This document provides an overview of fundamental networking and web architecture concepts, including:
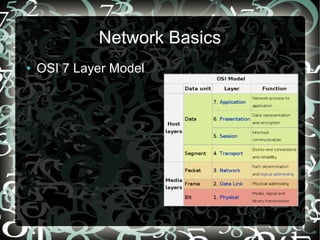
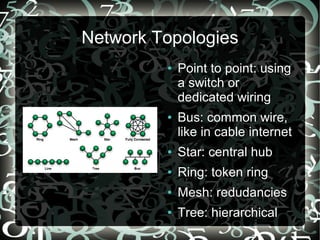
- The OSI 7-layer model and common network topologies like bus, star, and mesh.
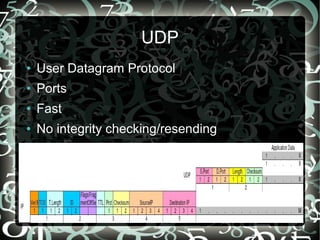
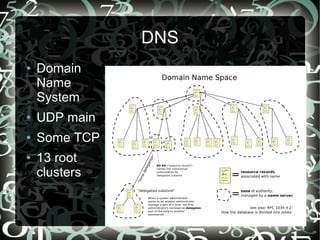
- Key protocols like IP, TCP, UDP, and DNS that enable communication and addressing on the internet.
- The basic architecture of the internet and how hardware and protocols interconnect networks.
- How static web pages are organized on websites and accessed via HTTP requests and responses with HTML content.
- REST-based architecture which allows web applications by treating resources as manipulable representations accessed through hypermedia links and queries rather than static pages.










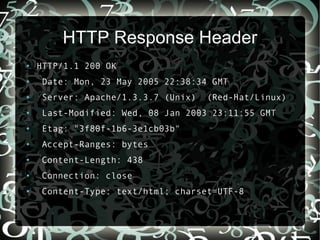
![HTTP Request
● User-Agent Opera/9.64 (X11; Linux i686; U; en)
Presto/2.1.1
● Host www.wired.com
● Accept text/html, application/xml;q=0.9,
application/xhtml+xml, image/png, image/jpeg,
image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, */*;q=0.1
● Accept-Language en-IN,en;q=0.9
● Accept-Charset iso-8859-1, utf-8, utf-16, *;q=0.1
● Accept-Encoding deflate, gzip, x-gzip, identity,
*;q=0
● Cookie [cut]
● Cookie2 $Version=1
● Proxy-Connection Keep-Alive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20091010-basic-100926121935-phpapp02/85/Network-concepts-16-320.jpg)