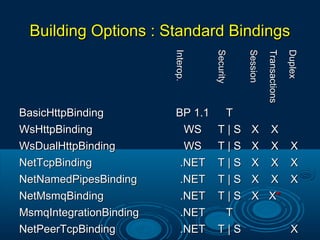
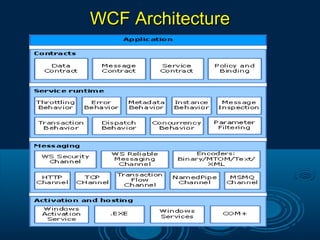
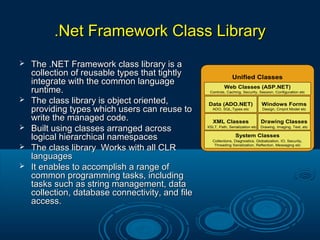
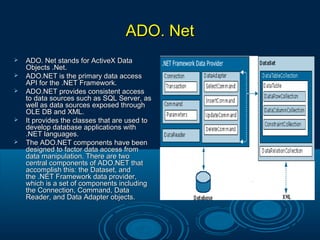
Microsoft .Net is a technology that allows the creation of web and windows applications with rich user interfaces. It supports multiple programming languages and uses the .Net framework to build and deploy applications. The .Net Framework includes a class library with reusable types that integrate with the common language runtime. It enables common programming tasks like string management, data collection, and database connectivity. ADO.Net provides the core data access components for .Net applications, including the Connection, Command, Data Reader, and Data Adapter objects to access data from sources like SQL Server. Key features of .Net include LINQ for querying different data sources, anonymous types, extension methods, and controls like ListView and DataPager for paging and sorting data.



![LINQLINQ
LINQ ProvidersLINQ Providers
LINQ to ObjectsLINQ to Objects
LINQ to SQLLINQ to SQL
LINQ to XMLLINQ to XML
LINQ to DatasetLINQ to Dataset
LINQ to Objects –LINQ to Objects –
used to query in memory collectionsused to query in memory collections
Ex:Ex: string[] tools = { “one", “two", “three", “four"};string[] tools = { “one", “two", “three", “four"};
var list = from t in tools select t;var list = from t in tools select t;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
foreach (string s in list) { sb.Append(s +foreach (string s in list) { sb.Append(s +
Environment.NewLine); }Environment.NewLine); }
MessageBox.Show(sb.ToString(), "Tools");MessageBox.Show(sb.ToString(), "Tools");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/net3-5-130502085908-phpapp01/85/Net-3-5-7-320.jpg)
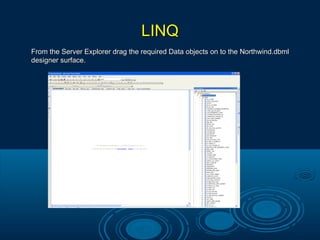


![LINQLINQ
LINQ to Dataset –LINQ to Dataset –
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) queries work on data sources thatLanguage-Integrated Query (LINQ) queries work on data sources that
implement the IENUMERABLE<T> interface or the IQueryable interface. Theimplement the IENUMERABLE<T> interface or the IQueryable interface. The
DataTable class does not implement either interface, AsEnumerable method must beDataTable class does not implement either interface, AsEnumerable method must be
called to use the DataTable as a source in the From clause of a LINQ query.called to use the DataTable as a source in the From clause of a LINQ query.
DataSet ds = new DataSet();DataSet ds = new DataSet();
FillDataSet(ds);FillDataSet(ds);
DataTable orders = ds.Tables ["SalesOrderHeader"];DataTable orders = ds.Tables ["SalesOrderHeader"];
var query = from order in orders.AsEnumerable() wherevar query = from order in orders.AsEnumerable() where
order.Field <bool>("OnlineOrderFlag") == trueorder.Field <bool>("OnlineOrderFlag") == true
select new { SalesOrderID = order.Field<int>("SalesOrderID"),select new { SalesOrderID = order.Field<int>("SalesOrderID"),
OrderDate = order.Field <DateTime>("OrderDate"),OrderDate = order.Field <DateTime>("OrderDate"), SalesOrderNumber =SalesOrderNumber =
order.Field<string>("SalesOrderNumber") };order.Field<string>("SalesOrderNumber") };
foreach (var onlineOrder in query)foreach (var onlineOrder in query)
{ Console.WriteLine ("Order ID: {0} Order date: {1:d} Order number:{ Console.WriteLine ("Order ID: {0} Order date: {1:d} Order number: {2}",{2}",
onlineOrder.SalesOrderID, onlineOrder.OrderDate,onlineOrder.SalesOrderID, onlineOrder.OrderDate,
onlineOrder.SalesOrderNumber); }onlineOrder.SalesOrderNumber); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/net3-5-130502085908-phpapp01/85/Net-3-5-12-320.jpg)

![Extension MethodsExtension Methods
Extension methods are defined as static methods but are called by using instanceExtension methods are defined as static methods but are called by using instance
method syntax.method syntax.
Their first parameter specifies which type the method operates on, and the parameterTheir first parameter specifies which type the method operates on, and the parameter
is preceded by the “this” modifier.is preceded by the “this” modifier.
Extension methods are only in scope when the namespace that contains theExtension methods are only in scope when the namespace that contains the
Extension method is explicitly imported into the source code with a using directive.Extension method is explicitly imported into the source code with a using directive.
public static class EMClasspublic static class EMClass
{{
public static int ToInt32Ext(this string s)public static int ToInt32Ext(this string s)
{ return Int32.Parse(s); }{ return Int32.Parse(s); }
}}
class Programclass Program
{{
static void Main(string[] args)static void Main(string[] args)
{{
string s = "9";string s = "9";
int i = s.ToInt32Ext();int i = s.ToInt32Ext();
Console.WriteLine(i);Console.WriteLine(i);
}}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/net3-5-130502085908-phpapp01/85/Net-3-5-14-320.jpg)