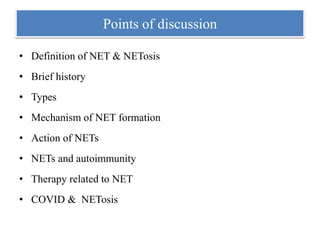
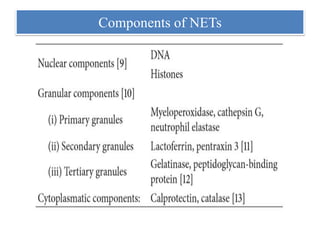
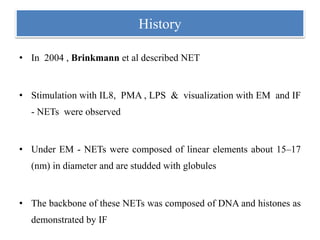
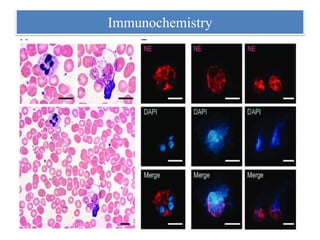
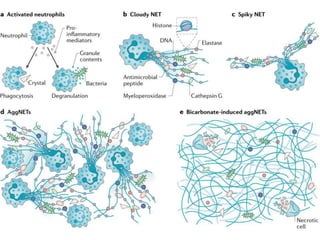
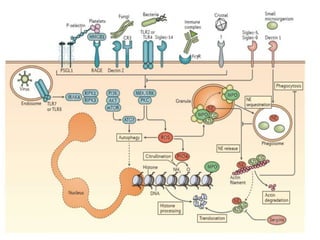
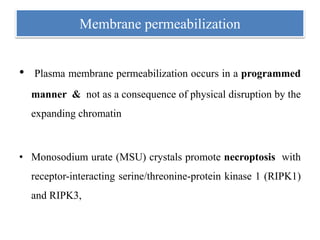
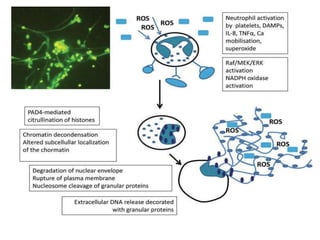
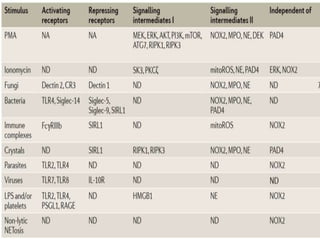
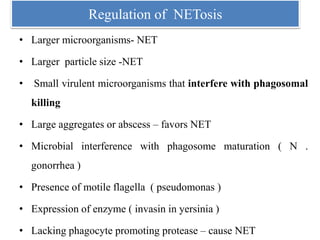
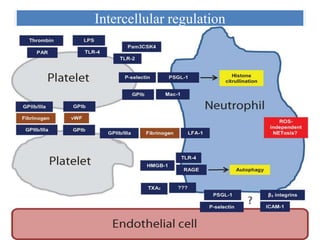
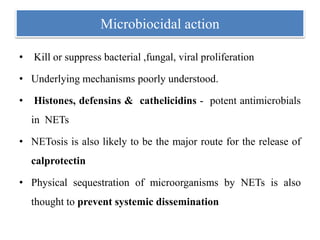
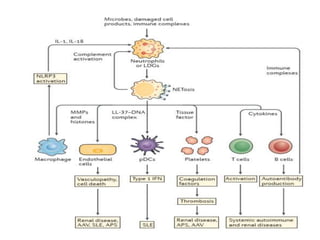
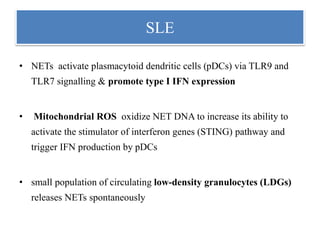
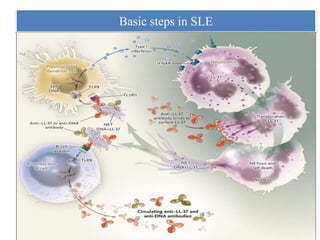
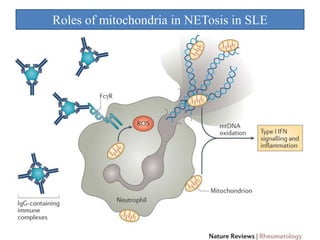
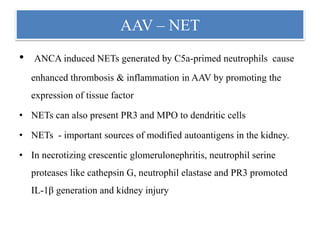
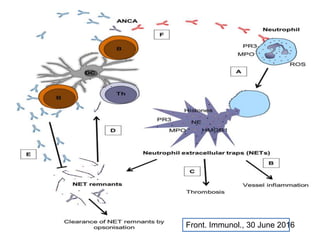
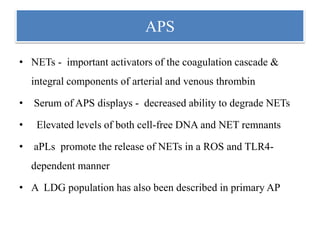
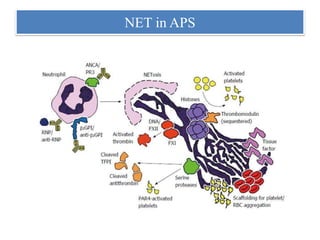
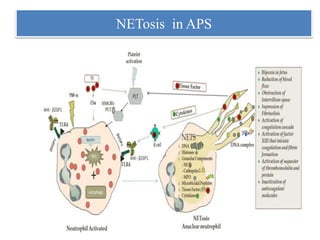
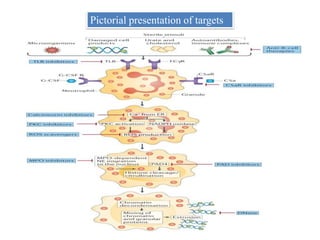
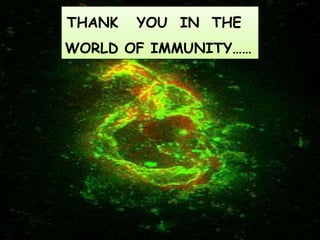
1. NETs are extracellular webs composed of DNA and proteins that are released by neutrophils to trap and kill microbes.
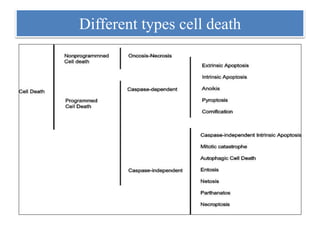
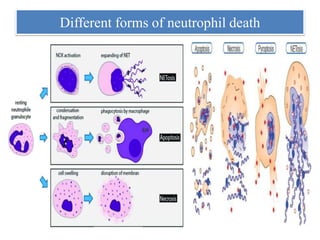
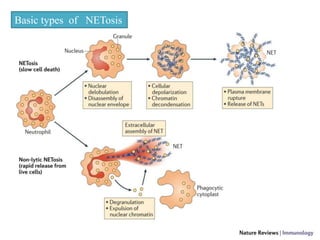
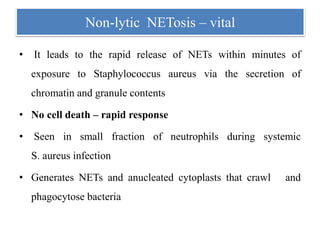
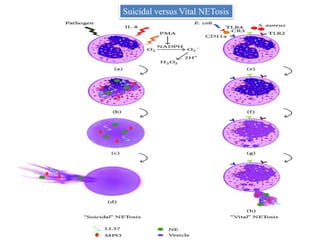
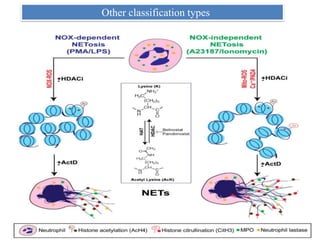
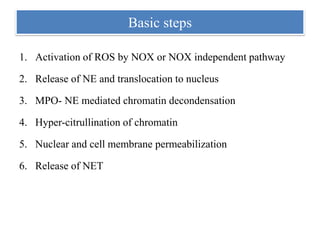
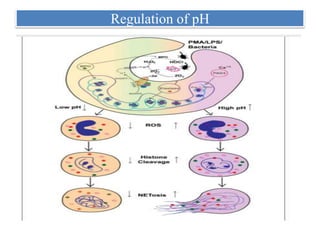
2. NET formation, called NETosis, can occur through either a lytic process involving cell death or a non-lytic process where cells remain alive.
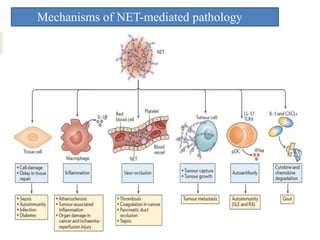
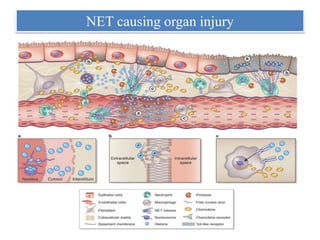
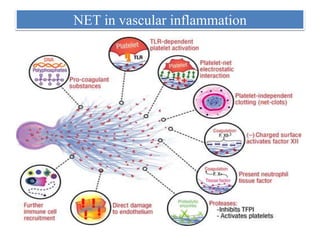
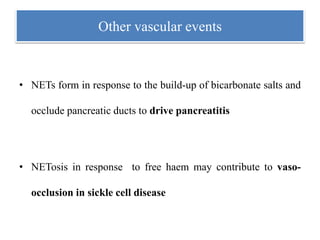
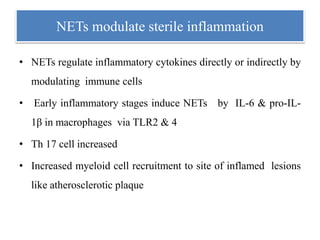
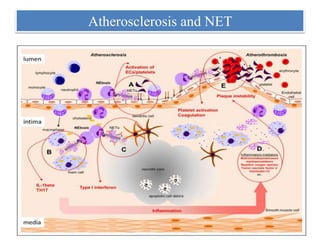
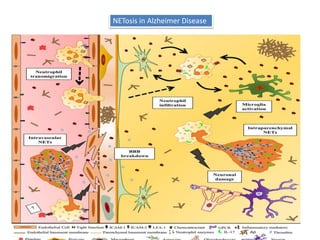
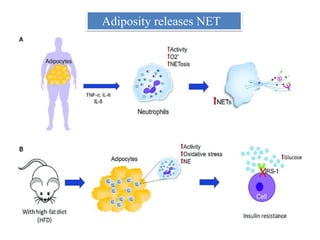
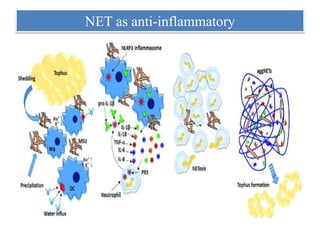
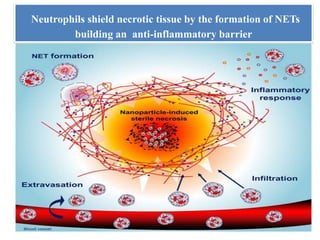
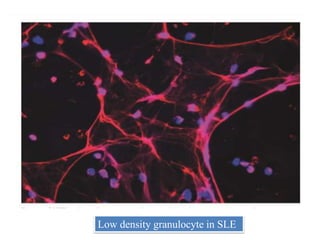
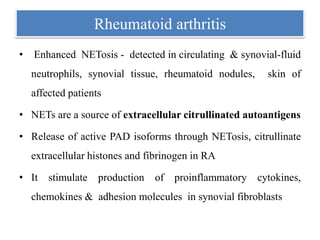
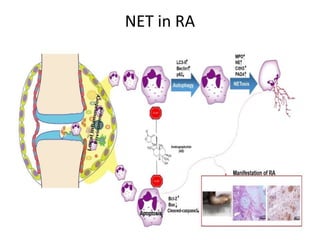
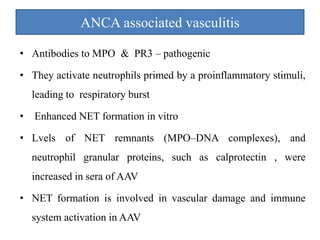
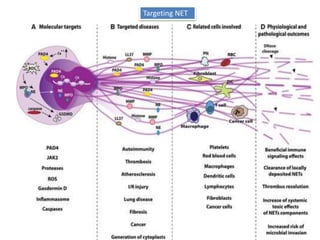
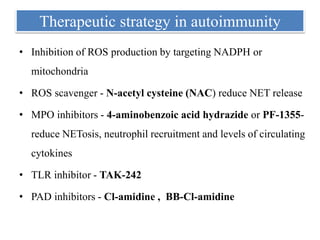
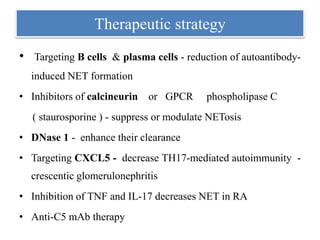
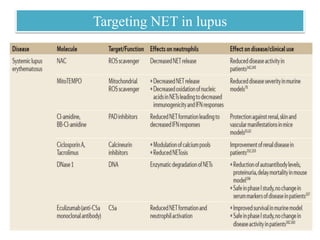
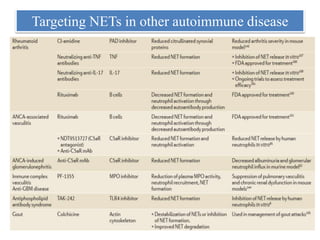
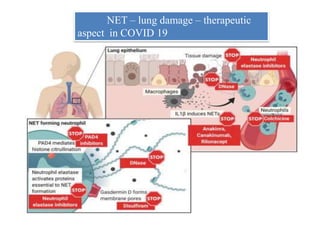
3. NETs can have both beneficial effects by killing microbes but also pathogenic effects by damaging tissues, promoting thrombosis, and providing autoantigens that stimulate autoimmunity. Many diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and vasculitis involve abnormal NET formation or responses.