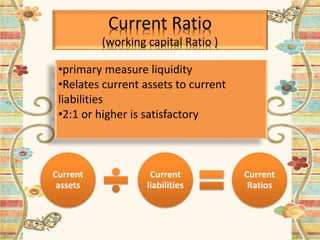
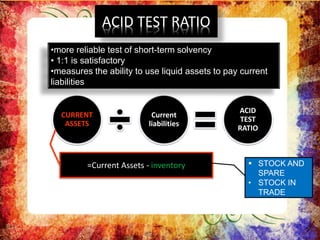
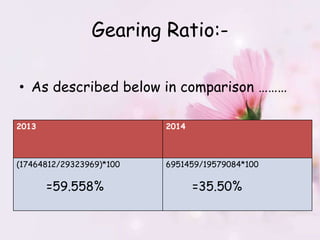
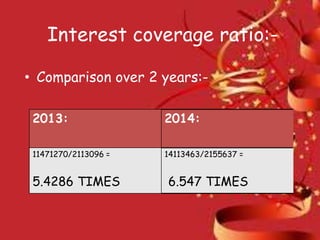
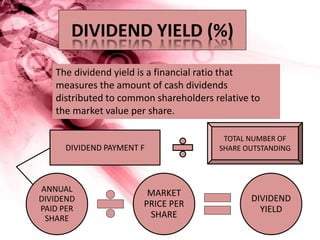
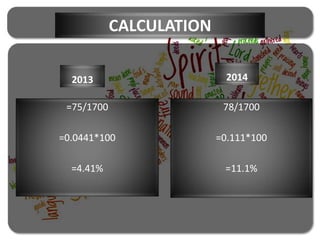
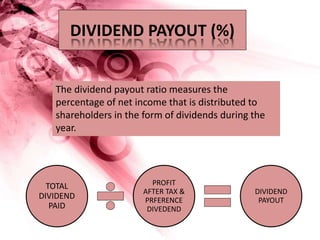
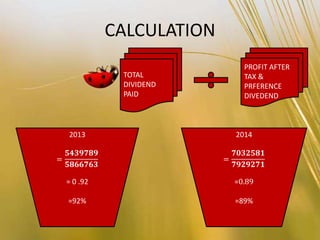
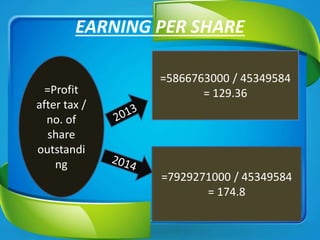
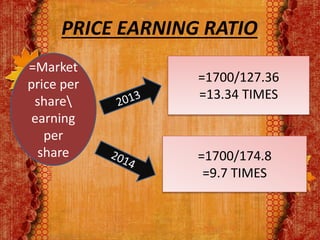
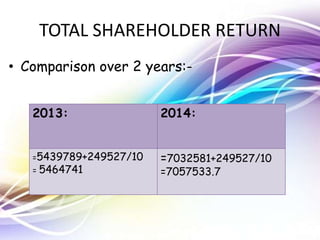
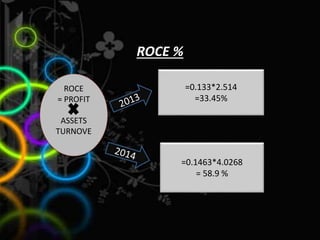
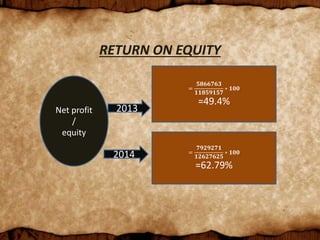
Nestle Pakistan is a subsidiary of Nestle S.A. that has been operating in Pakistan since 1988. It operates four factories producing foods such as milk, cereals and bottled water. The document analyzes Nestle Pakistan's financial ratios for 2013 and 2014, including current ratio, acid test ratio, gearing ratio, interest coverage ratio, inventory turnover, receivables collection period, and various profitability and investment ratios to evaluate the company's liquidity, leverage, efficiency and returns.