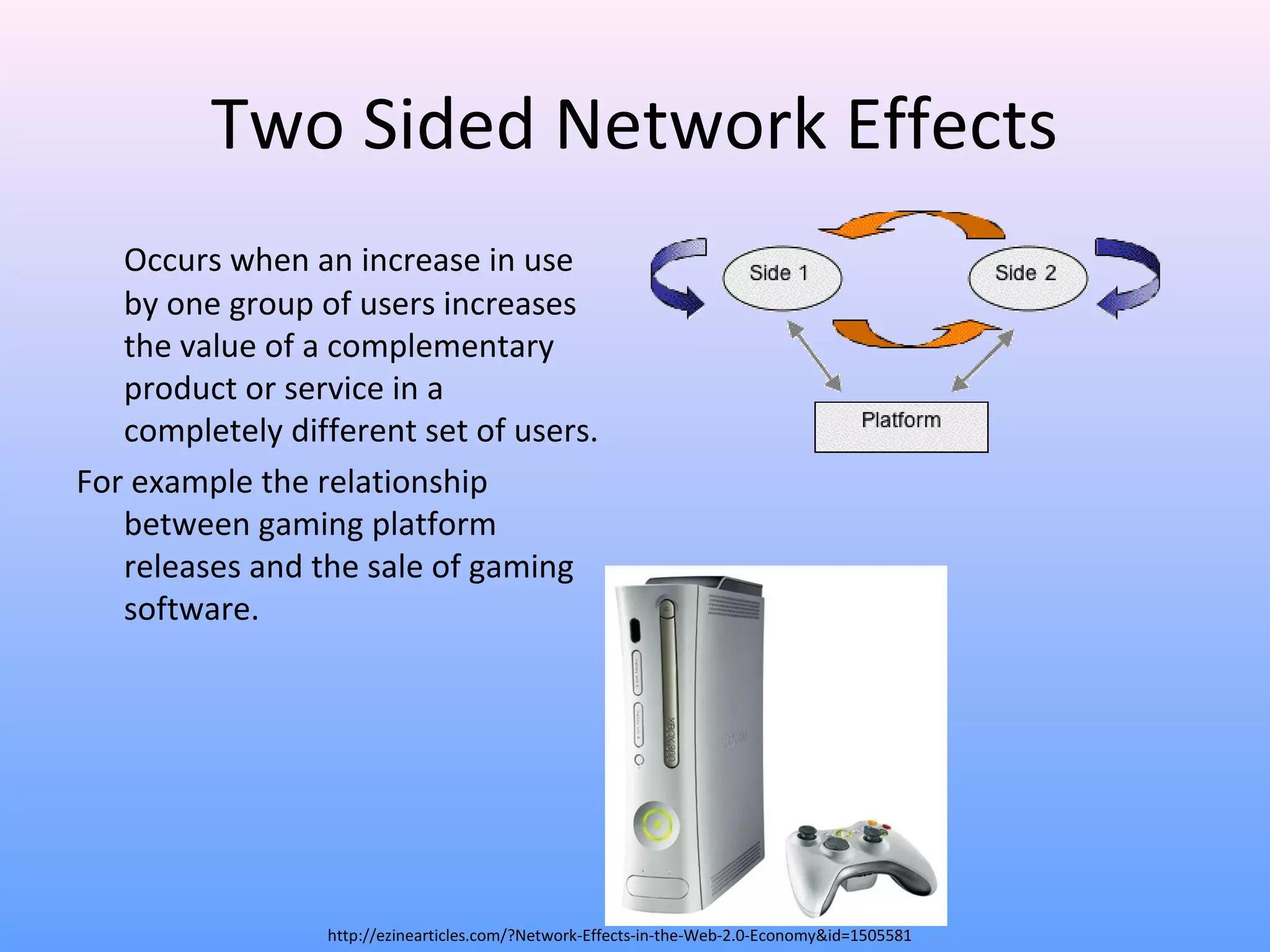
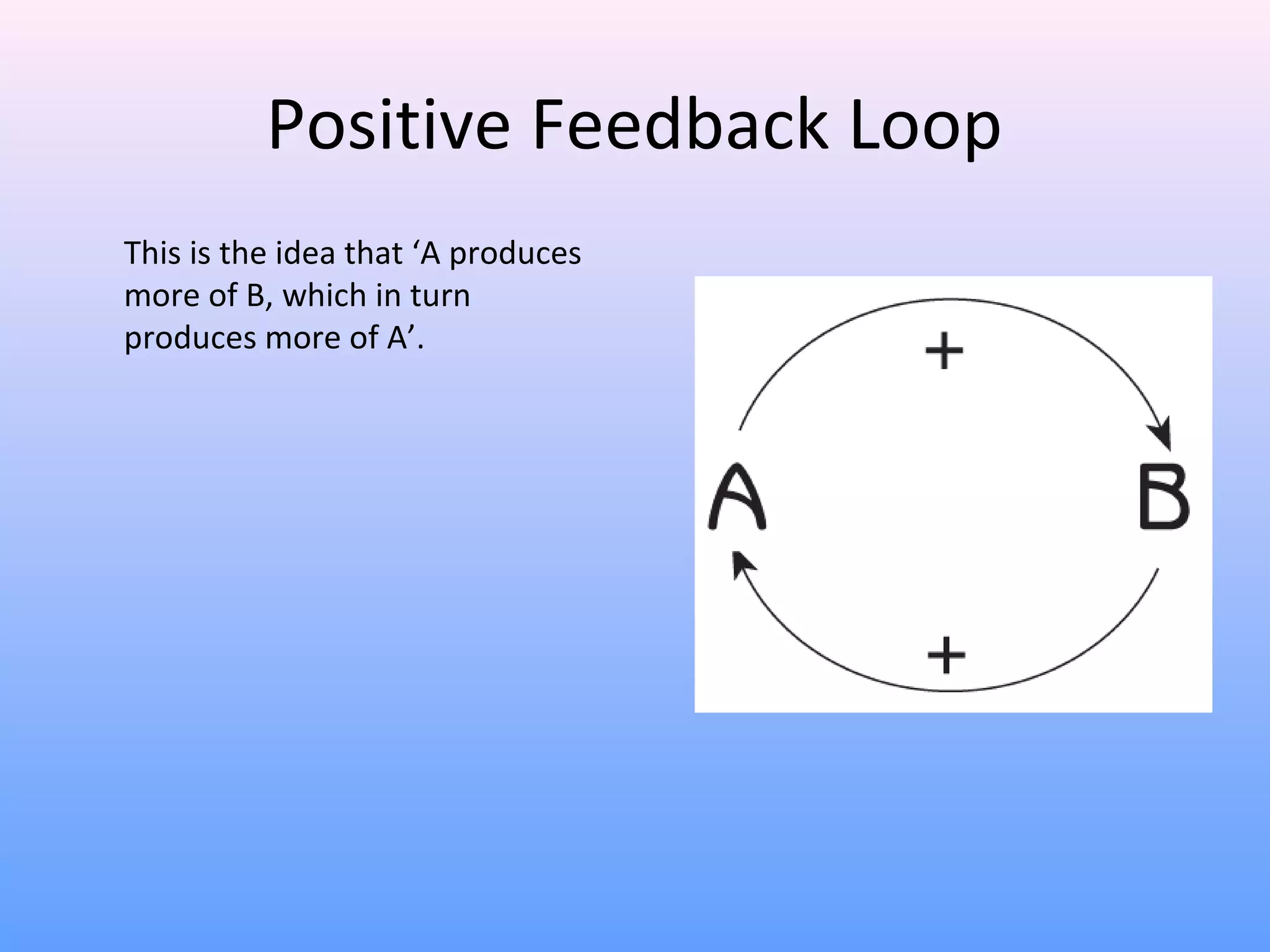
This document discusses network effects, which refers to the phenomenon where the value of a product or service increases as more people use it. There are several types of network effects including direct, indirect, two-sided, and social network effects. Examples given include how telephones and social networks like Facebook become more valuable as more people use them. A bandwagon effect and positive feedback loop can also occur within network effects. Both positive and negative network effects are explored.