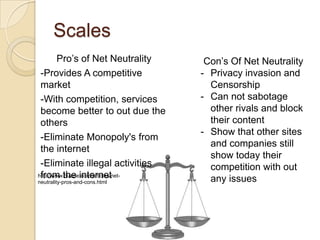
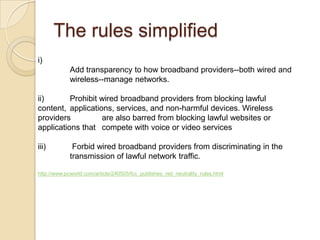
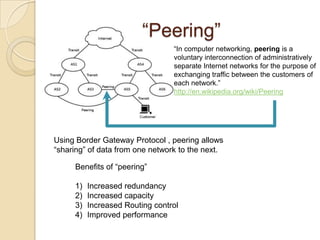
Net neutrality aims to ensure equal access to the internet for all users and companies by preventing internet service providers from favoring or blocking certain types of online content. Proponents argue this keeps the internet open and competitive, while opponents believe net neutrality discourages innovation. There is debate around how much regulation is optimal and whether some prioritization of internet traffic could be reasonable. The issue involves balancing open access with the business interests of internet companies.