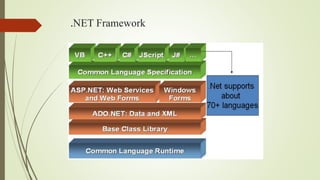
The document discusses the basics of .NET, including the Common Language Runtime (CLR) which provides a runtime environment for managed code. It also covers the Common Type System (CTS), Common Language Specification (CLS), Base Class Library (BCL), Portable Class Library, Dynamic Language Runtime, Windows Runtime (WinRT), ASP.NET, Windows Store Apps, Desktop Apps, and ADO.NET. The .NET Framework allows development across platforms using common languages and libraries.